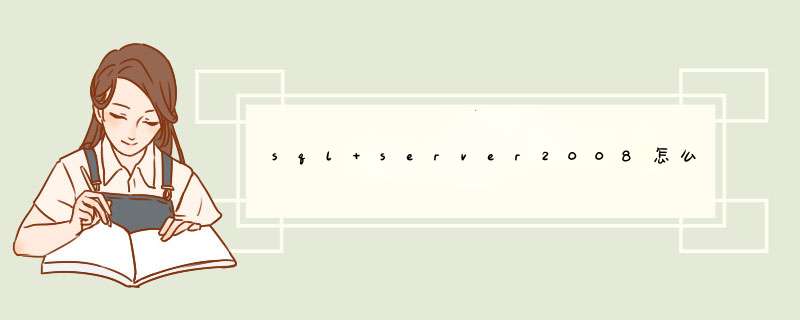
你是要写代码生成器么--这是查表的数量Select [name] from sysObjects Where xtype='U'and [name]<>'dtproperties' Order By [name]--得到数据库中所有用户视图Select [name] From sysObjects Where xtype='V' And [name]<>'syssegments' And [name]<>'sysconstraints' Order By [name]--获得指定表中所有的列Selectcname As ColumnName,tname As TypeNameFrom syscolumns c, systypes t, sysobjects oWhere cxtype = txusertypeAnd cid = oidAnd oname = 'Book'Order By ccolorder
TABLE 语句
具体语法:TABLE table_name [ORDER BY column_name] [LIMIT number [OFFSET number]]
其实从语法上看,可以排序,也可以过滤记录集,不过比较简单,没有 SELECT 那么强大。
示例 1
简单的建一张很小的表 y1,记录数为 10 条。表 t1,插入 10 条记录
mysql-(ytt/3305)->create table t1 (r1 int,r2 int);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (002 sec)
mysql-(ytt/3305)->insert into t1
with recursive aa(a,b) as (
select 1,1
union all
select a+1,ceil(rand()20) from aa where a < 10
) select from aa;
Query OK, 10 rows affected (000 sec)
Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
简单全表扫描mysql-(ytt/3305)->select from t1;+------+------+| r1 | r2 |+------+------+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 9 || 3 | 9 || 4 | 17 || 5 | 17 || 6 | 16 || 7 | 6 || 8 | 1 || 9 | 10 || 10 | 3 |+------+------+10 rows in set (000 sec)TABLE 结果mysql-(ytt/3305)->table t1;+------+------+| r1 | r2 |+------+------+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 9 || 3 | 9 || 4 | 17 || 5 | 17 || 6 | 16 || 7 | 6 || 8 | 1 || 9 | 10 || 10 | 3 |+------+------+10 rows in set (000 sec)
看下 table 的执行计划mysql-(ytt/3305)->explain table t1 order by r1 limit 2\G 1 row id: 1 select_type: SIMPLE table: t1 partitions: NULL type: ALLpossible_keys: NULL key: NULL key_len: NULL ref: NULL rows: 10 filtered: 10000 Extra: Using filesort1 row in set, 1 warning (000 sec)
其实可以看到 TABLE 内部被 MySQL 转换为 SELECT 了。mysql-(ytt/3305)->show warnings\G 1 row Level: Note Code: 1003Message: / select#1 / select `ytt``t1``r1` AS `r1`,`ytt``t1``r2` AS `r2` from `ytt``t1` order by `ytt``t1``r1` limit 21 row in set (000 sec)
那其实从上面简单的例子可以看到 TABLE 在内部被转成了普通的 SELECT 来处理。示例 2应用于子查询里的子表。这里要注意,内表的字段数量必须和外表过滤的字段数量一致。克隆表 t1 结构mysql-(ytt/3305)->create table t2 like t1;Query OK, 0 rows affected (002 sec)
克隆表 t1 数据mysql-(ytt/3305)->insert into t2 table t1;Query OK, 10 rows affected (000 sec)Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
table t1 被当做内表,表 t1 有两个字段,必须同时满足 t2 检索时过滤的字段也是两个。mysql-(ytt/3305)->select from t2 where (r1,r2) in (table t1);+------+------+| r1 | r2 |+------+------+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 9 || 3 | 9 || 4 | 17 || 5 | 17 || 6 | 16 || 7 | 6 || 8 | 1 || 9 | 10 || 10 | 3 |+------+------+10 rows in set (000 sec)
注意:这里如果过滤的字段数量和子表数量不一致,则会报错。
TABLE 语句
具体语法:TABLE table_name [ORDER BY column_name] [LIMIT number [OFFSET number]]
其实从语法上看,可以排序,也可以过滤记录集,不过比较简单,没有 SELECT 那么强大。
示例 1
简单的建一张很小的表 y1,记录数为 10 条。表 t1,插入 10 条记录
mysql-(ytt/3305)->create table t1 (r1 int,r2 int);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (002 sec)
mysql-(ytt/3305)->insert into t1
with recursive aa(a,b) as (
select 1,1
union all
select a+1,ceil(rand()20) from aa where a < 10
) select from aa;
Query OK, 10 rows affected (000 sec)
Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
简单全表扫描mysql-(ytt/3305)->select from t1;+------+------+| r1 | r2 |+------+------+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 9 || 3 | 9 || 4 | 17 || 5 | 17 || 6 | 16 || 7 | 6 || 8 | 1 || 9 | 10 || 10 | 3 |+------+------+10 rows in set (000 sec)TABLE 结果mysql-(ytt/3305)->table t1;+------+------+| r1 | r2 |+------+------+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 9 || 3 | 9 || 4 | 17 || 5 | 17 || 6 | 16 || 7 | 6 || 8 | 1 || 9 | 10 || 10 | 3 |+------+------+10 rows in set (000 sec)
看下 table 的执行计划mysql-(ytt/3305)->explain table t1 order by r1 limit 2\G 1 row id: 1 select_type: SIMPLE table: t1 partitions: NULL type: ALLpossible_keys: NULL key: NULL key_len: NULL ref: NULL rows: 10 filtered: 10000 Extra: Using filesort1 row in set, 1 warning (000 sec)
其实可以看到 TABLE 内部被 MySQL 转换为 SELECT 了。mysql-(ytt/3305)->show warnings\G 1 row Level: Note Code: 1003Message: / select#1 / select `ytt``t1``r1` AS `r1`,`ytt``t1``r2` AS `r2` from `ytt``t1` order by `ytt``t1``r1` limit 21 row in set (000 sec)
那其实从上面简单的例子可以看到 TABLE 在内部被转成了普通的 SELECT 来处理。示例 2应用于子查询里的子表。这里要注意,内表的字段数量必须和外表过滤的字段数量一致。克隆表 t1 结构mysql-(ytt/3305)->create table t2 like t1;Query OK, 0 rows affected (002 sec)
克隆表 t1 数据mysql-(ytt/3305)->insert into t2 table t1;Query OK, 10 rows affected (000 sec)Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
table t1 被当做内表,表 t1 有两个字段,必须同时满足 t2 检索时过滤的字段也是两个。mysql-(ytt/3305)->select from t2 where (r1,r2) in (table t1);+------+------+| r1 | r2 |+------+------+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 9 || 3 | 9 || 4 | 17 || 5 | 17 || 6 | 16 || 7 | 6 || 8 | 1 || 9 | 10 || 10 | 3 |+------+------+10 rows in set (000 sec)
注意:这里如果过滤的字段数量和子表数量不一致,则会报错。
1、打开Microsoft SQL Server 2012,选中需要查询所有表的数据库。
2、选中需要查询的表后,点击左上角的“新建查询”,如图。
3、点击“新建查询”后,会在右边d出一个编辑框,我们需要在这里编写sql语句,来查询该数据库下的所有表结构。
4、编写sql语句,点击“执行”,当然,这表语句我们可以根据实际情况,来改变条件只查询需要的表名。
5、这时,会在右下方出现最终的查询结果,name即该库下所有的表名。
1、首先打开安装的SQL数据库;
2、在打开的数据库页面左侧的菜单中,点击打开“数据库”;
3、右键需要查询标识ID的数据库,选择“新建查询”;
4、然后在右侧页面内输入“select空格数据库名字”;
5、然后点击右上角的“执行”;
6、在数据库的最下面所得到的查询结果就是查询的标识ID号。
查询MySQL数据库所有表名的SQL命令:
show tables;
查询MySQL数据库有表结构的SQL命令:
show create table tblName;
例如:show create table students;
CREATE TABLE `students` (
`sid` char(10) NOT NULL,
`sname` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`sex` char(1) NOT NULL,
`dob` date NOT NULL,
`phone` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`sid`),
KEY `index_tbl1_url` (`phone`(20))
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=gb2312
以上就是关于sql server2008怎么实现查询某个数据库中所有的表名全部的内容,包括:sql server2008怎么实现查询某个数据库中所有的表名、怎样用SQL语句查询一个数据库中的所有表、mysql中查询数据库中表名称和结构的sql语句是什么啊啊等相关内容解答,如果想了解更多相关内容,可以关注我们,你们的支持是我们更新的动力!
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)