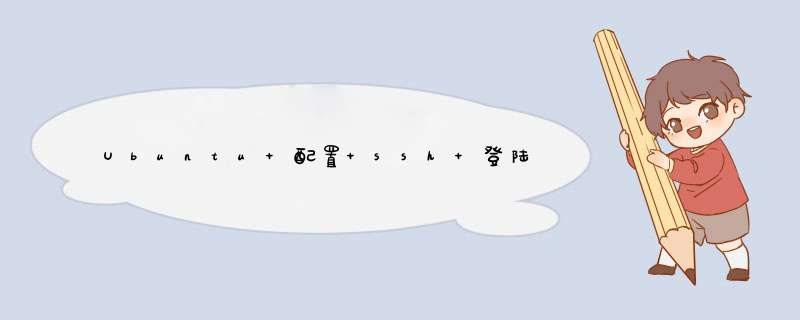
(ubuntu20)下面的输出表示 ssh 服务端没有安装
(ubuntu20)下面的输出表示 ssh 服务端已经安装
sudo apt install openssh-server
设置开机启动 ssh 服务(装完 openssh-server 默认就是开启的)
sudo systemctl enable ssh
设置开机默认不启动 ssh 服务
sudo systemctl disable ssh
启动 ssh 服务(装完 openssh-server 默认就已经启动了)
sudo systemctl start ssh
关闭 ssh 服务
sudo systemctl stop ssh
ubuntu20 默认使用 ufw 管理防火墙
查看防火墙状态
sudo ufw status
开启/关闭防火墙(ubuntu20 默认是关闭)
sudo ufw enable | disable
打开/关闭端口
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw deny ssh
端口也可以这么写
sudo ufw allow 443/tcp# (以https为例)
sudo ufw allow 8000:8100/udp# 开放 udp 端口 8000-8100
查看防火墙规则
sudo ufw status numbered
生成密钥
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C " your_email@domain.com "
把公钥拷贝到远程服务器上
ssh-copy-id -i <指定的公钥路径.pub>remote_username@server_ip_address
使用 用户名密码登陆
ssh user@ip# 然后输入密码
指定密钥登陆
ssh -i <私钥路径>user@<ip或机器名>-p <端口>
为指定机器配置私钥以自动登陆
vim .ssh/config
然后,就可以直接 ssh <ip或机器名>登录了
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
重启 ssh 服务(sshd)以使配置生效
sudo systemctl restart ssh
ubuntu版本是Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-66-generic x86_64),所有 *** 作在一台机器上进行。1. 安装:
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
2. 启动ssh服务:
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
3. 以账号密码ssh登录(不安全):
ssh root@localhost
通过以上命令以root身份登录会失败,第一是配置中默认不允许通过密码登录,另外是root密码由系统设置,需要先设置密码。root身份涉及到安全,一般强烈不建议这么做。但是我们为了研究一下,就是要用root身份登录怎么办?
1)修改登录配置。
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
打开这个配置文件后,找到配置项PermitRootLogin,当前的设置是prohibit-password。
PermitRootLogin prohibit-password
我们修改一下,设置为允许root身份以密码登录。
PermitRootLogin yes
#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password (这行保留,仅仅只是注释掉)
修改完成后,重启ssh服务生效。
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
2)修改root密码。
hhh:~$ sudo passwd
[sudo] password for hhh:
输入新的 UNIX 密码:
重新输入新的 UNIX 密码:
passwd:已成功更新密码
hhh:~$
按照以上命令成功修改后,就可以用root身份本地登录了。验证一下,用su命令后提示输入密码,成功登录后提示符从$变为#,说明进入root模式。通过exit可以退出root模式,退出后提示符又变回$。
hhh:~$ su
密码:
root@hhh:~# exit
exit
hhh:~$
3)以root身份ssh登录本机
hhh:~$ ssh root@localhost
root@localhost's password:
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-66-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
1 个可升级软件包。
0 个安全更新。
*** 需要重启系统 ***
Last login: Fri Apr 14 09:58:03 2017 from 127.0.0.1
root@hhh:~#exit
注销
Connection to localhost closed.
登录成功,试验完毕。为了回到安全状态,执行sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config,将原来注释掉的PermitRootLogin prohibit-password
打开,新添加的yes选项注释掉或者删掉。
4. 以公钥认证ssh登录
1)在客户端生成密钥对。
hhh:~$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "hhh@le.com"
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/hhh/.ssh/id_rsa): /home/hhh/.ssh/ida_rsa_hhh
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/hhh/.ssh/id_rsa_hhh.
Your public key has been saved in /home/hhh/.ssh/id_rsa_hhh.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:zB/IVbBNJ4hcdYXEiBN4eZTmvjSp7M9M889lTS1K5ZQ hhh@le.com
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| . ++O*=+o.|
| + *==+o. |
| .o=. E |
| + o .+ .|
| S ....o o|
| . o=. o.|
| ..o+o +|
| o+.o o.|
| ...+ ..o|
+----[SHA256]-----+
密钥文件默认存放在当前用户目录下的.ssh目录下,公钥文件是id_rsa.pub,私钥文件是id_rsa。如果之前已经生成过密钥对,需要重新指定文件路径存放新的密钥对,如上所示,将文件路径重新指定为/home/hhh/.ssh/ida_rsa_hhh。
2)将公钥上传到对应服务端
需要将客户端生成的公钥上传到服务器,并且拷贝到对应用户的.ssh目录下。我们这里是本地登录,客户端用户账号和服务端要登录的账号是同一个账号,所以这一步就省略掉了。然后,将公钥放入到授权文件中。
cd ~/.ssh
cat id_rsa_hhh.pub >>authorized_keys
chmod 0600 authorized_keys(仅允许本用户读写,否则可能被修改)
3)尝试ssh登录普通账号并退出
ssh hhh@localhost
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-66-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
1 个可升级软件包。
0 个安全更新。
*** 需要重启系统 ***
Last login: Thu Apr 13 17:28:07 2017 from 127.0.0.1
hhh:~$ exit
注销
Connection to localhost closed.
5. 尝试ssh登录root账号
hhh:~$ ssh root@localhost
root@localhost's password:
Permission denied, please try again.
无法登录。这里要解决两个问题,一个配置成可以root登录,另一个是要配置公钥文件。
首先,修改配置文件。sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config, 找到PermitRootLogin,将其后面no改为yes。
其次,类似普通用户的公钥文件配置,在/etc/ssh目录下做一个类似~/.ssh目录下的authorized_keys文件。此处,我们可以简单拷贝这个文件过来。sudo cp ~/.ssh/authorized_keys /etc/ssh/authorized_keys。这个authorized_keys里面如果存有多个公钥,将会带来安全隐患,所以要按需拷贝,此处只是为了省事,就直接把文件拷贝过来了。
再次试验,成功登录并退出。
hhh:~
$ ssh root@localhost
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-66-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
1 个可升级软件包。
0 个安全更新。
*** 需要重启系统 ***
Last login: Fri Apr 14 13:51:38 2017 from 127.0.0.1
root@hhh:~# exit
注销
Connection to localhost closed.
hhh:~$
试验结束,记得将原来的配置文件改回去并重启ssh服务。
设置开机启动,进入/etc/rc.local编辑配置
在最后插入两行
保存退出
这样即可在Ubuntu开机时自动启动ssh-server服务
进入 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 查找 PermitRootLogin 选项(可以利用:/PermitRootLogin的方法进行查找)
将这个选项后面的值(一般为prohibit-password)修改为 yes
修改完成后保存退出,需要重启ssh服务:
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)