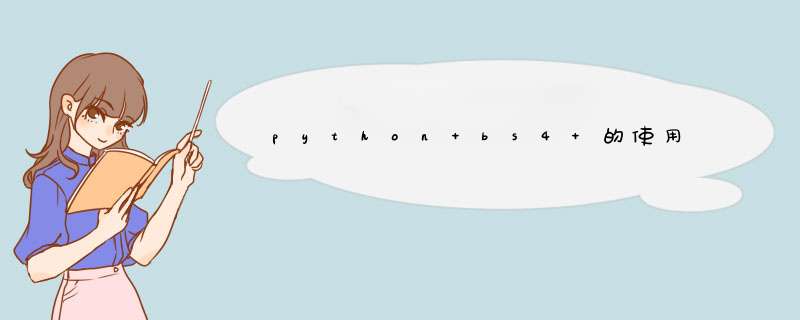
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title aq">
<b>
The Dormouse's story
</b>
</p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sistersand their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
html字符串创建BeautifulSoup对象 :
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser', from_encoding='utf-8')
print soup.title
输出第一个 title 标签的标签名称 :
print soup.title.name
输出第一个 title 标签的包含内容 :
print soup.title.string
输出第一个 title 标签的父标签的标签名称 :
print soup.title.parent.name
输出第一个 p 标签
print soup.p
输出第一个 p 标签的 class 属性内容 :
print soup.p['class']
输出第一个 a 标签的 href 属性内容 :
print soup.a['href']
'''''
soup的属性可以被添加,删除或修改. 再说一次, soup的属性 *** 作方法与字典一样
'''
修改第一个 a 标签的href属性为 http://www.baidu.com/
soup.a['href'] = ' http://www.baidu.com/'
给第一个 a 标签添加 name 属性 :
soup.a['name'] = u'百度'
删除第一个 a 标签的 class 属性为 :
del soup.a['class']
输出第一个 p 标签的所有子节点 :
print soup.p.contents
输出第一个 a 标签 :
print soup.a
输出所有的 a 标签,以列表形式显示 :
print soup.find_all('a')
输出第一个 id 属性等于 link3 的 a 标签 :
print soup.find(id="link3")
获取所有文字内容 :
print(soup.get_text())
输出第一个 a 标签的所有属性信息 :
print soup.a.attrs
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
获取 link 的 href 属性内容
print(link.get('href'))
对soup.p的子节点进行循环输出 :
for child in soup.p.children:
print(child)
正则匹配,名字中带有b的标签 :
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("b")):
print(tag.name)
import bs4#导入BeautifulSoup库
Soup = BeautifulSoup(html)#其中html 可以是字符串,也可以是句柄
需要注意的是,BeautifulSoup会自动检测传入文件的编码格式,然后转化为Unicode格式
通过如上两句话,BS自动把文档生成为如上图中的解析树。
版本四。根据查询相关公开信息显示,bs4全称:beautifulsoup4,意思为美丽的汤版本4可以在HTML或XML文件中提取数据的网页信息提取库。Python是一种跨平台的计算机程序设计语言,是一种面向对象的动态类型语言,被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越来越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)