A similar design idea appeared in the July 20, 2009, issue of EDN magazine.
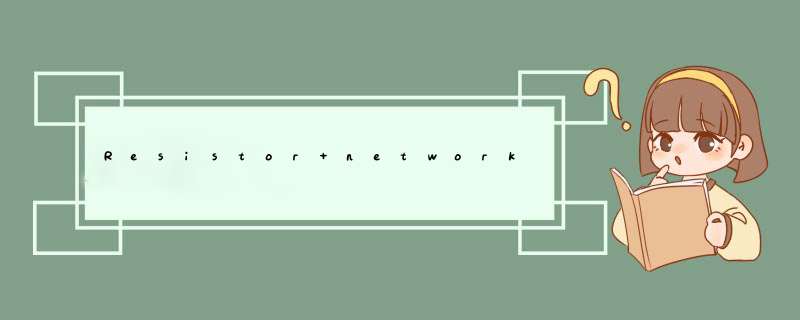
When a fixed-gain amplifier does not offer the optimum gain for an application, you can adjust the gain to a lower value by adding an external resistor network. This attenuation circuit works like a voltage-divider, but with a key difference: the external network is loaded down by input resistors internal to the fixed-gain amplifier (Figure 1). For the differential-input configuration, this system can be reduced to an equivalent half circuit for analysis (Figure 2).

Figure 1. The MAX9705 fixed-gain audio amplifier can be configured for signals that are differential (A) or single-ended (B).

Figure 2. For the differential configuration of Figure 1A, an equivalent half-circuit simplifies analysis.
Voltage gain for the differential configuration (Figure 1A) is determined as follows:
Where GAIN is the amplifier's fixed voltage gain in dB. (The MAX9705 differential audio amplifier is available in fixed-gain versions of 6, 12, 15.5, and 20dB; its input resistance is typically 20kΩ.)
For single-ended configurations, the gain is
These gain equations assume that the frequency is much higher than the cutoff frequency of the highpass filter formed by CIN and the equivalent input resistance of the circuit.
The fixed gain of the MAX9705 amplifier is typically within 5%; the internal input resistors have an absolute tolerance of ±40%, which must be considerd when calculating the resulting system gain. The tolerance of external resistors must also be accounted for by using a worst-case approach for calculating the gain tolerance. Replacing the resistor values with their maximum deviations from normal (i.e., the extreme values at the ± tolerance limits) yields the worst-case scenari
For the tightest tolerance, choose a small R1 with respect to Ri. Make sure to account for the source characteristics of VIN, which must be able to drive the equivalent load of the network. When determining final gain for the system, remember that the output impedance of VIN forms a voltage-divider with the input impedance of the attenuation circuit. This load (RIN) can be determined as follows.
For the differential configuration, RIN = R1 + Ri/(R2/2). RIN and CIN form a highpass filter whose cutoff frequency, F-3dB, is: F-3dB = 1/(2 × π × RIN × CIN).
For the single-ended configuration, RIN = R1 + Ri/(R2 + R1/Ri). Input impedance (ZIN) for the attenuation network is:
Where f is the input-signal frequency.
Deriving the highpass cutoff frequency for the single-ended case is less straightforward. To find F-3dB you must know the resistor values. Once they are known, you can solve the following equation for f = F-3dB: ZIN(f) = √2 × ZIN(f = 5000).
A spreadsheet is useful for determining the correct resistor values and system tolerances. Remember that resistors come in discrete values of resistance. They must be matched rather than simply calculated. A spreadsheet for determining custom gains and gain tolerances for both single-ended and differential configurations of the MAX9705 is available for download.
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)