
Pin Assignment (Top View)
DescriptionThe DS1672 is a low-voltage serial timekeeping IC. The DS1672 counts seconds in a 32-bit register. Using a 32-bit binary register instead of a BCD representation of the time and date, as many real-time clocks do, can be useful where time intervals are to be measured. The DS1672 operates from a low-voltage supply (2.0V, 3.0V, or 3.3V) and includes a VBACKUP input, which allows the DS1672 to continue running the counter from a backup supply, such as a battery, while the main supply is off.
The DS1672 also incorporates a trickle charger. The trickle charger register uses four bits to enable the charger. Two bits are used to select one of three current- limiting resistors and two bits to select one or zero series diodes. The trickle charger circuit is capable of charging a rechargeable battery or a large capacitor. The VBACKUP pin can also be connected to a nonrechargeable battery, such as a lithium coincell. In that case, the trickle charger should not be enabled.
In this example, the DS1672 is configured to charge a capacitor connected to VBACKUP.
A schematic of the circuit is shown in Figure 1. Figure 2 shows the discharge voltage versus time in a typical application. Software for initializing the DS1672 and reading the registers is shown in Figure 3.
More Detailed Image
Figure 1
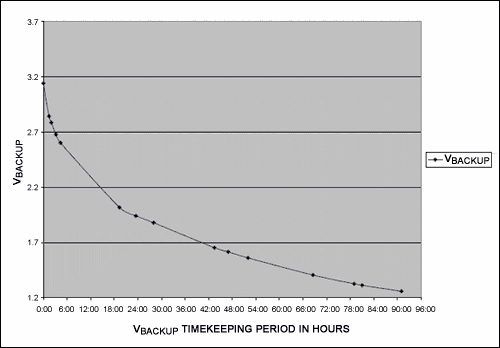
Figure 2. DS1672-3 VBACKUP Timekeeping Operation with 0.1F Backup Capacitor.
Figure 3. DS1672 Initialization Software
/***************************************************************************/ /* DS1672AN.C - This file is provided to show an example of communication */ /* routines for interfacing to the DS1672. These routines are provided */ /* for example only and are not supported by Dallas Semiconductor/Maxim */ /***************************************************************************/ #include/* Register declarations for DS5000 */ #define ACK 0 #define NACK 1 #define ADDRTC 0xd0 /* 2-wire addresses */ sbit scl = P1^0; /* 2-wire pin definitions */ sbit sda = P1^1; sbit RSTb = P0^2; void start2w(); void stop2w(); void writebyte2w(uchar d); uchar readbyte2w(int); void writebyte1672(); void initialize_DS1672(); void disp_clk_regs(); void en_tc(); unsigned long date2day(uint, uint, uint, uint, uint, uint); void day2date(unsigned long); /* global variables */ void start2w() /* --------- Initiate start condition ---------- */ { sda = 1; scl = 1; sda = 0; } void stop2w() /* ---------- Initiate stop condition ----------- */ { sda = 0; sda = 0; scl = 1; scl = 1; sda = 1; } void writebyte2w(uchar d) /* ----------------------------- */ { int i; scl = 0; for (i = 0;i < 8; i++) { if (d & 0x80) sda = 1; /* Send the msbits first */ else sda = 0; scl = 0; scl = 1; d = d << 1; /* do shift here to increase scl high time */ scl = 0; } sda = 1; /* Release the sda line */ scl = 0; scl = 1; if (sda) printf("Ack bit missing %02X\n",(unsigned int)d); scl = 0; } uchar readbyte2w(int b) /* ----------------------------------- */ { int i; uchar d; d = 0; sda = 1; /* Let go of sda line */ scl = 0; for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) /* read the msb first */ { scl = 1; d = d << 1; d = d | (unsigned char)sda; scl = 0; } sda = b; /* low for ack, high for nack */ scl = 1; scl = 0; sda = 1; /* Release the sda line */ return d; } void day2date(unsigned long x) /* ------ convert binary time to date format --- --- */ { int yrs = 99, mon = 99, day = 99, tmp, jday, hrs, min, sec; unsigned long j, n; j = x / 60; /* whole minutes since 1/1/70 */ sec = x - (60 * j); /* leftover seconds */ n = j / 60; min = j - (60 * n); j = n / 24; hrs = n - (24 * j); j = j + (365 + 366); /* whole days since 1/1/68 */ day = j / ((4 * 365) + 1); tmp = j % ((4 * 365) + 1); if(tmp >= (31 + 29)) /* if past 2/29 */ day++; /* add a leap day */ yrs = (j - day) / 365; /* whole years since 1968 */ jday = j - (yrs * 365) - day; /* days since 1/1 of current year */ if(tmp <= 365 && tmp >= 60) /* if past 2/29 and a leap year then */ jday++; /* add a leap day */ yrs += 1968; /* calculate year */ for(mon = 12; mon > 0; mon--) { switch(mon) { case 1: tmp = 0; break; case 2: tmp = 31; break; case 3: tmp = 59; break; case 4: tmp = 90; break; case 5: tmp = 120; break; case 6: tmp = 151; break; case 7: tmp = 181; break; case 8: tmp = 212; break; case 9: tmp = 243; break; case 10: tmp = 273; break; case 11: tmp = 304; break; case 12: tmp = 334; break; } if((mon > 2) && !(yrs % 4)) /* adjust for leap year */ tmp++; if(jday >= tmp) break; } day = jday - tmp + 1; /* calculate day in month */ printf("\n%04d %02d %02d %02d:%02d:%02d", yrs ,mon, day, hrs, min, sec); } /* ---- convert date to elapsed days in binary ---- */ unsigned long date2day(uint yr, uint mo, uint da, uint hrs, uint min, uint sec) { unsigned long x; /* the following is broken down for clarity */ x = 365 * (yr - 1970); /* calculate number of days for previous years */ x += (yr - 1969) >> 2; /* add a day for each leap year */ if((mo > 2) && (yr % 4 == 0)) /* add a day if current year is leap and past Feb 29th */ x++; switch(mo) { case 1: x += 0; break; case 2: x += 31; break; case 3: x += 59; break; case 4: x += 90; break; case 5: x += 120; break; case 6: x += 151; break; case 7: x += 181; break; case 8: x += 212; break; case 9: x += 243; break; case 10: x += 273; break; case 11: x += 304; break; case 12: x += 334; break; } x += da - 1; /* finally, add the days into the current month */ x = x * 86400; /* and calculate the number of seconds in all those days */ x += (hrs * 1800); /* add the number of seconds in the hours */ x += (hrs * 1800); /* add the number of seconds in the hours */ x += (min * 60); /* ditto the minutes */ x += sec; /* finally, the seconds */ return(x); } void writebyte1672() /* ----------------------------------------------- */ { uchar Add; uchar Data; /* Get Address & Data */ printf("\nEnter the Read Address\nADDRESS:"); scanf("%bx", &Add); printf("\nDATA:"); scanf("%bx", &Data); start2w(); writebyte2w(ADDRTC); writebyte2w(Add); writebyte2w(Data); stop2w(); } void initialize_DS1672() /* ----------------------------------------- */ /* Note: NO error checking is done on the user entries! */ { uchar a, b, c, d; uint yr, mn, dt, dy, hr, min, sec, day; unsigned long y; start2w(); writebyte2w(ADDRTC); writebyte2w(0x04); writebyte2w(0x00); /* enable the oscillator */ stop2w(); printf("\nEnter the year (1970-2099): "); scanf("%d", &yr); printf("\nEnter the month (1-12): "); scanf("%d", &mn); printf("\nEnter the date (1-31): "); scanf("%d", &dt); /* printf("\nEnter the day (1-7): "); */ /* scanf("%d", &dy); */ printf("\nEnter the hour (1-24): "); scanf("%d", &hr); printf("\nEnter the minute (0-59): "); scanf("%d", &min); printf("\nEnter the second (0-59): "); scanf("%d", &sec); y = date2day(yr, mn, dt, hr, min, sec); a = (y & 0xff); b = ((y >> 8) & 0xff); c = ((y >> 16) & 0xff); d = ((y >> 24) & 0xff); start2w(); writebyte2w(ADDRTC); /* write slave address, write 1672 */ writebyte2w(0x00); /* write register address, 1st clock register */ writebyte2w(a); writebyte2w(b); writebyte2w(c); writebyte2w(d); stop2w(); } void disp_clk_regs() /* ----------------------------------------- */ { uchar reg1, prv_sec = 99, reg2, reg3, reg4; unsigned long z; while(!RI) /* Read & Display Clock Registers */ start2w(); writebyte2w(ADDRTC); /* write slave address, write 1672 */ writebyte2w(0x00); /* write register address, 1st clock register */ start2w(); writebyte2w(ADDRTC | 1); /* write slave address, read 1672 */ reg1 = readbyte2w(ACK); /* starts w/last address stored in register pointer */ reg2 = readbyte2w(ACK); reg3 = readbyte2w(ACK); reg4 = readbyte2w(NACK); stop2w(); if(reg1 != prv_sec) /* display every time seconds change */ { z = reg4; z <<= 8; z += reg3; z <<= 8; z += reg2; z <<= 8; z += reg1; day2date(z); } prv_sec = reg1; } RI = 0; /* Swallow keypress to exit loop */ } void en_tc(dat) /* ----- enable the trickle-charger ------ */ { start2w(); writebyte2w(ADDRTC); writebyte2w(5); writebyte2w(dat); /* enable the trickle-charger */ stop2w(); } main (void) /* ----------------------------------------------------- */ { uchar i, M, M1; RSTb = 1; while (1) { printf("\nDS1672\n"); printf("I Init DS1672 D/E Disable/Enable TC\n"); printf("R Read Time W Write Byte\n"); printf("\nEnter Menu Selection:"); M = _getkey(); switch(M) { case 'R': case 'r': disp_clk_regs(); break; case 'W': case 'w': writebyte1672(); break; case 'D': case 'd': en_tc(0); break; case 'E': case 'e': en_tc(0xa6); break; case 'I': case 'i': initialize_DS1672(); break; } } }
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)