
教学目标
掌握分析三相异步电动机的机械特性;
掌握三相异步电动机的各种起动方法;
掌握三相异步电动机的回馈、反接、能耗制动运行状态。
3.1 Speed /Torque Curves
Vocabulary
1. power distribuTIon
2. electromagneTIcal torque
3. breakdown torque=stalling torque
4. asymptoTIc
5. abscissae
6. skew
7. full-pitch coil
Example
A three-phase,230V,60Hz,12kW,4 pole wound inducTIon motor has the following parameters expressed in Ω /phase.
R1=0.095 x1=0.68
x2=0.672 xm=18.7
Using MATLAB, plot the electromechanical torque Tmech as a function of rotor speed in r/min for rotor resistances of r2=0.1,0.2,0.5,1.0 and 1.5 Ω .
3.2 Starting of Induction Motors
Vocabulary
ball mill, crusher, compressor
terminal, a deep-bar cage
installation, maintenance
aperiodic component
resultant flux , stationary
inrush current , residual magnetisation
qualitative , inertia , parabola , kinetic
direct connection to the line
autotransformer
starting by star-delta switching
m.m.f = magnetomotive force 磁动势
rotating field 旋转磁场
ampere-turns 安匝
stator, rotor, primary (secondary) winding 定、转子初(次)级绕组
slip 转差,滑差
lamination 冲片,叠片;薄片
periphery 圆周
counterclockwise 反时针方向的
phase-sequence 相序
It is interesting to note that this expression could have been written down directly by applying the general theorem for maximum power transfer in such a series circuit; i.e. the load resistance must be equal to the impedance modulus of the remaining circuit components.
The starting torque can be increased up to the maximum figure merely by inserting an external resistance to bring r 2 up to (substitute s=1 in eqn. (2.7)), this value is much higher than the natural rotor resistance
In a number of industries motors must satisfy very strict speed characteristic requirements, both in respect to range and smoothness of control and also in respect to economical operation. From the point of view of speed-control characteristics, induction motors are inferior to d.c. motors, the shortcoming being the greater the wider the range of control.
1. State in which quadrants a machine operates
a. As a brake
b. As a motor
c. As a generator
2. Under what circumstances is reduced voltage starting required ?
3. Name four types of circuit diagrams and describe the purpose of each.
o 转子串电阻分级起动
作图法计算起动电阻 :
先画固有机械特性;
确定最大起动转矩 T 1 及切换转矩 T 2 ;
作第一级起动机械特性;
作第二级起动机械特性;
作第三级起动机械特性;
完成作图。
解析法计算起动电阻
3.3 三相异步电动机的制动
能耗制动
基本原理
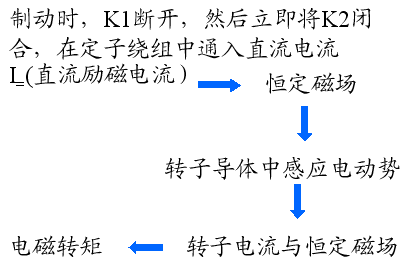
制动停车过程中,系统原来贮存的动能消耗了,这部分能量主要被电动机转换为电能消耗在转子回路中,与他励直流电动机的能耗制动过程相似。因此,上述过程亦称之为能耗制动。
o 定子等效电流
三相异步电动机能耗制动过程中电磁转矩 T 的产生,是由于转子与定子磁通势之间有相对运动;相对运动速度的大小与方向不同,则转矩 T 的大小与方向也随之不同。
分析能耗制动状态下运行的三相异步电动机,可以用三相交流电流产生的旋转磁通势 等效替代直流磁通势 ,在等效替代后,就可以使用电动运行状态时的分析方法与所得结论。等效替代的条件是:
(1) 用 等效 ,需保持磁通势幅值不变,
(2) 用 等效 ,需保持磁通势与转子之间相对转述 ( 即转差 ) 不变,为 0-n=-n 。
o 转差率及等值电路
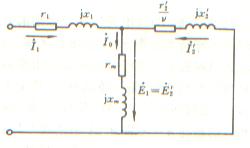
机械特性
特点:
v 异步电动机能耗制动的机械特性与定子接三相交流电源运行时的机械特性相似。
v 当直流励磁一定,而转子电阻增加时,产生最大制动转矩时的转速随之增加,但是产生的最大转矩值不变。
v 转子电路电阻不变,而增大直流励磁电流时,产生的最大制动转矩增大,但产生最大转矩时的转速不变。
反接制动
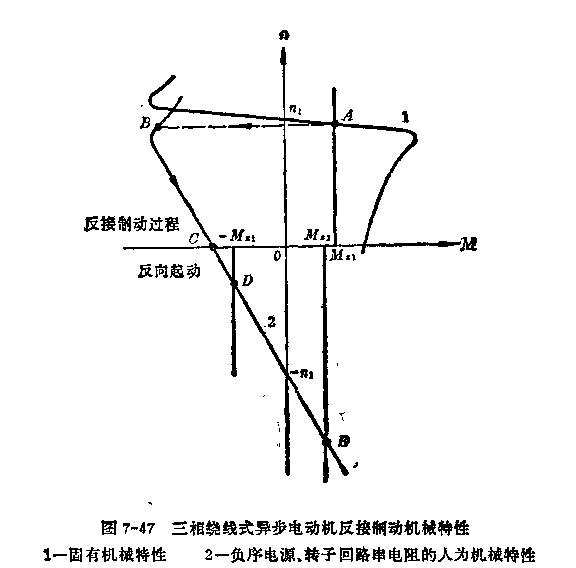
倒拉反转运行
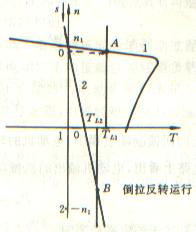
拖动位能性恒转矩负载运行的三相绕线式异步电动机,若在转子回路内串人一定值的电阻,电动机转速可以降低。如果所串的电阻超过某一数值后,电动机还要反转,运行于第Ⅳ象限,称之为倒拉反转运行状态。
倒拉反转运行时负载向电动机送入机械功率是靠负载储存的位能的减小,是位能性负载倒过来拉着电动机反转。
回馈制动运行
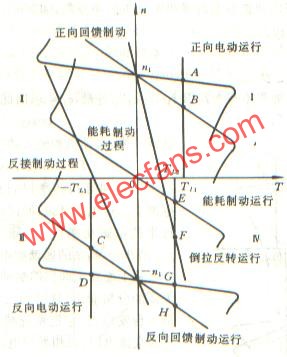
电动机运行于第Ⅳ象限, T>0 , n<0 ,称为反向回馈制动。起重机高速放下重物时,经常采用反向回馈制动运行方式。
反向回馈制动运行时,电动机的功率关系与正向回馈制动过程是一样的,电动机是一台发电机,它把负载位能减少而输入的机械功率变为电功率,然后回送给电网。从节能的观点看问题,反向回馈制动下放重物比能耗制动下放重物要好。
运行在正向电动状态的三相异步电动机,当拖动的负载是位能恒转矩负载时,如果进行反接制动停车,当转速降到 n=0 时若不采取听出措施,那么电动机将会反接起动,并最后运行于反向回馈制动状态。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)