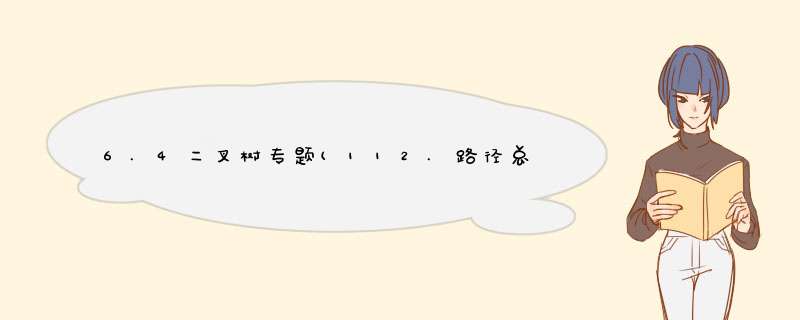
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
//此题最开始我的想法是用递归的写法
if(root==nullptr) return false;
return travel(root, targetSum-root->val);
}
//第一步确定函数返回值,和函数的参数
bool travel(TreeNode* cur, int count){
//函数的返回值我决定用bool。
if(cur->left==nullptr && cur->right==nullptr && count==0) return true;
if(cur->left==nullptr && cur->right==nullptr && count!=0) return false;
if(cur->left){
count -= cur->left->val;
if(travel(cur->left, count)) return true;
//这一步是有回溯的思想在其中的,如果当前节点没有产生返回值,则回溯
count += cur->left->val;
}
if(cur->right){
count -= cur->right->val;
if(travel(cur->right, count)) return true;
count += cur->right->val;
}
//注意这一点是必须要写的!因为当上面执行完后说明没有满足节点的点,要返回false
return false;
}
};
这道题跟上面如出一辙,我用同样的递归方法解决
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
//这道题跟112完全一样,无非就是需要我们记录一下路径
//我决定还是用递归的方式来解决这道题目
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if(root == nullptr) return ans;
vector<int> vec;
vec.push_back(root->val);
travel(root, targetSum-root->val, ans, vec);
return ans;
}
void travel(TreeNode* cur, int count, vector<vector<int>>& ans, vector<int>& vec){
if(cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr && count == 0){
ans.push_back(vec);
return;
}
if(cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr && count != 0) return;
if(cur->left){
vec.push_back(cur->left->val);
count-=cur->left->val;
travel(cur->left, count, ans, vec);
count+=cur->left->val;
vec.pop_back();
}
if(cur->right){
vec.push_back(cur->right->val);
count-=cur->right->val;
travel(cur->right, count, ans, vec);
count+=cur->right->val;
vec.pop_back();
}
}
};
这道题我的做法有一点繁琐,明天会再做一下
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
//这道题我不看解析还真是有点迷糊呢,明确如下几点和几个步骤
//1. 记住中序遍历为左->中->右
//2. 后续遍历为左->右->中
//3. 前序遍历加后续遍历不可能确定唯一一颗二叉树,因为没有办法分辨左右
//好我们来讲一下做题的的步骤
//后续遍历的最后一个节点是我们的根节点
if(inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return nullptr;
return build(inorder, postorder);
}
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder){
//因为我们让postorder一直在d出
if(postorder.size() == 0) return nullptr;
//然后找到后续遍历数组的最后一个点做我们的根节点
int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size()-1];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
int index;
//然后以root的值为中间节点切割中序遍历数组,找到左右两个值
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++){
if(inorder[i] == root->val){
index = i;
break;
}
}
//找到被切割后的两个前序vector
vector<int> left_inorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin()+index);
vector<int> right_inorder(inorder.begin()+index+1, inorder.end());
//有一点大家一定记住,切割后的两个数组的大小,跟pop过的后续数组的大小是一致的
//然后再以被切割后的两个前序数组的大小来切割后续数组
postorder.pop_back();
vector<int> left_postorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin()+left_inorder.size());
vector<int> right_postorder(postorder.begin()+left_inorder.size(), postorder.end());
root->left = build(left_inorder, left_postorder);
root->right = build(right_inorder, right_postorder);
return root;
}
};
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)