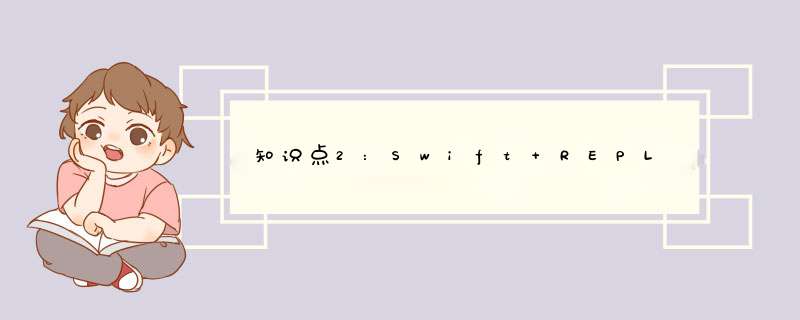
sudo xcode-select -s /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/xcrun swift 定义常/变量
1> let name:String = "ZhangSan"
name: String = "ZhangSan"
2> var age:Int = 15
age: Int = 15
3> print("Name is:\(name),Age is:\(age)")
Name is:ZhangSan,Age is:15
定义函数
4> func play(name:String,age:Int) ->String{
5. return "The boy Name is:\(name),Age is:\(age) playing"
6. }
7> play(name:name,age:age)
$R0: String = "The boy Name is:ZhangSan,Age is:15 playing"
//帮助:
输入:help
//退出:
输入:quit
//将光标移动到当前行的开始处:
输入: Control+A
//将光标移动到当前行的结束处:
输入: Control+E 9> :help
The REPL (Read-Eval-Print-Loop) acts like an interpreter. Valid
statements, expressions, and declarations are immediately compiled and
executed.
The complete set of LLDB debugging commands are also available as described
below.
Commands must be prefixed with a colon at the REPL prompt (:quit for
example.) Typing just a colon followed by return will switch to the LLDB
prompt.
Type “< path” to read in code from a text file “path”.
Debugger commands:
apropos -- List debugger commands related to a word or subject.
breakpoint -- Commands for operating on breakpoints (see 'help b'
for shorthand.)
command -- Commands for managing custom LLDB commands.
disassemble -- Disassemble specified instructions in the current
target. Defaults to the current function for the
current thread and stack frame.
expression -- Evaluate an expression on the current thread.
Displays any returned value with LLDB's default
formatting.
frame -- Commands for selecting and examing the current
thread's stack frames.
gdb-remote -- Connect to a process via remote GDB server. If no
host is specifed, localhost is assumed.
gui -- Switch into the curses based GUI mode.
help -- Show a list of all debugger commands, or give
details about a specific command.
kdp-remote -- Connect to a process via remote KDP server. If no
UDP port is specified, port 41139 is assumed.
language -- Commands specific to a source language.
log -- Commands controlling LLDB internal logging.
memory -- Commands for operating on memory in the current
target process.
platform -- Commands to manage and create platforms.
plugin -- Commands for managing LLDB plugins.
process -- Commands for interacting with processes on the
current platform.
quit -- Quit the LLDB debugger.
register -- Commands to access registers for the current thread
and stack frame.
reproducer -- Commands for manipulating reproducers. Reproducers
make it possible to capture full debug sessions with
all its dependencies. The resulting reproducer is
used to replay the debug session while debugging the
debugger.
Because reproducers need the whole the debug session
from beginning to end, you need to launch the
debugger in capture or replay mode, commonly though
the command line driver.
Reproducers are unrelated record-replay debugging,
as you cannot interact with the debugger during
replay.
script -- Invoke the script interpreter with provided code and
display any results. Start the interactive
interpreter if no code is supplied.
session -- Commands controlling LLDB session.
settings -- Commands for managing LLDB settings.
source -- Commands for examining source code described by
debug information for the current target process.
statistics -- Print statistics about a debugging session
target -- Commands for operating on debugger targets.
thread -- Commands for operating on one or more threads in the
current process.
trace -- Commands for loading and using processor trace
information.
type -- Commands for operating on the type system.
version -- Show the LLDB debugger version.
watchpoint -- Commands for operating on watchpoints.
Current command abbreviations (type ':help command alias' for more info):
add-dsym -- Add a debug symbol file to one of the target's current
modules by specifying a path to a debug symbols file or by
using the options to specify a module.
attach -- Attach to process by ID or name.
b -- Set a breakpoint using one of several shorthand formats.
bt -- Show the current thread's call stack. Any numeric argument
displays at most that many frames. The argument 'all'
displays all threads. Use 'settings set frame-format' to
customize the printing of individual frames and 'settings
set thread-format' to customize the thread header.
c -- Continue execution of all threads in the current process.
call -- Evaluate an expression on the current thread. Displays any
returned value with LLDB's default formatting.
continue -- Continue execution of all threads in the current process.
detach -- Detach from the current target process.
di -- Disassemble specified instructions in the current target.
Defaults to the current function for the current thread and
stack frame.
dis -- Disassemble specified instructions in the current target.
Defaults to the current function for the current thread and
stack frame.
display -- Evaluate an expression at every stop (see 'help target
stop-hook'.)
down -- Select a newer stack frame. Defaults to moving one frame, a
numeric argument can specify an arbitrary number.
env -- Shorthand for viewing and setting environment variables.
exit -- Quit the LLDB debugger.
f -- Select the current stack frame by index from within the
current thread (see 'thread backtrace'.)
file -- Create a target using the argument as the main executable.
finish -- Finish executing the current stack frame and stop after
returning. Defaults to current thread unless specified.
history -- Dump the history of commands in this session.
Commands in the history list can be run again using
"!". "!-" will re-run the command that is
commands from the end of the list (counting the
current command).
image -- Commands for accessing information for one or more target
modules.
j -- Set the program counter to a new address.
jump -- Set the program counter to a new address.
kill -- Terminate the current target process.
l -- List relevant source code using one of several shorthand
formats.
list -- List relevant source code using one of several shorthand
formats.
n -- Source level single step, stepping over calls. Defaults to
current thread unless specified.
next -- Source level single step, stepping over calls. Defaults to
current thread unless specified.
nexti -- Instruction level single step, stepping over calls.
Defaults to current thread unless specified.
ni -- Instruction level single step, stepping over calls.
Defaults to current thread unless specified.
p -- Evaluate an expression on the current thread. Displays any
returned value with LLDB's default formatting.
parray -- parray -- lldb will evaluate EXPRESSION
to get a typed-pointer-to-an-array in memory, and will
display COUNT elements of that type from the array.
po -- Evaluate an expression on the current thread. Displays any
returned value with formatting controlled by the type's
author.
poarray -- poarray -- lldb will evaluate
EXPRESSION to get the address of an array of COUNT objects
in memory, and will call po on them.
print -- Evaluate an expression on the current thread. Displays any
returned value with LLDB's default formatting.
q -- Quit the LLDB debugger.
r -- Launch the executable in the debugger.
rbreak -- Sets a breakpoint or set of breakpoints in the executable.
re -- Commands to access registers for the current thread and
stack frame.
repl -- Evaluate an expression on the current thread. Displays any
returned value with LLDB's default formatting.
run -- Launch the executable in the debugger.
s -- Source level single step, stepping into calls. Defaults to
current thread unless specified.
shell -- Run a shell command on the host.
si -- Instruction level single step, stepping into calls.
Defaults to current thread unless specified.
sif -- Step through the current block, stopping if you step
directly into a function whose name matches the
TargetFunctionName.
step -- Source level single step, stepping into calls. Defaults to
current thread unless specified.
stepi -- Instruction level single step, stepping into calls.
Defaults to current thread unless specified.
t -- Change the currently selected thread.
tbreak -- Set a one-shot breakpoint using one of several shorthand
formats.
undisplay -- Stop displaying expression at every stop (specified by
stop-hook index.)
up -- Select an older stack frame. Defaults to moving one frame,
a numeric argument can specify an arbitrary number.
v -- Show variables for the current stack frame. Defaults to all
arguments and local variables in scope. Names of argument,
local, file static and file global variables can be
specified. Children of aggregate variables can be specified
such as 'var->child.x'. The -> and [] operators in 'frame
variable' do not invoke operator overloads if they exist,
but directly access the specified element. If you want to
trigger operator overloads use the expression command to
print the variable instead.
It is worth noting that except for overloaded operators,
when printing local variables 'expr local_var' and 'frame
var local_var' produce the same results. However, 'frame
variable' is more efficient, since it uses debug information
and memory reads directly, rather than parsing and
evaluating an expression, which may even involve JITing and
running code in the target program.
var -- Show variables for the current stack frame. Defaults to all
arguments and local variables in scope. Names of argument,
local, file static and file global variables can be
specified. Children of aggregate variables can be specified
such as 'var->child.x'. The -> and [] operators in 'frame
variable' do not invoke operator overloads if they exist,
but directly access the specified element. If you want to
trigger operator overloads use the expression command to
print the variable instead.
It is worth noting that except for overloaded operators,
when printing local variables 'expr local_var' and 'frame
var local_var' produce the same results. However, 'frame
variable' is more efficient, since it uses debug information
and memory reads directly, rather than parsing and
evaluating an expression, which may even involve JITing and
running code in the target program.
vo -- Show variables for the current stack frame. Defaults to all
arguments and local variables in scope. Names of argument,
local, file static and file global variables can be
specified. Children of aggregate variables can be specified
such as 'var->child.x'. The -> and [] operators in 'frame
variable' do not invoke operator overloads if they exist,
but directly access the specified element. If you want to
trigger operator overloads use the expression command to
print the variable instead.
It is worth noting that except for overloaded operators,
when printing local variables 'expr local_var' and 'frame
var local_var' produce the same results. However, 'frame
variable' is more efficient, since it uses debug information
and memory reads directly, rather than parsing and
evaluating an expression, which may even involve JITing and
running code in the target program.
x -- Read from the memory of the current target process.
For more information on any command, type ':help '. 欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)