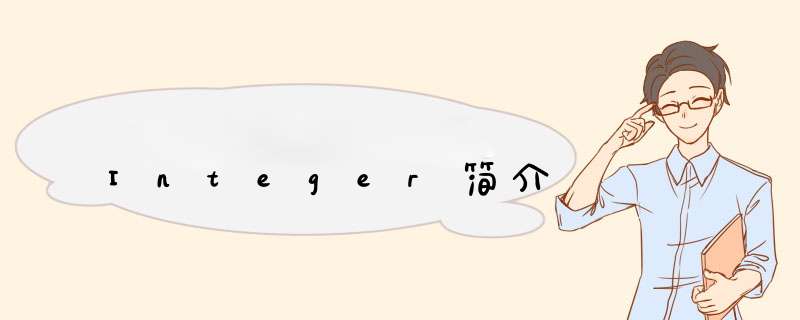
// 当创建范围为[-128,127]时 Integer a = 1; Integer b = 1; Integer c = new Integer(1); System.out.println("a == b :" + (a == b)); System.out.println("a == c :" + (a == c)); System.out.println();// 当创建范围不为[-128,127]时 Integer d = 128; Integer e = 128; Integer f = new Integer(128); System.out.println("d == e :" + (d == e)); System.out.println("d == f :" + (d == f)); System.out.println("d e f 互不相等(false为正确测试结果):" + (d == e || d == f || e == f)); System.out.println();// 包装类均为值传递 Integer g = 0; Integer h = new Integer(130); Test1(g); Test2(h); System.out.println("g = "+g); System.out.println("h = "+h); } static voID Test1(Integer t) { t = 1; System.out.println("Test1内: t = " + t); } static voID Test2(Integer t) { t = 131; System.out.println("Test2内: t = " + t); }}原文:https://blog.csdn.net/Cactus_Lrg/article/details/81489299
测试结果如下:
a == b :true
a == c :false
d == e :false
d == f :false
d e f 互不相等(false为正确测试结果):false
Test1内: t = 1
Test2内: t = 131
g = 0
h = 130
以上是内存溢出为你收集整理的Integer简介全部内容,希望文章能够帮你解决Integer简介所遇到的程序开发问题。
如果觉得内存溢出网站内容还不错,欢迎将内存溢出网站推荐给程序员好友。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)