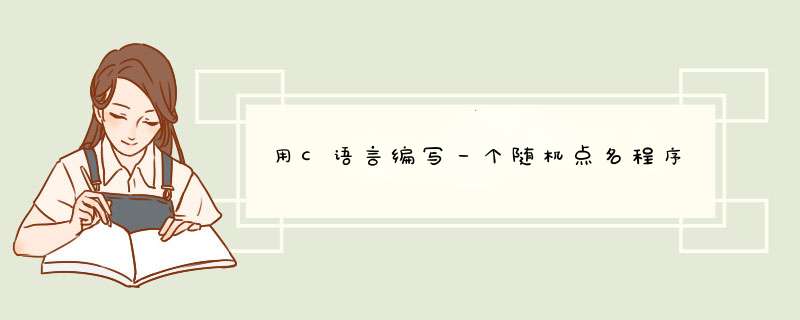
例:
#include<stdio.h>/*standardinput&output*/
#include<stdlib.h>/*standardlibary*/
#include<string.h>/*string*/
#include<conio.h>/*ConsoleInput/Output*/
#include<time.h>
structstudentinfo/*学生信息的结构体*/
{
charsNo[5];/*学生编号*/
charsxueNo[14];/*学号*/
charsname[20];/*学生的姓名*/
}st[100];
charhash[100]={0};/*链表的数组*/
intmain()
{
inti=0,j=0,flag=0,RN,*a;
FILE*fp;
charch,filename[20]={0},line[100]={0};
printf("Pleaseinputfilename:");
//fflush(stdin);/*用来清空输入缓存,以便不影响后面输入的东西*/
gets(filename);/*键盘输入文件名*/
fp=fopen(filename,"r");/*openreadonly*/
printf("名单如下:\n");/*显示所有的学生信息*/
while(fgets(line,sizeof(line)-1,fp))
{
if(line[0]!='\n'&&line[0]!='')
{
sscanf(line,"%s%s%s\n",st[i].sNo,st[i].sxueNo,st[i].sname);/*文件输入*/
printf("%s\n%s\n%s\n",st[i].sNo,st[i].sxueNo,st[i].sname);/*打印出来*/
i++;/*统计人数*/
}
}
/*设置随机数种子*/
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
/*sizeof(类型符)是计算类型所占字节数,sizeof(int)是int所占字节数,再乘以i,得到i个int型数据的总字节数。malloc函数用于动态开辟一块内存空间,参数为开辟的内存空间字节数,返回开辟的内存空间的首地址指针。*/
a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*i);
memset(a,-1,sizeof(a));/*将已开辟内存空间a的第4个字节设置为-1*/
printf("按空格键点名,其他键退出:");
fflush(stdin);
while((ch=getch())=='')
/*while(!(ch=getch())==NULL)*/
{
if(flag==i)/*如果flag等于总人数*/
{
printf("%s\n","点名结束");
break;
}
RN=rand()%i;/*产生一个随机数*/
while(hash[RN]==1)/*判断有没有完成某个一个学生点名*/
RN=rand()%i;/*产生随机数*/
flag++;/*计数*/
printf("\n~~~~~\n%s\n%s\n%s\n------------\n",st[RN].sNo,st[RN].sxueNo,st[RN].sname);/*输出学生的信息*/
hash[RN]=1;
}
}
扩展资料:printf函数使用注意事项
1、域宽
%d:按整型数据的实际长度输出。
如果想输出指定宽度可以指定域宽,%md-->m域宽,打印出来以后,在控制台上,显示m位;
如果我们要打印的数的位数如果超过我们设定m则原样输出;
如果我们要打印的数的位数如果小于我们设定的位数,则补空白,具体如下:
如果m为正数,则左对齐(左侧补空白);
如果m为负数,则右对齐(右侧补空白)。
2、转义字符
如果想输出字符"%",则应该在“格式控制”字符串中用连续两个%表示。
如:printf("%f%%",1.0/3);输出结果:0.333333%。
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define STU_NUM_MAX 64 // 假设最多有64个学生
struct Student
{
char name[10]
int stuID
}stu[STU_NUM_MAX]
int exist[STU_NUM_MAX] // 用以保存被点过名
static int index=0 // 记住点名的次数
void Iitialize(){
for(int i=0i<STU_NUM_MAXi++) exist[i]=0
}
bool IsExist(int id){
for(int i=0i<STU_NUM_MAXi++)
if(exist[i]==id) return true //已存在
return false // 不存在
}
void Add() // 添加数据
{
FILE *fp
int stu_num
printf("\t\t You want to input the number of student?:")
scanf("%d",&stu_num)
for (int i=0i<stu_numi++){
printf("\n")
printf("\t\tPlease input student ID:")
scanf("%d",&stu[i].stuID)
printf("\t\tPlease input student name:")
scanf("%s",stu[i].name)
fflush(stdin)
}
if((fp=fopen("stu.dat","ab"))==NULL) {
printf("Can't open file\n")
exit(1)
}
for(int j=0j<stu_numj++)
{
if(fwrite(&stu[j],sizeof(struct Student),1,fp)!=1)
printf("Error writing file.\n")
}
fclose(fp)
}
void rollcall() // 随机点名
{
FILE *fp
if((fp=fopen("stu.dat","rb"))==NULL)
{
printf("Can't open file.\n")
exit(1)
}
srand((unsigned)time(NULL))
int i=0
int randID=rand()%(64-1+1)+1 // 1~64
printf("\t\t随机点到的学号为:%d\n\t\t%s\t%s\n",randID,"StuID","StuName")
do
{
fseek(fp,i*sizeof(struct Student),SEEK_SET)
if(fread(&stu[i],sizeof(struct Student),1,fp))
{
if(stu[i].stuID==randID&&!IsExist(randID)){
printf("\t\t%4d\t%5s\n",stu[i].stuID,stu[i].name)
exist[index++]=randID
break}
}
i++
}while(!feof(fp))
fclose(fp)
}
int main()
{
int select=0
char answer='y'
Iitialize()
do
{
printf("1.添加数据 2.随机点名 3.退出\n请选择:")
fflush(stdin)
scanf("%d",&select)
switch(select)
{
case 1:
Add()
break
case 2:
rollcall()
break
case 3:
return 0
}
fflush(stdin)
printf("You want to continue?:")
scanf("%c",&answer)
} while (answer=='y'||answer=='Y')
return 0
}
上面的代码,我留下几个细节问题留给你自己学着解决,都是很简单的:
上面的代码,我没有对重复的学号作判断。
上面的代码,我没有把点名存放到另一个文件,而是用数组替代(可以实现的也很简单)。我怕写得代码太多,百度限制提交。
上面的代码,是测试数据,stu.dat目标文件并没有64个学生,我只写入了12条数据。
上面的代码,我没有对数据数量(最多64条)作判断。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)