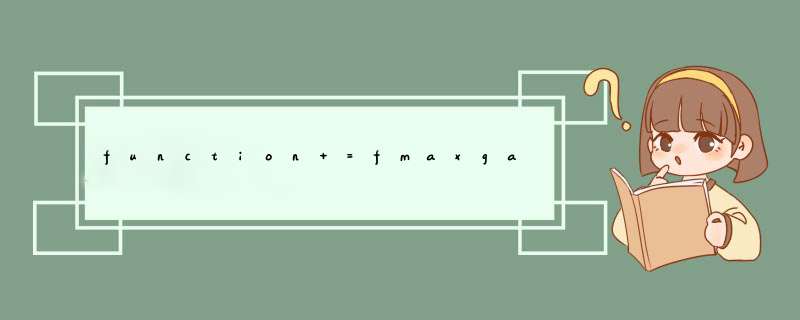
说明: fga.m 为遗传算法的主程序采用二进制Gray编码,采用基于轮盘赌法的非线性排名选择,
均匀交叉,变异 *** 作,而且还引入了倒位 *** 作!
function
[BestPop,Trace]=fga(FUN,LB,UB,eranum,popsize,pCross,pMutation,pInversion,options)
%
[BestPop,Trace]=fmaxga(FUN,LB,UB,eranum,popsize,pcross,pmutation)
% Finds a
maximum of a function of several variables.
% fmaxga solves problems of the
form:
% max F(X) subject to: LB <= X <=
UB
%
BestPop - 最优的群体即为最优的染色体群
%
Trace - 最佳染色体所对应的目标函数值
%
FUN - 目标函数
%
LB-
自变量下限
% UB
- 自变量上限
% eranum-
种群的代数,取100--1000(默认200)
% popsize -
每一代种群的规模;此可取50--200(默认100)
% pcross
- 交叉概率,一般取0.5--0.85之间较好(默认0.8)
% pmutation -
初始变异概率,一般取0.05-0.2之间较好(默认0.1)
% pInversion-
倒位概率,一般取0.05-0.3之间较好(默认0.2)
% options -
1*2矩阵,options(1)=0二进制编码(默认0),option(1)~=0十进制编
%码,option(2)设定求解精度(默认1e-4)
%
%
------------------------------------------------------------------------
T1=clock
if nargin<3, error('FMAXGA requires at least three input
arguments')end
if nargin==3,
eranum=200popsize=100pCross=0.8pMutation=0.1pInversion=0.15options=[0
1e-4]end
if nargin==4,
popsize=100pCross=0.8pMutation=0.1pInversion=0.15options=[0 1e-4]end
if
nargin==5, pCross=0.8pMutation=0.1pInversion=0.15options=[0 1e-4]end
if
nargin==6, pMutation=0.1pInversion=0.15options=[0 1e-4]end
if nargin==7,
pInversion=0.15options=[0 1e-4]end
if find((LB-UB)>0)
error('数据输入错误,请重新输入(LB<UB):')
end
s=sprintf('程序运行需要约%.4f
秒钟时间,请稍等......',(eranum*popsize/1000))
disp(s)
global m n NewPop children1 children2 VarNum
bounds=[LBUB]'bits=[]VarNum=size(bounds,1)
precision=options(2)%由求解精度确定二进制编码长度
bits=ceil(log2((bounds(:,2)-bounds(:,1))'
./
precision))%由设定精度划分区间
[Pop]=InitPopGray(popsize,bits)%初始化种群
[m,n]=size(Pop)
NewPop=zeros(m,n)
children1=zeros(1,n)
children2=zeros(1,n)
pm0=pMutation
BestPop=zeros(eranum,n)%分配初始解空间BestPop,Trace
Trace=zeros(eranum,length(bits)+1)
i=1
while
i<=eranum
for
j=1:m
value(j)=feval_r(FUN(1,:),(b2f(Pop(j,:),bounds,bits)))%计算适应度
end
[MaxValue,Index]=max(value)
BestPop(i,:)=Pop(Index,:)
Trace(i,1)=MaxValue
Trace(i,(2:length(bits)+1))=b2f(BestPop(i,:),bounds,bits)
[selectpop]=NonlinearRankSelect(FUN,Pop,bounds,bits)%非线性排名选择
[CrossOverPop]=CrossOver(selectpop,pCross,round(unidrnd(eranum-i)/eranum))
%采用多点交叉和均匀交叉,且逐步增大均匀交叉的概率
%round(unidrnd(eranum-i)/eranum)
[MutationPop]=Mutation(CrossOverPop,pMutation,VarNum)%变异
[InversionPop]=Inversion(MutationPop,pInversion)%倒位
Pop=InversionPop%更新
pMutation=pm0+(i^4)*(pCross/3-pm0)/(eranum^4)
%随着种群向前进化,逐步增大变异率至1/2交叉率
p(i)=pMutation
i=i+1
end
t=1:eranum
plot(t,Trace(:,1)')
title('函数优化的遗传算法')xlabel('进化世代数(eranum)')ylabel('每一代最优适应度(maxfitness)')
[MaxFval,I]=max(Trace(:,1))
X=Trace(I,(2:length(bits)+1))
hold
onplot(I,MaxFval,'*')
text(I+5,MaxFval,['FMAX='
num2str(MaxFval)])
str1=sprintf('进化到 %d 代 ,自变量为 %s 时,得本次求解的最优值
%f\n对应染色体是:%s',I,num2str(X),MaxFval,num2str(BestPop(I,:)))
disp(str1)
%figure(2)plot(t,p)%绘制变异值增大过程
T2=clock
elapsed_time=T2-T1
if
elapsed_time(6)<0
elapsed_time(6)=elapsed_time(6)+60
elapsed_time(5)=elapsed_time(5)-1
end
if
elapsed_time(5)<0
elapsed_time(5)=elapsed_time(5)+60elapsed_time(4)=elapsed_time(4)-1
end
%像这种程序当然不考虑运行上小时啦
str2=sprintf('程序运行耗时 %d 小时 %d 分钟 %.4f
秒',elapsed_time(4),elapsed_time(5),elapsed_time(6))
disp(str2)
%初始化种群
%采用二进制Gray编码,其目的是为了克服二进制编码的Hamming悬崖缺点
function
[initpop]=InitPopGray(popsize,bits)
len=sum(bits)
initpop=zeros(popsize,len)%The
whole zero encoding individual
for i=2:popsize-1
pop=round(rand(1,len))
pop=mod(([0 pop]+[pop
0]),2)
%i=1时,b(1)=a(1)i>1时,b(i)=mod(a(i-1)+a(i),2)
%其中原二进制串:a(1)a(2)...a(n),Gray串:b(1)b(2)...b(n)
initpop(i,:)=pop(1:end-1)
end
initpop(popsize,:)=ones(1,len)%The whole
one encoding individual
%解码
function [fval] = b2f(bval,bounds,bits)
% fval -
表征各变量的十进制数
% bval - 表征各变量的二进制编码串
% bounds - 各变量的取值范围
%
bits - 各变量的二进制编码长度
scale=(bounds(:,2)-bounds(:,1))'./(2.^bits-1)
%The range of the variables
numV=size(bounds,1)
cs=[0
cumsum(bits)]
for
i=1:numV
a=bval((cs(i)+1):cs(i+1))
fval(i)=sum(2.^(size(a,2)-1:-1:0).*a)*scale(i)+bounds(i,1)
end
%选择 *** 作
%采用基于轮盘赌法的非线性排名选择
%各个体成员按适应值从大到小分配选择概率:
%P(i)=(q/1-(1-q)^n)*(1-q)^i,
其中 P(0)>P(1)>...>P(n), sum(P(i))=1
function [selectpop]=NonlinearRankSelect(FUN,pop,bounds,bits)
global m
n
selectpop=zeros(m,n)
fit=zeros(m,1)
for i=1:m
fit(i)=feval_r(FUN(1,:),(b2f(pop(i,:),bounds,bits)))%以函数值为适应值做排名依据
end
selectprob=fit/sum(fit)%计算各个体相对适应度(0,1)
q=max(selectprob)%选择最优的概率
x=zeros(m,2)
x(:,1)=[m:-1:1]'
[y
x(:,2)]=sort(selectprob)
r=q/(1-(1-q)^m)%标准分布基值
newfit(x(:,2))=r*(1-q).^(x(:,1)-1)%生成选择概率
newfit=cumsum(newfit)%计算各选择概率之和
rNums=sort(rand(m,1))
fitIn=1newIn=1
while
newIn<=m
if
rNums(newIn)<newfit(fitIn)
selectpop(newIn,:)=pop(fitIn,:)
newIn=newIn+1
else
fitIn=fitIn+1
end
end
%交叉 *** 作
function
[NewPop]=CrossOver(OldPop,pCross,opts)
%OldPop为父代种群,pcross为交叉概率
global m n
NewPop
r=rand(1,m)
y1=find(r<pCross)
y2=find(r>=pCross)
len=length(y1)
if
len>2&mod(len,2)==1%如果用来进行交叉的染色体的条数为奇数,将其调整为偶数
y2(length(y2)+1)=y1(len)
y1(len)=[]
end
if
length(y1)>=2
for
i=0:2:length(y1)-2
if
opts==0
[NewPop(y1(i+1),:),NewPop(y1(i+2),:)]=EqualCrossOver(OldPop(y1(i+1),:),OldPop(y1(i+2),:))
else
[NewPop(y1(i+1),:),NewPop(y1(i+2),:)]=MultiPointCross(OldPop(y1(i+1),:),OldPop(y1(i+2),:))
end
end
end
NewPop(y2,:)=OldPop(y2,:)
%采用均匀交叉
function [children1,children2]=EqualCrossOver(parent1,parent2)
global n children1
children2
hidecode=round(rand(1,n))%随机生成掩码
crossposition=find(hidecode==1)
holdposition=find(hidecode==0)
children1(crossposition)=parent1(crossposition)%掩码为1,父1为子1提供基因
children1(holdposition)=parent2(holdposition)%掩码为0,父2为子1提供基因
children2(crossposition)=parent2(crossposition)%掩码为1,父2为子2提供基因
children2(holdposition)=parent1(holdposition)%掩码为0,父1为子2提供基因
%采用多点交叉,交叉点数由变量数决定
function [Children1,Children2]=MultiPointCross(Parent1,Parent2)
global n Children1 Children2
VarNum
Children1=Parent1
Children2=Parent2
Points=sort(unidrnd(n,1,2*VarNum))
for
i=1:VarNum
Children1(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i))=Parent2(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i))
Children2(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i))=Parent1(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i))
end
%变异 *** 作
function [NewPop]=Mutation(OldPop,pMutation,VarNum)
global m n
NewPop
r=rand(1,m)
position=find(r<=pMutation)
len=length(position)
if
len>=1
for i=1:len
k=unidrnd(n,1,VarNum)%设置变异点数,一般设置1点
for
j=1:length(k)
if
OldPop(position(i),k(j))==1
OldPop(position(i),k(j))=0
else
OldPop(position(i),k(j))=1
end
end
end
end
NewPop=OldPop
%倒位 *** 作
function [NewPop]=Inversion(OldPop,pInversion)
global m n
NewPop
NewPop=OldPop
r=rand(1,m)
PopIn=find(r<=pInversion)
len=length(PopIn)
if
len>=1
for
i=1:len
d=sort(unidrnd(n,1,2))
if
d(1)~=1&d(2)~=n
NewPop(PopIn(i),1:d(1)-1)=OldPop(PopIn(i),1:d(1)-1)
NewPop(PopIn(i),d(1):d(2))=OldPop(PopIn(i),d(2):-1:d(1))
NewPop(PopIn(i),d(2)+1:n)=OldPop(PopIn(i),d(2)+1:n)
end
end
end
能为用户带来实实在在价值应该就是很成功了,江苏省中医院100%的核心业务系统都运行在Nutanix的平台之上,因为采用了Nutanix数据库管理工具Era,置备新数据库的时间减少了90%,克隆所需的时间由以前的4天缩短到4个小时,新服务上线的周期也从2~4天缩短到4~6小时▪⋅除此之外,Nutanix数据库管理工具Era在金融、医疗、制造等不同领域均有成功案例,而且还在不断“加厚”自身平台,增加了包括 Nutanix Era 在内的 PaaS 层的功能和服务,此外还有安全服务、Nutanix Flow、KPS 平台等,完全可以通过自动化来简化数据库管理。
首先,破译的第一步就是寻找密文中出现超过一次的字母。有两种情况可能导致这样的重复发生。最有可能的是明文中同样的字母序列使用密钥中同样的字母加了密;另外还有一种较小的可能性是明文中两个不同的字母序列通过密钥中不同部分加了密,碰巧都变成了密文中完全一样的序列。假如我们限制在长序列的范围内,那么第二种可能性可以很大程度地被排除,这种情况下,我们多数考虑到4个字母或4个以上的重复序列。破译的第二步是确定密钥的长度,又看看这一段先:
关键词 F O R E S T F O R E S T F O R E S T F O R E S T F O R
明 文 b e t t e r t o d o w e l l t h a n t o s a y w e l l
密 文 G S K X W K Y C U S O X Q Z K L S G Y C J E Q P J Z C
第一个YC出现后到第二个YC的结尾一共有12个字母(U S O X Q Z K L S G Y C)
那么密钥的长度应是12的约数---1,2,3,4,6,12之中的一个(其中,1可排除)。
技巧
1.A-E段,U-Z段以及O-T段的特征比较显著,可先从这些方面着手;
2.如果一些字符串出现的频率较多,不妨猜猜,特别要注意THE,-ING等的出现;
3.要留意那些图表中没有出现的字母,很多时候也会是突破点,如X与Z的空缺;
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)