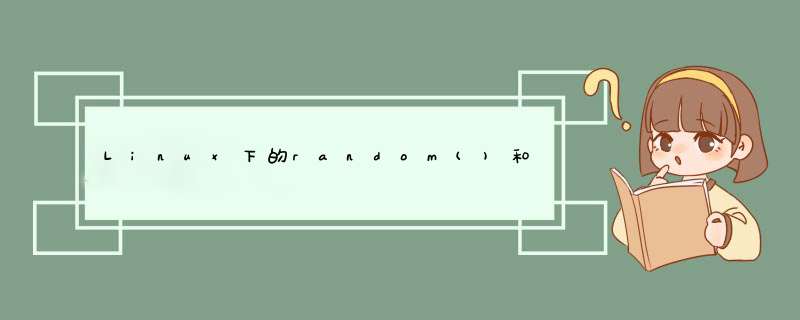
long random(void)
int rand(void)
void srand(unsigned seed)
random返回的是一个0到(2^31 - 1)的long类型整数
rand返回的是一个0到RAND_MAX的int类型整数
而你这里产生的随机数序列是一样的,这个很好解释,因为你知道srand,但是你却不知道还有一个srandom,这个函数是为random设置种子的,参数和srand一样。
我的帮助手册上甚至是这么写的:
The random() and srandom() functions have (almost) the same calling sequence
and initialization properties as the rand(3) and srand(3) functions. The
difference is that rand(3) produces a much less random sequence -- in fact,
the low dozen bits generated by rand go through a cyclic pattern. All of
the bits generated by random() are usable. For example, `random()&01' will
produce a random binary value.
=============================
希望我的回答能给你带来帮助
下面大概分几个方面进行罗列:Linux要包含
[cpp]
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
等头文件,而windows下则是包含
[cpp]
#include <winsock.h>
。
Linux中socket为整形,Windows中为一个SOCKET。
Linux中关闭socket为close,Windows中为closesocket。
Linux中有变量socklen_t,Windows中直接为int。
因为linux中的socket与普通的fd一样,所以可以在TCP的socket中,发送与接收数据时,直接使用read和write。而windows只能使用recv和send。
设置socet选项,比如设置socket为非阻塞的。Linux下为
[cpp]
flag = fcntl (fd, F_GETFL)
fcntl (fd, F_SETFL, flag | O_NONBLOCK)
,Windows下为
[cpp]
flag = 1
ioctlsocket (fd, FIONBIO, (unsigned long *) &flag)
。
当非阻塞socket的TCP连接正在进行时,Linux的错误号为EINPROGRESS,Windows的错误号为WSAEWOULDBLOCK。
file
Linux下面,文件换行是"\n",而windows下面是"\r\n"。
Linux下面,目录分隔符是"/",而windows下面是"\"。
Linux与Windows下面,均可以使用stat调用来查询文件信息。但是,Linux只支持2G大小,而Windows只支持4G大小。为了支持更大的文件查询,可以在Linux环境下加
_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64定义,在Windows下面使用_stat64调用,入参为struct __stat64。
Linux中可根据stat的st_mode判断文件类型,有S_ISREG、S_ISDIR等宏。Windows中没有,需要自己定义相应的宏,如
[cpp]
#define S_ISREG(m) (((m) &0170000) == (0100000))
#define S_ISDIR(m) (((m) &0170000) == (0040000))
Linux中删除文件是unlink,Windows中为DeleteFile。
time
Linux中,time_t结构是长整形。而windows中,time_t结构是64位的整形。如果要在windows始time_t为32位无符号整形,可以加宏定义,_USE_32BIT_TIME_T。
Linux中,sleep的单位为秒。Windows中,Sleep的单位为毫秒。即,Linux下sleep (1),在Windows环境下则需要Sleep (1000)。
Windows中的timecmp宏,不支持大于等于或者小于等于。
Windows中没有struct timeval结构的加减宏可以使用,需要手动定义:
[cpp]
#define MICROSECONDS (1000 * 1000)
#define timeradd(t1, t2, t3) do { \
(t3)->tv_sec = (t1)->tv_sec + (t2)->tv_sec \
(t3)->tv_usec = (t1)->tv_usec + (t2)->tv_usec % MICROSECONDS \
if ((t1)->tv_usec + (t2)->tv_usec >MICROSECONDS) (t3)->tv_sec ++ \
} while (0)
#define timersub(t1, t2, t3) do { \
(t3)->tv_sec = (t1)->tv_sec - (t2)->tv_sec \
(t3)->tv_usec = (t1)->tv_usec - (t2)->tv_usec \
if ((t1)->tv_usec - (t2)->tv_usec <0) (t3)->tv_usec --, (t3)->tv_usec += MICROSECONDS \
} while (0)
调用进程
Linux下可以直接使用system来调用外部程序。Windows最好使用WinExec,因为WinExec可以支持是打开还是隐藏程序窗口。用WinExec的第二个入参指明,如
SW_SHOW/SW_HIDE。
杂项
Linux为srandom和random函数,Windows为srand和rand函数。
Linux为snprintf,Windows为_snprintf。
同理,Linux中的strcasecmp,Windows为_stricmp。
错误处理
Linux下面,通常使用全局变量errno来表示函数执行的错误号。Windows下要使用GetLastError ()调用来取得。
Linux环境下仅有的
这些函数或者宏,Windows中完全没有,需要用户手动实现。
atoll
[cpp]
long long
atoll (const char *p)
{
int minus = 0
long long value = 0
if (*p == '-')
{
minus ++
p ++
}
while (*p >= '0' &&*p <= '9')
{
value *= 10
value += *p - '0'
p ++
}
return minus ? 0 - value : value
}
gettimeofday
[cpp]
#if defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(_MSC_EXTENSIONS)
#define EPOCHFILETIME 11644473600000000Ui64
#else
#define EPOCHFILETIME 11644473600000000ULL
#endif
struct timezone
{
int tz_minuteswest
int tz_dsttime
}
int
gettimeofday (struct timeval *tv, struct timezone *tz)
{
FILETIME ft
LARGE_INTEGER li
__int64 t
static int tzflag
if (tv)
{
GetSystemTimeAsFileTime (&ft)
li.LowPart = ft.dwLowDateTime
li.HighPart = ft.dwHighDateTime
t = li.QuadPart /* In 100-nanosecond intervals */
t -= EPOCHFILETIME /* Offset to the Epoch time */
t /= 10 /* In microseconds */
tv->tv_sec = (long) (t / 1000000)
tv->tv_usec = (long) (t % 1000000)
}
if (tz)
{
if (!tzflag)
{
_tzset ()
tzflag++
}
tz->tz_minuteswest = _timezone / 60
tz->tz_dsttime = _daylight
}
return 0
}
编译相关
当前函数,Linux用__FUNCTION__表示,Windows用__func__表示。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Socket 编程 windows到Linux代码移植遇到的问题
1)头文件
windows下winsock.h/winsock2.h
linux下sys/socket.h
错误处理:errno.h
2)初始化
windows下需要用WSAStartup
linux下不需要
3)关闭socket
windows下closesocket(...)
linux下close(...)
4)类型
windows下SOCKET
linux下int
如我用到的一些宏:
#ifdef WIN32
typedef int socklen_t
typedef int ssize_t
#endif
#ifdef __LINUX__
typedef int SOCKET
typedef unsigned char BYTE
typedef unsigned long DWORD
#define FALSE 0
#define SOCKET_ERROR (-1)
#endif
5)获取错误码
windows下getlasterror()/WSAGetLastError()
linux下errno变量
6)设置非阻塞
windows下ioctlsocket()
linux下fcntl() <fcntl.h>
7)send函数最后一个参数
windows下一般设置为0
linux下最好设置为MSG_NOSIGNAL,如果不设置,在发送出错后有可 能会导致程序退出。
8)毫秒级时间获取
windows下GetTickCount()
linux下gettimeofday()
3、多线程
多线程: (win)process.h --〉(linux)pthread.h
_beginthread -->pthread_create
_endthread -->pthread_exit
-----------------------------------------------------------------
windows与linux平台使用的socket均继承自Berkeley socket(rfc3493),他们都支持select I/O模型,均支持使用getaddrinfo与getnameinfo实现协议无关编程。但存在细微差别,
主要有:
头文件及类库。windows使用winsock2.h(需要在windows.h前包含),并要链接库ws2_32.lib;linux使用netinet/in.h, netdb.h等。
windows下在使用socket之前与之后要分别使用WSAStartup与WSAClean。
关闭socket,windows使用closesocket,linux使用close。
send*与recv*函数参数之socket长度的类型,windows为int,linux为socklen_t,可预编译指令中处理这一差异,当平台为windows时#define socklen_t unsigned int。
select函数第一个参数,windows忽略该参数,linux下该参数表示集合中socket的上限值,一般设为sockfd(需select的socket) + 1。
windows下socket函数返回值类型为SOCKET(unsigned int),其中发生错误时返回INVALID_SOCKET(0),linux下socket函数返回值类型int, 发生错误时返回-1。
另外,如果绑定本机回环地址,windows下sendto函数可以通过,linux下sendto回报错:errno=22, Invalid arguement。一般情况下均绑定通配地址。
转载jlins
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)