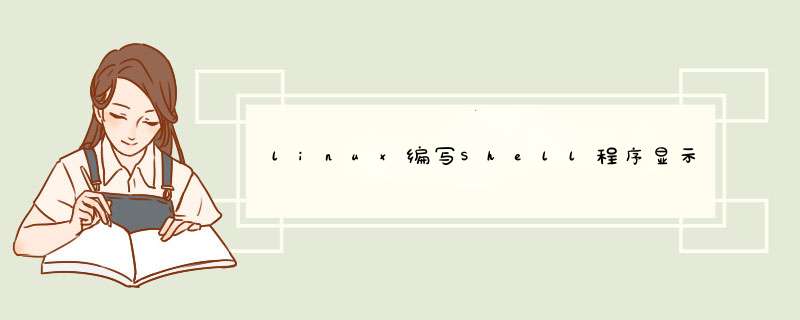
do
b=$(($i%6))
a=$(($i%7))
[[ $(($a+$b)) != 0 &&$(($b*$a)) == 0 ]] &&echo $i
done
不用写吧,本来有个 bc 命令可用,没有下载就成.非要写一个,zsh 的function里有一个,名 zcalc,
贴上来给你
#!/usr/bin/zsh -i
#
# Zsh calculator. Understands most ordinary arithmetic expressions.
# Line editing and history are available. A blank line or `q' quits.
#
# Runs as a script or a function. If used as a function, the history
# is remembered for reuse in a later call (and also currently in the
# shell's own history). There are various problems using this as a
# script, so a function is recommended.
#
# The prompt shows a number for the current line. The corresponding
# result can be referred to with $<line-no>, e.g.
# 1>32 + 10
# 42
# 2>$1 ** 2
# 1764
# The set of remembered numbers is primed with anything given on the
# command line. For example,
# zcalc '2 * 16'
# 1>32 # printed by function
# 2>$1 + 2 # typed by user
# 34
# 3>
# Here, 32 is stored as $1. This works in the obvious way for any
# number of arguments.
#
# If the mathfunc library is available, probably understands most system
# mathematical functions. The left parenthesis must be adjacent to the
# end of the function name, to distinguish from shell parameters
# (translation: to prevent the maintainers from having to write proper
# lookahead parsing). For example,
# 1>sqrt(2)
# 1.4142135623730951
# is right, but `sqrt (2)' will give you an error.
#
# You can do things with parameters like
# 1>pi = 4.0 * atan(1)
# too. These go into global parameters, so be careful. You can declare
# local variables, however:
# 1>local pi
# but note this can't appear on the same line as a calculation. Don't
# use the variables listed in the `local' and `integer' lines below
# (translation: I can't be bothered to provide a sandbox).
#
# Some constants are already available: (case sensitive as always):
# PI pi, i.e. 3.1415926545897931
# E e, i.e. 2.7182818284590455
#
# You can also change the output base.
# 1>[#16]
# 1>
# Changes the default output to hexadecimal with numbers preceded by `16#'.
# Note the line isn't remembered.
# 2>[##16]
# 2>
# Change the default output base to hexadecimal with no prefix.
# 3>[#]
# Reset the default output base.
#
# This is based on the builtin feature that you can change the output base
# of a given expression. For example,
# 1>[##16] 32 + 20 / 2
# 2A
# 2>
# prints the result of the calculation in hexadecimal.
#
# You can't change the default input base, but the shell allows any small
# integer as a base:
# 1>2#1111
# 15
# 2>[##13] 13#6 * 13#9
# 42
# and the standard C-like notation with a leading 0x for hexadecimal is
# also understood. However, leading 0 for octal is not understood --- it's
# too confusing in a calculator. Use 8#777 etc.
#
# Options: -#<base>is the same as a line containing just `[#<base>],
# similarly -##<base>they set the default output base, with and without
# a base discriminator in front, respectively.
#
#
# To do:
# - separate zcalc history from shell history using arrays --- or allow
# zsh to switch internally to and from array-based history.
emulate -L zsh
setopt extendedglob
local line ans base defbase forms match mbegin mend psvar optlist opt arg
local compcontext="-math-"
integer num outdigits outform=1
# We use our own history file with an automatic pop on exit.
history -ap "${ZDOTDIR:-$HOME}/.zcalc_history"
forms=( '%2$g' '%.*g' '%.*f' '%.*E' )
zmodload -i zsh/mathfunc 2>/dev/null
: ${ZCALCPROMPT="%1v>"}
# Supply some constants.
float PI E
(( PI = 4 * atan(1), E = exp(1) ))
# Process command line
while [[ -n $1 &&$1 = -(|[#-]*) ]]do
optlist=${1[2,-1]}
shift
[[ $optlist = (|-) ]] &&break
while [[ -n $optlist ]]do
opt=${optlist[1]}
optlist=${optlist[2,-1]}
case $opt in
('#') # Default base
if [[ -n $optlist ]]then
arg=$optlist
optlist=
elif [[ -n $1 ]]then
arg=$1
shift
else
print "-# requires an argument" >&2
return 1
fi
if [[ $arg != (|\#)[[:digit:]]## ]]then
print - "-# requires a decimal number as an argument" >&2
return 1
fi
defbase="[#${arg}]"
esac
done
done
for (( num = 1num <= $#num++ ))do
# Make sure all arguments have been evaluated.
# The `$' before the second argv forces string rather than numeric
# substitution.
(( argv[$num] = $argv[$num] ))
print "$num>$argv[$num]"
done
psvar[1]=$num
while vared -cehp "${(%)ZCALCPROMPT}" linedo
[[ -z $line ]] &&break
# special cases
# Set default base if `[#16]' or `[##16]' etc. on its own.
# Unset it if `[#]' or `[##]'.
if [[ $line = (#b)[[:blank:]]#('[#'(\#|)(<->|)']')[[:blank:]]#(*) ]]then
if [[ -z $match[4] ]]then
if [[ -z $match[3] ]]then
defbase=
else
defbase=$match[1]
fi
print -s -- $line
line=
continue
else
base=$match[1]
fi
else
base=$defbase
fi
print -s -- $line
case ${${line##[[:blank:]]#}%%[[:blank:]]#} in
q) # Exit if `q' on its own.
return 0
norm) # restore output format to default
outform=1
sci[[:blank:]]#(#b)(<->)(#B))
outdigits=$match[1]
outform=2
fix[[:blank:]]#(#b)(<->)(#B))
outdigits=$match[1]
outform=3
eng[[:blank:]]#(#b)(<->)(#B))
outdigits=$match[1]
outform=4
local([[:blank:]]##*|))
eval $line
line=
continue
*)
# Latest value is stored as a string, because it might be floating
# point or integer --- we don't know till after the evaluation, and
# arrays always store scalars anyway.
#
# Since it's a string, we'd better make sure we know which
# base it's in, so don't change that until we actually print it.
eval "ans=\$(( $line ))"
# on error $ans is not setlet user re-edit line
[[ -n $ans ]] || continue
argv[num++]=$ans
psvar[1]=$num
esac
if [[ -n $base ]]then
print -- $(( $base $ans ))
elif [[ $ans = *.* ]] || (( outdigits ))then
printf "$forms[outform]\n" $outdigits $ans
else
printf "%d\n" $ans
fi
line=
done
return 0
支援小数点,+ - * / , ok
你可以用计算工具bc来算,再导回shell如:
#!/bin/sh
x=0.02
x=`echo "scale=3$x+0.02" | bc `
echo $x
如果要控制循环,x<0.06显然是不能用的,但你可以用x<6,然后把最终结果用bc除以100呗~
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)