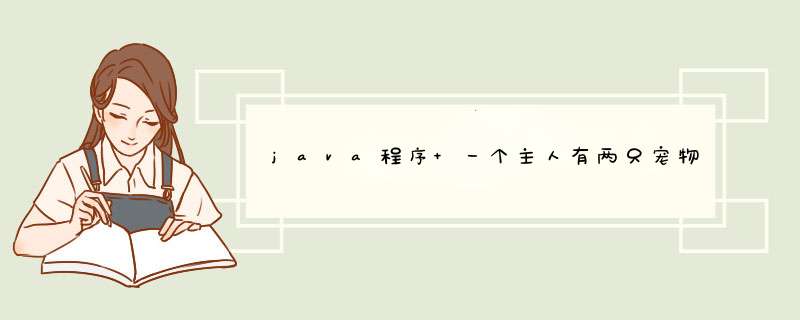
public static void main(String args[]) {
磨如碰 Animal a1 = new Animal("猫","小花","鱼")
瞎谈Animal a2 = new Animal("狗","旺财","骨头")
a1.eat()a2.ert()
}
}
class Animal {
String species
String animalName
String foodName
Animal(String 橡陵species,String animalName,String foodName) {
this.species = species
this.animalNam e= animalName
this.foodName = foodName
}
public void eat() {
System.out.print("我的"+species+","+animalName +" 吃了 :"+foodName)
}
}
//我也才学java不到一个月,我就能理解这么多
//还可以写继承的。亦可以写成多线程的。
//继承就是把Animal类当父类,再写两个类继承它。这里又可以复习多态,哈哈。
//多线程就是同事喂这俩动物。
public class Run {public static void main(String[] args) {
Master master = new Master()
master.feedDog("鸡骨头")
master.feedCat("鸡骨头")
}
}
class Master {
private Pet mPet
private Food mFood
public void feedCat(String food) {
mPet = new Cat()
mFood = new Food(food)
mPet.eat(mFood)
}
public void feedDog(String food) {
mPet = new Dog()
mFood = new Food(food)
mPet.eat(mFood)
}
}
class Dog extends Pet{
@Override
public void eat(Food food) {
System.out.println("正在喂小狗吃"+food.getFood())
if (food.getFood().matches(Food.BONE)) {
System.out.println("小狗正在吃"+food.getFood()+"!")
}else {
System.out.println("但是小狗不喜欢吃"差姿租+food.getFood()+"!")
}
}
}
class Cat extends Pet{
@Override
public void eat(Food food) {
System.out.println("正在喂小猫吃"+food.getFood())
if (food.getFood().matches(Food.FISH)) {
System.out.println("小猫正在吃"+food.getFood()+"!")
}else {
System.out.println("但是小猫不喜欢册棚吃"+food.getFood()+"!")
}
}
}
class Food {
public final static String BONE = ".*骨.*"
public final static String FISH = ".*鱼.*"
private String food
public String getFood() {
return food
}
public void setFood(String food) {
this.food = food
}
public Food(String food) {
this.food = food
}
}
class Pet 虚兆{
public void eat(Food food) {
}
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)