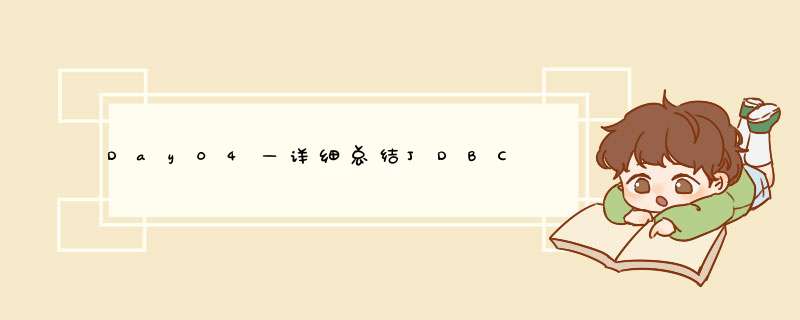
//1:注册驱动(需要有驱动包) //2:获取连接 //3:准备sql //4:创建sql发送器 即 *** 作sql的对象 //5:sql执行 //6:获取数据并展示 //7:关闭资源注意
使用jdbc 主要是进行 DML *** 作 对数据的增删改查演示的表: 二:statement 语句 2.1:增删改
@Test
public void test01() throws SQLException {
//1:注册驱动(需要有驱动包) (也可以不用写 默认会自动加载)
// Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
//2:获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
String name = "root";
String password = "123456";
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, name, password);
//4:创建sql发送器 即 *** 作sql的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
) {
//3:准备sql
// String sql = "insert into users values(4,"zbb","123456","赵冰冰")";
String sql = "delete from users where id = 4";
//5:sql执行
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
//6:获取数据并展示
System.out.println("i = " + i);
//7:关闭资源使用 try - with -resource 资源可以自动关闭
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.2:查
1.查询一条记录
将一条记录封装为对象 2.查询多条记录
使用集合存储多个对象
注意:
1. 当sql 中出现别名时 在获取结果集数据时 使用 名字获取数据时 注意是使用别名
String sql = "select id, username uname ,password, nickname from user";
String username = resultSet.getString("uname"); 2.在获取数据时 获取数据的方式 有四种
get数据类型(字段的下标); 下标从1开始
get数据类型(别名); getObject(字段的下标);
getObject(别名);
@Test
public void test02() {
//2:获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
String name = "root";
String password = "123456";
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, name, password);
//4:创建sql发送器 即 *** 作sql的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
) {
//String sql = "select * from users where id = 3";
String sql = "select * from users";
//5:sql执行
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//6:获取数据并展示
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
Object id = resultSet.getObject(1);
Object name1 = resultSet.getObject(2);
Object pwd = resultSet.getObject(3);
Object nickName = resultSet.getObject(4);
//直接打印
//System.out.println("id = " + id + ",name = " + name1 + ",password = " + pwd + " ,nickName =" + nickName);
Integer id1 = (Integer)id;
String name2 = (String)name1;
String password2 = (String)pwd;
String nickName2 = (String)nickName;
User user = new User(id1,name2,password2,nickName2);
//封装成一个实体类进行打印
// System.out.println("user = " + user);
list.add(user);
}
//打印表中所有数据
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//7:关闭资源使用 try - with -resource 资源可以自动关闭
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
封装成实体类:
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String password;
private String nickName;
public User() {
}
public User(Integer id, String name, String password, String nickName) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
this.nickName = nickName;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getNickName() {
return nickName;
}
public void setNickName(String nickName) {
this.nickName = nickName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + ''' +
", password='" + password + ''' +
", nickName='" + nickName + ''' +
'}';
}
}
2.3:statement对象的弊端
使用 statment 容易出现的问题:2.4:sql注入演示
1. sql拼接 比较麻烦 2.sql拼接 有sql注入问题
输入的数据不满足sql的校验 依然可以获取所有的数据
@Test
public void test03() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String name3 = scanner.nextLine();
// System.out.println("请输入密码");
// String password = scanner.nextLine();
//2:获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
String name = "root";
String password = "123456";
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, name, password);
//4:创建sql发送器 即 *** 作sql的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
) {
//String sql = "select * from users where id = 3";
// String sql = "select * from users";
String sql = "select * from users where name = '"+name3+"'"; //ls' or 1 = '1 sql注入
//5:sql执行
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//6:获取数据并展示
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
Object id = resultSet.getObject(1);
Object name1 = resultSet.getObject(2);
Object pwd = resultSet.getObject(3);
Object nickName = resultSet.getObject(4);
//直接打印
//System.out.println("id = " + id + ",name = " + name1 + ",password = " + pwd + " ,nickName =" + nickName);
Integer id1 = (Integer)id;
String name2 = (String)name1;
String password2 = (String)pwd;
String nickName2 = (String)nickName;
User user = new User(id1,name2,password2,nickName2);
//封装成一个实体类进行打印
// System.out.println("user = " + user);
list.add(user);
}
//打印表中所有数据
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//7:关闭资源使用 try - with -resource 资源可以自动关闭
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
三:PreparedStatement 语句对statement优化
3.1:PreparedStatement 语句
PreparedStatement:解决了 sql拼接 和sql注入问题 PreparedStatement 是 Statement的孩子 PreparedStatement 预编译对象3.2:PreparedStatement 增删改
@Test
public void test01() throws SQLException {
//1:注册驱动
//2:获取链接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8","root","123456");
//3:准备sql
String sql = "insert into users values(?,?,?,?)";
//4:创建对象
PreparedStatement pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5:填充数据
pst.setObject(1, 4);
pst.setObject(2, "gbb");
pst.setObject(3, "123456");
pst.setObject(4, "郭冰冰");
//5:执行sql
int i = pst.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("i = " + i);
//6:关闭资源
pst.close();
connection.close();
}
3.3:PreparedStatement查
@Test
public void test02() throws SQLException {
//1:注册驱动
//2:获取链接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8","root","123456");
//3:准备sql
//查询一条
// String sql = "select * from users where id = ?";
//查询所有
String sql = "select * from users";
//4:创建对象
PreparedStatement pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5:填充数据
//查询
// pst.setObject(1, 2);
//5:执行sql
// int i = pst.executeUpdate();
ResultSet resultSet = pst.executeQuery();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
String name1 = resultSet.getString(2);
String pwd = resultSet.getString(3);
String nickName = resultSet.getString(4);
//直接打印
// System.out.println("id = " + id + ",name = " + name1 + ",password = " + pwd + " ,nickName =" + nickName);
//封装成一个实体类进行打印
// System.out.println("user = " + user);
User user = new User(id,name1,pwd,nickName);
list.add(user);
}
list.forEach(System.out::println);
// System.out.println("i = " + i);
//6:关闭资源
pst.close();
connection.close();
}
3.4:获取自动增长键
//传入参数 Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS 返回自动增长值
PreparedStatement pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
ResultSet resultSet = pst.getGeneratedKeys();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
System.out.println("id = " + id);
}
@Test
public void test01() throws SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456");
// String sql = "insert into users values(null,?,?,?)";
String sql = "insert into users values(null,?,?,?)";
//传入参数 Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS 返回自动增长值
PreparedStatement pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
//填充数据
pst.setString(1, "zbb");
pst.setString(2, "123456");
pst.setString(3, "赵冰冰");
//获取数据
int i = pst.executeUpdate();
//数据展示
System.out.println("i = " + i);
//获取自动增长值
ResultSet resultSet = pst.getGeneratedKeys();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
System.out.println("id = " + id);
}
resultSet.close();
pst.close();
connection.close();
}
}
3.4:批处理
注意点:(需要配置url)
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc_test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
主要方法:addBatch() 和 executeBatch()
@Test
public void test02() throws SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456");
String sql = "insert into users values(null,?,?,?)";
//传入参数 Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS 返回自动增长值
PreparedStatement pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
//填充数据
pst.setString(1, "fbb" + i);
pst.setString(2, "123456");
pst.setString(3, "范冰冰" + i);
pst.addBatch();
}
pst.executeBatch();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用的时间" + (end - start));
//获取数据
// pst.executeUpdate();
//数据展示
pst.close();
connection.close();
}
四:JDBC封装工具包
4.1:jdbc:properties 文件(每一句末尾绝对不能放;否则报错)
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql:///test?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
user=root
password=123456
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true #url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myexer user=root password=1234564.2:JDBC封装工具包 property的作用
properties.load(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
public class JDBCUtils {
static String url;
static String user;
static String password;
static {
//1.创建Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
Class.forName(driver);
url = properties.getProperty("url");
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("----------------");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//硬编码
public static Connection getConnection() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, IOException {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
public static void closeResource(ResultSet resultSet, Connection connection, Statement statement) throws SQLException {
//此为工具方法 部门资源可能没有值 因此在关闭前 进行非空校验
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
}
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)