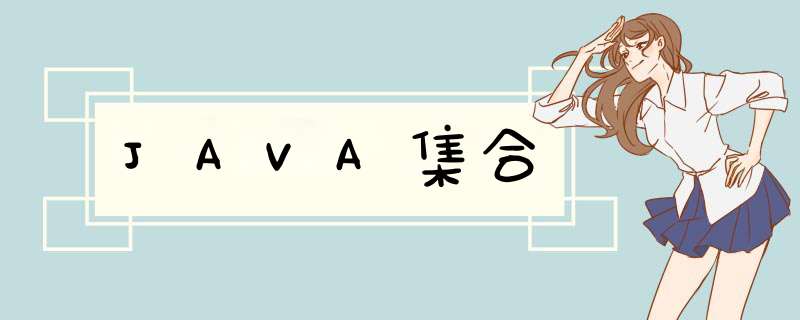
addAll(Collection coll1)将coll1集合中的元素添加到当前集合中
isEmpty()判断当前集合是否为空
Collection接口-集合
Collection接口-常用方法
1、add()方法
boolean add(E e) //向集合中插入一个元素
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello world");
c.add(100);
c.add(3.14);
c.add(true);
2、clear()方法
void clear() //清空集合中的元素,从这个集合中移除所有的元素
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.clear();
3、isEmpty()方法
boolean isEmpty() //返回 true如果集合不包含任何元素。判断集合是否为空
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello world");
c.add(100);
c.add(3.14);
c.add(true);
boolean bool = c.isEmpty(); // false
4、contains()方法
boolean contains(Object o) //返回 true如果集合包含指定元素,判断集合是否包含此元素
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello world");
c.add(100);
c.add(3.14);
c.add(true);
boolean bool = c.contains(100); //true
boolean bools = c.contains(200); //false
5、size()方法
int size() //返回此集合中的元素的数目。返回集合中的元素个数
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello world");
c.add(100);
c.add(3.14);
c.add(true);
int i = c.size(); // 4
c.clear();
int j = c.size(); // 0
6、remove()方法
boolean remove(Object o) //从这个集合中移除指定元素的一个实例,如果它是存在的。删除集合中的一个元素
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello world");
c.add(100);
c.add(3.14);
c.add(true);
boolean bool = c.remove(100); //true
int i = c.size(); // 3
boolean bools = c.remove(200); //false
7、toArray()方法
Object[] toArray() // 返回包含此集合中所有元素的数组。
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello world");
c.add(100);
c.add(3.14);
c.add(true);
Object[] objects = c.toArray(); // 返回一个Object类型的数组,并把集合中的所有元素,存在数组中
使用迭代器遍历集合:
Iterator iterator=coll.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象。
使用foreach循环遍历集合:
for(Object obj:coll){ //重新创建一个obj,将coll中每个值赋给obj,不改变coll中值
System.out.println(obj);
}
使用foreach循环遍历数组:
int[] arr=new int[]{1,2,3};
for(int i:arr){
System.out.println(i);
}
JDK7中HashMap的实现原理
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)