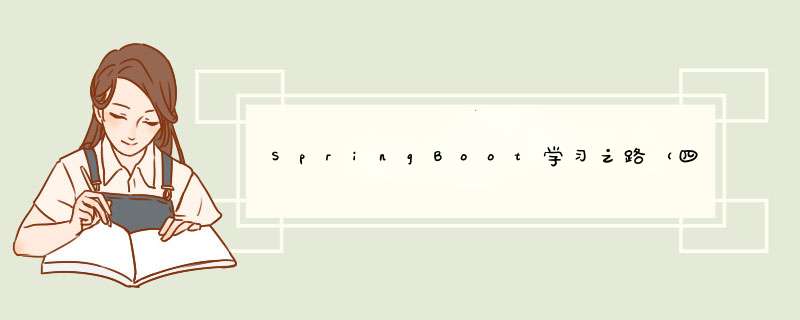
1、在resource目录下新建一个testMyproperty.properties配置文件
#对实体类对象Myporperty进行属性设置 test.id=1 test.name=Jerry
2、在src/main/com/chen/domain下自定义一个配置类MyProperty
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Configuration //表明当前类是一个自定义配置类
//@Component // 可以替换@Configuration和@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyProperty.class)这两个注解
@PropertySource("classpath:testMyproperty.properties")// 指定自定义配置文件的路径和名称
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyProperty.class)//表明开启当前配置类的属性注入功能
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")// 批量注入,将testMyproperty.properties前缀为test的属性值注入到当前配置类的属性中
public class MyProperty {
private Integer id;
private String name;
// 省略setter方法和getter方法
// 省略toString方法
}
3、编写测试类
import com.chen.domain.MyProperty;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Demo01ApplicationTest {
@Autowired
private MyProperty myProperty;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(myProperty);
}
}
4、运行测试类
二、使用@importResource加载XML配置文件这种配置方式在实际开发中特殊情况下才会使用。SpringBoot”约定优于配置“思想更推荐使用配置类的方式代替XML配置
传统的Spring项目主要基于XML配置文件,在SpringBoot中使用@importResource可以用来兼容Spring项目加载外部的XML配置文件
@importResource注解标注在一个配置类上,通常会将这个注解放到SpringBoot的启动类上,使用时指定XML配置文件的路径和名称
1、在src/main/com/chen/domain下新建一个MyBean类
public class MyBean {
}
2、在xml中配置这个Bean交给Spring容器来管理
在resource下新建一个目录beanxml,在该目录下新建一个beans.xml配置文件
3、在SpringBoot的启动类上加入注解@importResource
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.importResource;
@SpringBootApplication//标明当前类为SpringBoot启动类
@importResource("classpath:beanxml/beans.xml")//指定加载自定义XML配置文件的路径和名称
public class Demo01Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Demo01Application.class,args);
}
}
4、编写配置类
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Demo01ApplicationTest {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;//Spring容器实例
@Test
public void test(){
//判断容器中是否有myBean这个实例
boolean myBean = applicationContext.containsBean("myBean");
System.out.println(myBean);
}
}
5、运行测试类
结果表明,外部xml配置的bean已经被容器成功加载
三、使用@Configuration自定义配置文件使用@Configuration注解指定配置类,它的作用和XML配置是一样的,配置类中的@Bean注解方法返回的对象将作为Bean注入Spring容器中,并且在默认情况下,使用@Bean注解的方法名就是组件名
1、在src/main/com/chen/domain下新建一个myConfigBean类
public class myConfigBean {
}
2、在src/main/com/chen新建一个config包,在该包下新建一个myConfig类
import com.chen.domain.myConfigBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class myConfig {
@Bean//将返回值对象作为bean添加到Spring容器中,beanName即为方法名,也可以通过@Bean("XXX")来指定beanName为XXX
public myConfigBean myConfigBean(){
return new myConfigBean();
}
}
3、编写配置类
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Demo01ApplicationTest {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;//Spring容器实例
@Test
public void test(){
//判断容器中是否有myConfigBean这个实例
boolean myBean = applicationContext.containsBean("myConfigBean");
System.out.println(myBean);
}
}
4、运行结果
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)