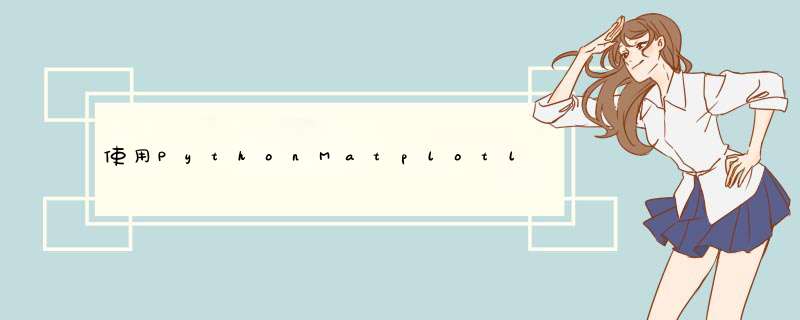
我发现的一种方法是生成颜色图,然后将其投影到极轴上。这是一个有效的示例-
尽管其中包括一个令人讨厌的骇客(明确注释)。我敢肯定有一种方法可以调整限制,或者(更难)编写自己的限制
Transform来解决它,但是我还没有完全解决这个问题。我以为致电的范围
Normalize会做到这一点,但显然不会。
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom matplotlib import cmimport matplotlib as mplfig = plt.figure()display_axes = fig.add_axes([0.1,0.1,0.8,0.8], projection='polar')display_axes._direction = 2*np.pi ## This is a nasty hack - using the hidden field to ## multiply the values such that 1 become 2*pi ## this field is supposed to take values 1 or -1 only!!norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(0.0, 2*np.pi)# Plot the colorbar onto the polar axis# note - use orientation horizontal so that the gradient goes around# the wheel rather than centre outquant_steps = 2056cb = mpl.colorbar.Colorbarbase(display_axes, cmap=cm.get_cmap('hsv',quant_steps), norm=norm, orientation='horizontal')# aesthetics - get rid of border and axis labels cb.outline.set_visible(False)display_axes.set_axis_off()plt.show() # Replace with plt.savefig if you want to save a file这产生
如果您想要戒指而不是轮子,请在此之前
plt.show()或
plt.savefig
display_axes.set_rlim([-1,1])
这给
按照@EelkeSpaak的注释-
如果按照OP将图形另存为SVG,则以下是处理所得图形的提示:所得SVG图像的小元素相互接触且不重叠。这会导致某些渲染器(Inkscape,Adobe
Reader,可能不在打印中)中的灰色线条模糊。一个简单的解决方案是使用例如Inkscape或Illustrator对每个单独的渐变元素应用较小的缩放比例(例如120%)。请注意,您必须将变换单独应用于每个元素(上述软件提供了自动执行此功能的功能),而不是整个图形,否则无效。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)