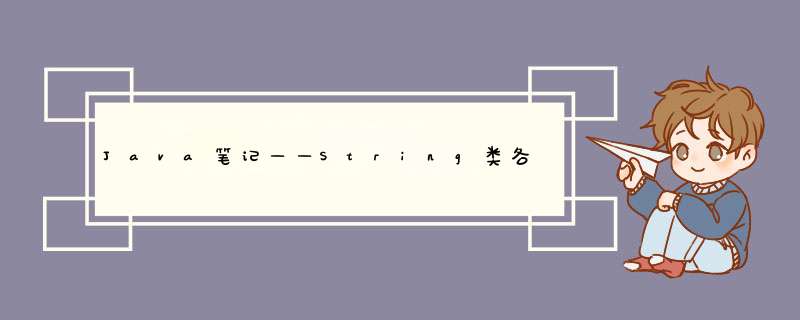
System.out.println(s.indexOf(“owo”)); // 4
System.out.println(s.indexOf(“ovo”)); //不存在,返回-1
System.out.println("=============");
// public int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)
// 返回指定字符第一次出现的索引,以指定的索引开始搜索,搜索范围包括指定的索引
System.out.println(s.indexOf(‘l’,4)); // 8
System.out.println(s.indexOf(‘e’,1)); // 1
System.out.println(s.indexOf(‘h’,1)); //不存在,返回-1
System.out.println("=============");
//int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex)
//返回指定字符串第一次出现的索引,以指定的索引开始搜索
System.out.println(s.indexOf(“owo”,2)); // 4
System.out.println(s.indexOf(“owo”,8)); //不存在,返回-1
System.out.println("=============");
//public String substring(int beginIndex) 截取一段字符串
// 子字符串以指定索引处的字符开头,包括指定索引处,并扩展到该字符串的末尾。
System.out.println(s.substring(3)); // loworld
// 索引超出范围,返回空字符串
String ss = s.substring(10);
System.out.println(ss.equals("")); // true
System.out.println("=============");
//public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)
//子串截取范围左闭右开,开始于指定beginIndex并延伸到字符索引endIndex-1
System.out.
《一线大厂Java面试题解析+后端开发学习笔记+最新架构讲解视频+实战项目源码讲义》
【docs.qq.com/doc/DSmxTbFJ1cmN1R2dB】 完整内容开源分享
println(s.substring(1,3)); // el
//System.out.println(s.substring(1,12)); //数组下标越界异常
}
}
String类的转化方法String类实现转换功能的方法有
byte[] getBytes() —— 转换为字节数组
char[] toCharArray() —— 转换为字符数组
static String valueOf(char[] chs) —— 字符数组转换为字符串
static String valueOf(int i) —— int值转换为字符串
String toLowerCase() —— 字符串全部小写
String toUpperCase() —— 字符串全部大写
String concat(String str) —— 将指定字符串连接到原字符串的后面
package test.StringDemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = “helloWORLD”;
//public byte[] getBytes()
// 使用平台的默认字符集将此String编码为字节序列,将结果存储到新的字节数组中。
byte[] b = s.getBytes();
for(int i=0;i System.out.println(b[i]); } //也可以像下面这样打印,只需要一行 //[104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 87, 79, 82, 76, 68] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b)); System.out.println("==============="); //char[] toCharArray()将此字符串转换为新的字符数组。 //由原先的字符串变成字符数组 char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for(char c:chars){ System.out.println©; } //[h, e, l, l, o, W, O, R, L, D] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars)); System.out.println("==============="); //将字符数组转换为字符串 //static String valueOf(char[] chs) System.out.println(String.valueOf(chars)); //helloWORLD //同理这里也可以将int类型的数据转换为字符串类型 String ss = String.valueOf(20); System.out.println(ss); //20 System.out.println("==============="); //String toLowerCase() 将字符串内容全部转化成小写 System.out.println(s.toLowerCase()); //helloworld // String toUpperCase(),将字符串内容全部转大写 System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()); //HELLOWORLD System.out.println(s); //helloWORLD,s自身的值并没有被改变 System.out.println("==============="); //public String concat(String str)将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾 System.out.println(s.concat(“java”)); //helloWORLDjava //这里同样需要注意的是 String s2 = null; //这里会报空指针异常的错误 //System.out.println(s2.concat(“nothing”)); } } 实现替换功能的方法 String replace(char old,char new) String replace(String old,String new) package test.StringDemo; public class demo10 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = “helloworld”; //String replace(char old,char new)替换字符 //将字符串中所有的l替换成a,返回一个新的字符串 String s1 = s.replace(‘l’,‘a’); System.out.println(s1); //heaaoworad //String replace(String old,String new)替换字符串 String s2 = s.replace(“owo”,“ovo”); System.out.println(s2); //hellovorld //如果被替换的字符串不存在,返回原来的字符串 String s3 = s.replace(“abc”,“efg”); System.out.println(s3); //helloworld } } String trim() package test.StringDemo; public class demo11 { public static void main(String[] args) { //去除字符串两边的空格 String s = " hello "; System.out.println(s); System.out.println(s.trim()); } } int compareTo(String str) —— 按位置比较字符串 int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) ——按位置比较字符串,忽略大小写 package test.StringDemo; public class demo12 { public static void main(String[] args) { //当前面的字符不相同时 String s1 = “hello”; //h的ASCII码值为104 String s2 = “hello”; String s3 = “java”; //j的ASCII码值为106 String s4 = “apache”; //a的ASCII码值为97 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); //0 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); //-2 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); //7 //当前面的字符相同时 String ss1 = “hel”; String ss2 = “helloworld”; System.out.println(s1.compareTo(ss1)); //2 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(ss2)); //-5 //忽略大小写 String s5 = “Hello”; //H的ASCII码值为72 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s5)); //32 System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s5)); //0 } } 这里可以来看一下compareTo的源码 public int compareTo(String anotherString) { int len1 = value.length; int len2 = anotherString.value.length; int lim = Math.min(len1, len2); char v1[] = value; char v2[] = anotherString.value; int k = 0; while (k < lim) { char c1 = v1[k]; char c2 = v2[k]; if (c1 != c2) { return c1 - c2; } k++; } return len1 - len2; } 这里可以简单的总结为, 当对应位置的字符不相同时,返回的值是ASCII码值相减的结果。 当对应位置的字符都相同,但是字符个数不相同时,返回的是字符串长度相减的结果。 题目一:统计一个字符串中大写字母,小写字母,数字出现的次数 package test.StringDemo; public class demo8 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = “helloHello123World”; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); int Bigcount = 0; int Smallcount = 0; int Numcount = 0; for(char c:chars){ if(c>=‘A’&&c<=‘Z’){ Bigcount++; } else if(c>=‘a’&&c<=‘z’){ Smallcount++; } //这里注意一下,不能用(int)c的方式,因为字符’1’对应的int值是49 else if(c>=‘0’&&c<=‘9’){ Numcount++; } } System.out.println(“大写字母个数”+Bigcount +“小写字母个数”+Smallcount +“数字个数”+Numcount); } } 题目二:把一个字符串的首字母转成大写,其余的都是小写 package test.StringDemo; public class demo9 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = “helloWORLD”; String sHead = s.substring(0,1); System.out.println(sHead); String sTail = s.substring(1); System.out.println(sTail); String sLower = sTail.toLowerCase(); String sUpper = sHead.toUpperCase(); String sWhole = sUpper+sLower; System.out.println(sWhole); //也可以合成进一步里面写 String ss = s.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() .concat(s.substring(1).toLowerCase()); System.out.println(ss); } } 题目三,反转字符串 package test.StringDemo; public class demo13 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = “hello”; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); char[] c = new char[chars.length]; String s1 = “”; for(int i=chars.length-1;i>=0;i–){ s1 += chars[i]; } System.out.println(s1); } } 题目四:统计某一段字符串出现的次数 欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)