最近在复习Spring的面试题,关于Spring Bean的生命周期一直没有很深入的理解,自己结合源码参考了网上的几篇文章,写了一点东西,方便理解。
参考文章:帅地玩编程 阿风的架构笔记
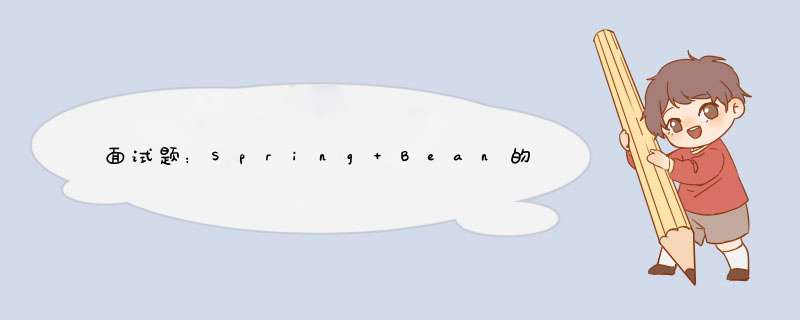
- Spring 启动,查找并加载需要被 Spring 管理的 Bean,进行 Bean 的实例化;
- Bean 实例化后,对 Bean 的引入和值注入到 Bean 的属性中;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口的话,Spring 将 Bean 的 Id 传递给 setBeanName() 方法;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 setBeanFactory() 方法,将 BeanFactory 容器实例传入;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 Bean 的 setApplicationContext() 方法,将 Bean 所在应用上下文引用传入进来;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,Spring 将调用它们的 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。类似地,如果 Bean 使用 init-method 声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的 postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法;
- 此时,Bean 已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了。它们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到应用上下文被销毁;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,Spring 将调用它的 destory() 接口方法,同样,如果 Bean 使用了 destory-method 声明销毁方法,该方法也会被调用。
让我们结合源码捋一遍这个过程,主要的过程在org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java这个类中
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java initializeBean()方法 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口的话,Spring 将 Bean 的 Id 传递给 setBeanName() 方法;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 setBeanFactory() 方法,将 BeanFactory 容器实例传入;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 Bean 的 setApplicationContext() 方法,将 Bean 所在应用上下文引用传入进来;
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
// 如果Bean实现了Aware接口
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
// 如果实现了BeanNameAware接口,则调用Bean的setBeanName方法
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
// 如果实现了BeanClassLoaderAware接口,则调用Bean的setBeanClassLoader方法
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
// 如果实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,则调用Bean的setBeanFactory方法
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.java
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
//....//
//如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 Bean 的 setApplicationContext() 方法,
//将 Bean 所在应用上下文引用传入进来;
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法;
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
// 该方法是Spring后置处理器中的方法
// 该方法是在Bean实例化(new)之后,初始化(设置各种属性)之前会被调用
// 在调用afterPropertiesSet方法之前会被调用
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
// 在bean初始化之后会被调用
// 在调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法或者init-method指定的方法执行之后调用.
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
- 如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,Spring 将调用它们的 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。类似地,如果 Bean 使用 init-method 声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用;
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
// 判断bean对象是否为InitializingBean的实例
// 如果实现了InitializingBean接口,则只掉调用bean的afterPropertiesSet方法
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的 postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法;
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
调用Bean对象的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 该步骤中会创建代理类.
// 在bean初始化之后会被调用
// 在调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法或者init-method指定的方法执行之后调用.
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
- 此时,Bean 已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了。它们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到应用上下文被销毁;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,Spring 将调用它的 destory() 接口方法,同样,如果 Bean 使用了 destory-method 声明销毁方法,该方法也会被调用。
DisposableBeanAdapter.java
@Override
public void destroy() {
//...//
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'");
}
try {
// 9. 若实现 DisposableBean 接口,则执行 destory()方法
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction
总结:
- 首先是实例化、属性赋值、初始化、销毁这 4 个大阶段;
- 再是初始化的具体 *** 作,有 Aware 接口的依赖注入、BeanPostProcessor 在初始化前后的处理以及 InitializingBean 和 init-method 的初始化 *** 作;
- 销毁的具体 *** 作,有注册相关销毁回调接口,最后通过DisposableBean 和 destory-method 进行销毁。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)