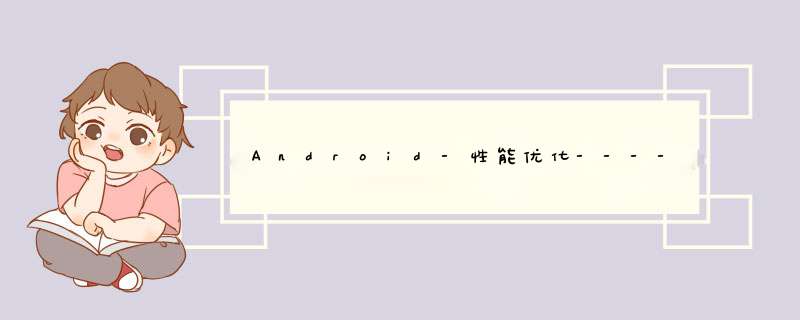
classpath ‘com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.5.2’
classpath ‘com.hujiang.aspectjx:gradle-android-plugin-aspectjx:2.0.0’
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
在app下的build.gradle添加依赖
apply plugin: ‘android-aspectjx’
在dependencies中添加
implementation ‘org.aspectj:aspectjrt:1.9.4’
然后创建一个类
package com.noahedu.myapplication.aspectj;
import android.util.Log;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class MyApplicationAspectj {
@Around(“call(* com.noahedu.myapplication.MyApplication.**(…))”)
public void getTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
Log.e("MyApplicationAspectj " ,(name + " cost " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time)));
}
}
这样我们运行的时候,就会直接在logcat中打印出application中的onCreate方法中所有调用方法的耗时情况了
2020-07-10 14:22:27.151 1619-1619/? E/MyApplicationAspectj: taskOne cost 150
2020-07-10 14:22:29.203 1619-1619/com.noahedu.myapplication E/MyApplicationAspectj: taskTwo cost 2052
2020-07-10 14:22:29.554 1619-1619/com.noahedu.myapplication E/MyApplicationAspectj: taskThrid cost 351
2020-07-10 14:22:30.556 1619-1619/com.noahedu.myapplication E/MyApplicationAspectj: taskFour cost 1001
这样我们几乎没有碰Application中的任何代码,也就够得出各个方法的耗时,几乎对代码无侵入。
6、启动优化的工具选择 6.1 traceviewTraceView是Android SDK中内置的一个工具,他可以加载trace文件,以图形化的形式展示相应代码的执行时间,次数及调用栈,便于我们分析。
Debug.startMethodTracing(“MyApplication”);
//TODO
Debug.stopMethodTracing();
运行项目就可以我们的SD卡中找到对应的trace文件了,如果是Android studio可以直接在右下角找到
DeviceFileExporer -->sdcard --> Android – > data -->files —>自己项目的包名
然后双击即可查看文件了
优点:使用简单,图形形式展示所执行的时间,调用栈等。
缺点:会影响到我们优化的方向,由于是图形化展示,也是比较占用CPU资源的,所以得到的时间往往是比实际的要大。
上面介绍了多了几个获取任务执行时间的方式和工具,那么当我们知道某个方法耗时了,我们该怎么处理呢?
package com.noahedu.myapplication;
import android.app.Application;
import android.os.Debug;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Debug.startMethodTracing(“MyApplication”);
taskOne();
taskTwo();
taskThrid();
taskFour();
Debug.stopMethodTracing();
}
public void taskOne(){
try {
Thread.sleep(150);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void taskTwo(){
try {
Thread.sleep(2050);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void taskThrid(){
try {
Thread.sleep(350);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void taskFour(){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
现在application的onCreate方法中有几个任务,各个耗时是不一样的。可能很多同学就会说了,异步处理啊,开线程,放到线程池中,或者创建一个IntentService来执行。那么我们就要考虑几个问题了
第一:异步处理,如果在某个页面需要用到某个SDK,但是又没有初始化完成呢?
第二:假如说taskTwo需要taskOne的某个返回值呢?怎么保证taskOne在taskTwo之前执行完毕呢?
第三:开线程,开多少个线程呢?多了会造成资源浪费,少了资源又没有合理的利用。
我个人觉得针对于启动优化,在Application中的onCreate()进行初始化任务 *** 作,我们首先需要对这些任务进行一个优先级划分,针对于那些优先级高的任务,我们可以优先进行处理,对于那些优先级较低的,我们可以适当的延迟进行加载。
其次有很多同学喜欢把那些优先级较低的任务进行延迟加载,比如new Handler().postDelayed(),这种我觉得是非常不可取的,假如说放在postDelayed中的任务耗时2s,延迟1s进行处理,那么在执行2s任务的过程中,有用户进行 *** 作,那岂不是很卡吗,很明显,这是指标不治本的。
7.1 启动器的思想针对上面说的几个痛点,怎么在处理上面的几个痛点,又能保证代码的可维护性呢?换句话说就是一个新人不需要理解整个过程,直接就可以开干呢?那么,启动器来了。
启动器核心思想:充分利用CPU多核,自动梳理任务顺序
1、任务全部封装成Task对象,传入到集合中。
2、根据所有的任务依赖关系,形成一个有向无环图,然后通过拓扑排序排列出任务的执行流程
3、通过CountDownLatch来控制某一个任务是否执行完毕才进行下一步。
4、线程池创建核心线程的数量,由手机的核数量决定的。
进行任务排序
package com.noahedu.launchertool.launchstarter.sort;
import com.noahedu.launchertool.launchstarter.task.Task;
import com.noahedu.launchertool.launchstarter.utils.DispatcherLog;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.collection.ArraySet;
public class TaskSortUtil {
private static List sNewTasksHigh = new ArrayList<>();// 高优先级的Task
Set dependSet = new ArraySet<>(); DispatcherLog.i("task analyse cost makeTime " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - makeTime)); @NonNull pri 《Android学习笔记总结+最新移动架构视频+大厂安卓面试真题+项目实战源码讲义》 【docs.qq.com/doc/DSkNLaERkbnFoS0ZF】 完整内容开源分享 vate static void printAllTaskName(List newTasksAll) { public static List getTasksHigh() { // 仅仅是保护性代码 执行任务代码 package com.noahedu.launchertool.launchstarter.task; import android.os.Looper; import com.noahedu.launchertool.launchstarter.TaskDispatcher;
public class DispatchRunnable implements Runnable { public DispatchRunnable(Task task) { @Override public DispatchRunnable(Task task) { @Override 欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出
public static synchronized List getSortResult(List originTasks,
List
long makeTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Graph graph = new Graph(originTasks.size());
for (int i = 0; i < originTasks.size(); i++) {
Task task = originTasks.get(i);
if (task.isSend() || task.dependsOn() == null || task.dependsOn().size() == 0) {
continue;
}
for (Class cls : task.dependsOn()) {
int indexOfDepend = getIndexOfTask(originTasks, clsLaunchTasks, cls);
if (indexOfDepend < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(task.getClass().getSimpleName() +
" depends on " + cls.getSimpleName() + " can not be found in task list ");
}
dependSet.add(indexOfDepend);
graph.addEdge(indexOfDepend, i);
}
}
List indexList = graph.topologicalSort();
List newTasksAll = getResultTasks(originTasks, dependSet, indexList);
printAllTaskName(newTasksAll);
return newTasksAll;
}
private static List getResultTasks(List originTasks,
Set dependSet, List indexList) {
List newTasksAll = new ArrayList<>(originTasks.size());
List newTasksDepended = new ArrayList<>();// 被别人依赖的
List newTasksWithOutDepend = new ArrayList<>();// 没有依赖的
List newTasksRunAsSoon = new ArrayList<>();// 需要提升自己优先级的,先执行(这个先是相对于没有依赖的先)
for (int index : indexList) {
if (dependSet.contains(index)) {
newTasksDepended.add(originTasks.get(index));
} else {
Task task = originTasks.get(index);
if (task.needRunAsSoon()) {
newTasksRunAsSoon.add(task);
} else {
newTasksWithOutDepend.add(task);
}
}
}
// 顺序:被别人依赖的————》需要提升自己优先级的————》需要被等待的————》没有依赖的
sNewTasksHigh.addAll(newTasksDepended);
sNewTasksHigh.addAll(newTasksRunAsSoon);
newTasksAll.addAll(sNewTasksHigh);
newTasksAll.addAll(newTasksWithOutDepend);
return newTasksAll;
}
if (true) {
return;
}
for (Task task : newTasksAll) {
DispatcherLog.i(task.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
return sNewTasksHigh;
}
private static int getIndexOfTask(List originTasks,
List
int index = clsLaunchTasks.indexOf(cls);
if (index >= 0) {
return index;
}
final int size = originTasks.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (cls.getSimpleName().equals(originTasks.get(i).getClass().getSimpleName())) {
return i;
}
}
return index;
}
}
import android.os.Process;
import com.noahedu.launchertool.launchstarter.stat.TaskStat;
import com.noahedu.launchertool.launchstarter.utils.DispatcherLog;
private Task mTask;
private TaskDispatcher mTaskDispatcher;
this.mTask = task;
}
public DispatchRunnable(Task task,TaskDispatcher dispatcher) {
this.mTask = task;
this.mTaskDispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public void run() {
DispatcherLog.i(mTask.getClass().getSimpleName()
r;
this.mTask = task;
}
public DispatchRunnable(Task task,TaskDispatcher dispatcher) {
this.mTask = task;
this.mTaskDispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public void run() {
DispatcherLog.i(mTask.getClass().getSimpleName()

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)