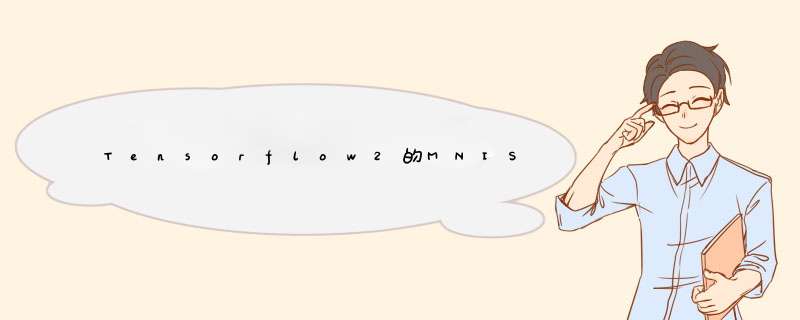
首先是个关于这个的长截图,包括结果以及代码:
使用长截图的方法,目前可行的是Chrome里F12,其他参照后面链接,edge的浏览器目前不可以
(1条消息) 新版Edge如何长截图_今天怎么又下雨的博客-CSDN博客_edge长截图https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44122062/article/details/105855048另外可以使用QQ进行长截屏:
用电脑如何截长图,我懂你要的 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/358417947
下面长截图为相应的代码及结论:
需要代码及实际的步骤的可以参考下文:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
print("Tensorflow version:", tf.__version__)
mnist =tf.keras.datasets.mnist (train_images,train_labels),(test_images,test_labels)= mnist.load_data()
print("Train image shape:",train_images.shape,"Train label shape:",train_labels.shape)
print("Test image shape:",test_images.shape,"Test label shape:",test_labels.shape)
print("image data:",train_images[1])
print("train labels:",train_labels[1])
def plot_image(image):
plt.imshow(image.reshape(28,28),cmap='binary')
plt.show()
plot_image(train_images[1])
total_num =len(train_images) print(total_num) valid_split =0.2 train_num=int(total_num*(1-valid_split)) train_x =train_images[:train_num] train_y =train_labels[:train_num] valid_x=train_images[train_num:] valid_y=train_labels[train_num:] test_x = test_images test_y =test_labels valid_x.shape
进行数据的转换,转换为行向量:
train_x =train_x.reshape(-1,784) valid_x =valid_x.reshape(-1,784) test_x= test_x.reshape(-1,784)
进行归一化处理,因为像素是255,但对于实际自己数据需要使用:
train_x=tf.cast(train_x/255.0,tf.float32) valid_x=tf.cast(valid_x/255.0,tf.float32) test_x =tf.cast(test_x/255.0,tf.float32)
对于12列数据的一般数据归一化:
# 归一化处理
for i in range(12):
x_data[:,i]=(x_data[:,i]-x_data[:,i].min())/(x_data[:,i].max()-x_data[:,i].min())
对label进行热码处理:
#对标签数据进行独热编码 train_y= tf.one_hot(train_y,depth=10) valid_y= tf.one_hot(valid_y,depth=10) test_y= tf.one_hot(test_y,depth=10)
build the model :
# build the model
def model(x,w,b):
pred = tf.matmul(x,w)+b
return tf.nn.softmax(pred)
#准备变量 W = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([784,10],mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.float32)) # don;t forget the random B = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(10),dtype = tf.float32) print(W) print(B)
define the loss function:
def loss(x,y,w,b):
pred =model(x,w,b)
#loss_=tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentroy(y_true=y,y_pred=pred)
loss_= tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true=y,y_pred=pred)
return tf.reduce_mean(loss_)
#设置超参数 training_epochs =20 learning_rate =0.001 batch_size = 50 #批量训练一次的样本
def grad(x,y,w,b):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
loss_ =loss(x,y,w,b)
return tape.gradient(loss_,[w,b])
#返回梯度向量损失函数的,注意编程时的结构顺序
#选择优化器 optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate) # help apply_gradients
def accuracy(x,y,w,b):
pred =model(x,w,b)
correct_prediction =tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
训练函数:
loss_list_train =[]
loss_list_valid =[]
acc_list_train =[]
acc_list_valid =[]
W_list=[]
B_list=[]
total_step = int (train_num/batch_size)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for step in range(total_step):
xs=train_x[step*batch_size:(step+1)*batch_size,:]
ys=train_y[step*batch_size:(step+1)*batch_size]
grads = grad(xs,ys,W,B)
#calculate the stiffness W B
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads,[W,B]))
loss_train =loss(train_x,train_y,W,B).numpy()
loss_valid =loss(valid_x,valid_y,W,B).numpy()
acc_train =accuracy(train_x,train_y,W,B).numpy()
acc_valid =accuracy(valid_x,valid_y,W,B).numpy()
loss_list_train.append(loss_train)
loss_list_valid.append(loss_valid)
acc_list_train.append(acc_train)
acc_list_valid.append(acc_valid)
print("epoch={:3d},train_loss={:.4f},valid_loss={:.4f},train_acc={:.4f},valid_acc={:.4f}".format(epoch+1,loss_train,loss_valid,acc_train,acc_valid))
# graph
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("loss")
plt.plot(loss_list_train,'blue',label="Train_loss")
plt.plot(loss_list_valid,'red',label="Valid_loss")
plt.legend(loc=1)
# graph
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("acc")
plt.plot(acc_list_train,'blue',label="Train_acc")
plt.plot(acc_list_valid,'red',label="Valid_acc")
plt.legend(loc=1)
准确率结果:
acc_test = accuracy(test_x,test_y,W,B).numpy
print("Test accuracy:",acc_test)
数据的预测:
def predict(x, w, b):
pred = model(x, w, b)
result = tf.argmax(pred, 1).numpy()
return result
pred_test=predict(test_x,W,B) print(pred_test)
进行数字的可视化:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np
主要可视化代码,注意相应结构顺序:
def plot_images(images, labels, preds, index=0, num=10): # 定义之后一次最多可以显示10张图片
fig = plt.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(10, 4) # 设置幕布的长和宽
if num > 10:
num = 10
for i in range(0, num):
ax = plt.subplot(2, 5, i + 1) # 起到了规划图形之间的分布 同时也有i的循环来指定输出哪一幅图像
# ax.imshow(np.reshape(images[index], (28, 28)), cmap='binary')
tmp = images[index]
tmp = tmp.reshape(28, 28)
ax.imshow(tmp, cmap='binary')
title = "label=" + str(labels[index])
if len(preds) > 0: # 因为有时只是想输出图像 可能会在没有预测值之前
title += ",predict=" + str(preds[index])
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=10) # fontsize是字体大小
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
index += 1
plt.show()
最后显示命令:
plot_images(test_images,test_labels,pred_test,10,10)
总结:以上为完整的MNIST的TensorFlow2实现过程,相应的文件会单独上传
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)