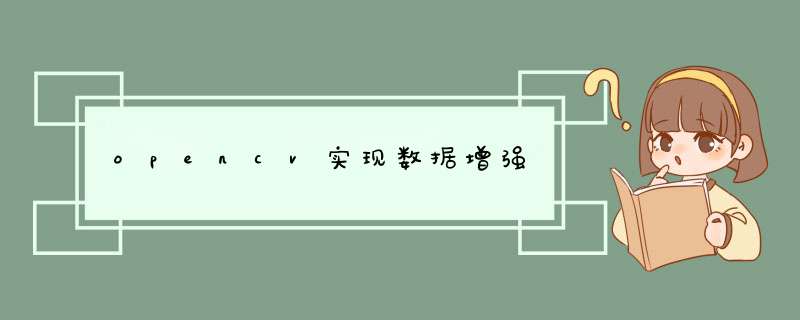
import os
from os import listdir
from os.path import join
import random
import cv2
import numpy as np
#翻转
def fanzhuan(img):
x = cv2.flip(img, 0) # x轴
x1 = cv2.flip(img, 1) # y轴
x2 = cv2.flip(img, -1) # x,y轴
return x1
#单独缩放1
def Re(img,n,m):
rows, cols = img.shape[:2]
size=(int(cols*n),int(rows*m))
y=cv2.resize(img,size)
return y
#平移
def move(img,n,m):
M=np.float32([[1,0,n],[0,1,m]])
move=cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(img.shape[1],img.shape[0]))
return move
#单独缩放2 缺点会把图像size为长宽相等,会失去一些特征
def suofang(img):
mapx=np.zeros(img.shape[:2],np.float32)
mapy = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], np.float32)
rows,cols=img.shape[:2]
for i in range (rows):
for j in range(cols):
if 0.1*colsthres:
output[i][j]=255
else:
output[i][j]=img[i][j]
return output
# rows,cols=img.shape[:2]
#裁剪
def caijian(img):
rows1,cols1=img.shape[:2]
start_row,start_col=int(rows1*0.1875),int(cols1*0.15)
end_row,end_col=int(rows1*0.8125),int(cols1*0.8)
cropped=img[start_row:end_row,start_col:end_col]
return cropped
#缩放,旋转
def resize_RO(img,n,m):
H, W = img.shape[:2]
n = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((W/ 2, H / 2), n, m) #n代表旋转角度,m为缩放尺度
Rotato= cv2.warpAffine(img, n, (W, H))
return Rotato
#
if __name__ =='__main__':
# 此部分是遍历文件夹下图像
# test_image_path="" # 文件路径
# image_filenames=[join(test_image_path,x) for x in listdir (test_image_path)]
# for image_filename in image_filenames:
# assert os.path.exists(image_filename),"file:'{}' does not exist.".format(image_filename)
# img=cv2.imshow("ori",image_filename)
# 单张图片 *** 作 1011/0967/-1
img = cv2.imread("G:\111\end0.jpg", -1)
# move(img,-10,-20) #平移
# fanzhuan(img) #翻转
# suofang(img) #缩放
# sp_noise(img, 0.02) #椒盐噪声
# caijian(img) #裁剪
# resize_RO(img, 30, 0.5) #缩放加旋转
# img = np.hstack([img2, img6,img14]) # 一个窗口多img显示
#显示
cv2.imshow("Data enhancement",img)
#保存单张
cv2.imwrite(".\img\1.jpg",img) # 完整路径
#保存多张
cv2.imwrite(".\img\" + to_str(i) + ".jpg",img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)