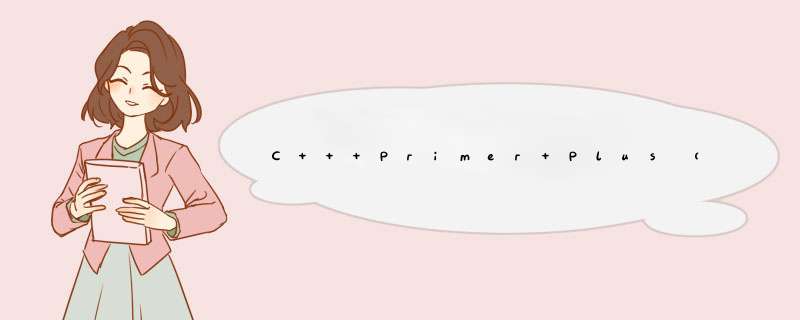
// inline.cpp -- using an inline function #include// an inline function definition inline double square(double x) { return x * x; } int main() { using namespace std; double a, b; double c = 13.0; a = square(5.0); b = square(4.5 + 7.5); // can pass expressions cout << "a = " << a << ", b = " << b << "n"; cout << "c = " << c; cout << ", c squared = " << square(c++) << "n"; cout << "Now c = " << c << "n"; // cin.get(); return 0; }
执行结果:
a = 25, b = 144 c = 13, c squared = 169 Now c = 14firstref.cpp
// firstref.cpp -- defining and using a reference #includeint main() { using namespace std; int rats = 101; int & rodents = rats; // rodents is a reference cout << "rats = " << rats; cout << ", rodents = " << rodents << endl; rodents++; cout << "rats = " << rats; cout << ", rodents = " << rodents << endl; // some implementations require type casting the following // addresses to type unsigned cout << "rats address = " << &rats; cout << ", rodents address = " << &rodents << endl; // cin.get(); return 0; }
执行结果:
rats = 101, rodents = 101 rats = 102, rodents = 102 rats address = 00CFF9C4, rodents address = 00CFF9C4secref.cpp
// secref.cpp -- defining and using a reference #includeint main() { using namespace std; int rats = 101; int & rodents = rats; // rodents is a reference cout << "rats = " << rats; cout << ", rodents = " << rodents << endl; cout << "rats address = " << &rats; cout << ", rodents address = " << &rodents << endl; int bunnies = 50; rodents = bunnies; // can we change the reference? cout << "bunnies = " << bunnies; cout << ", rats = " << rats; cout << ", rodents = " << rodents << endl; cout << "bunnies address = " << &bunnies; cout << ", rodents address = " << &rodents << endl; // cin.get(); return 0; }
执行结果:
rats = 101, rodents = 101 rats address = 00CFFDB4, rodents address = 00CFFDB4 bunnies = 50, rats = 50, rodents = 50 bunnies address = 00CFFD9C, rodents address = 00CFFDB4swaps.cpp
// swaps.cpp -- swapping with references and with pointers #includevoid swapr(int & a, int & b); // a, b are aliases for ints void swapp(int * p, int * q); // p, q are addresses of ints void swapv(int a, int b); // a, b are new variables int main() { using namespace std; int wallet1 = 300; int wallet2 = 350; cout << "wallet1 = $" << wallet1; cout << " wallet2 = $" << wallet2 << endl; cout << "Using references to swap contents:n"; swapr(wallet1, wallet2); // pass variables cout << "wallet1 = $" << wallet1; cout << " wallet2 = $" << wallet2 << endl; cout << "Using pointers to swap contents again:n"; swapp(&wallet1, &wallet2); // pass addresses of variables cout << "wallet1 = $" << wallet1; cout << " wallet2 = $" << wallet2 << endl; cout << "Trying to use passing by value:n"; swapv(wallet1, wallet2); // pass values of variables cout << "wallet1 = $" << wallet1; cout << " wallet2 = $" << wallet2 << endl; // cin.get(); return 0; } void swapr(int & a, int & b) // use references { int temp; temp = a; // use a, b for values of variables a = b; b = temp; } void swapp(int * p, int * q) // use pointers { int temp; temp = *p; // use *p, *q for values of variables *p = *q; *q = temp; } void swapv(int a, int b) // try using values { int temp; temp = a; // use a, b for values of variables a = b; b = temp; }
执行效果:
wallet1 = 0 wallet2 = 0 Using references to swap contents: wallet1 = 0 wallet2 = 0 Using pointers to swap contents again: wallet1 = 0 wallet2 = 0 Trying to use passing by value: wallet1 = 0 wallet2 = 0cubes.cpp
// cubes.cpp -- regular and reference arguments #includedouble cube(double a); double refcube(double &ra); int main() { using namespace std; double x = 3.0; cout << cube(x); cout << " = cube of " << x << endl; cout << refcube(x); cout << " = cube of " << x << endl; // cin.get(); return 0; } double cube(double a) { a *= a * a; return a; } double refcube(double &ra) { ra *= ra * ra; return ra; }
执行结果:
27 = cube of 3 27 = cube of 27strc_ref.cpp
//strc_ref.cpp -- using structure references #include#include struct free_throws { std::string name; int made; int attempts; float percent; };//free_throws结构 void display(const free_throws & ft); void set_pc(free_throws & ft); free_throws & accumulate(free_throws &target, const free_throws &source); int main() { free_throws one = { "Ifelsa Branch", 13, 14 }; free_throws two = { "Andor Knott", 10, 16 }; free_throws three = { "Minnie Max", 7, 9 }; free_throws four = { "Whily Looper", 5, 9 }; free_throws five = { "Long Long", 6, 14 }; free_throws team = { "Throwgoods", 0, 0 }; free_throws dup; set_pc(one); display(one);//调用display函数 //Name: Ifelsa Branch Made: 13 Attempts : 14 Percent : 92.8571 display(team);//Name: Throwgoods //Made: 0 Attempts : 0 Percent : 0 // use return value as argument display(accumulate(team, two));//调用display函数 //Name: Throwgoods //Made : 10 Attempts : 16 Percent : 62.5 accumulate(accumulate(team, three), four);//其中22=10+7+5 34=16+9+9 //这里调用accumulate函数和前面的two累加到一起 display(team);//Name: Throwgoods //Made: 22 Attempts : 34 Percent : 64.7059 // use return value in assignment dup = accumulate(team, five);//22+6(five)=28 34+14(five)=48 std::cout << "Displaying team:n"; display(team);//Name: Throwgoods //Made: 28 Attempts : 48 Percent : 58.3333 std::cout << "Displaying dup after assignment:n"; display(dup);//Name: Throwgoods //Made: 28 Attempts : 48 Percent : 58.3333 set_pc(four); // ill-advised assignment accumulate(dup, five) = four;//首先将five的数据添加到dup中,再将four的内容覆盖dup的内容 std::cout << "Displaying dup after ill-advised assignment:n"; display(dup);//Name: Whily Looper //Made: 5 Attempts : 9 Percent : 55.5556 // std::cin.get(); return 0; } void display(const free_throws & ft) { using std::cout; cout << "Name: " << ft.name << 'n'; cout << " Made: " << ft.made << 't'; cout << "Attempts: " << ft.attempts << 't'; cout << "Percent: " << ft.percent << 'n'; } void set_pc(free_throws & ft) { if (ft.attempts != 0) ft.percent = 100.0f *float(ft.made) / float(ft.attempts);//相当于100*13/14=92.85714285 else ft.percent = 0; } free_throws & accumulate(free_throws & target, const free_throws & source) { target.attempts += source.attempts; target.made += source.made; set_pc(target); return target; }
执行结果:
Name: Ifelsa Branch Made: 13 Attempts: 14 Percent: 92.8571 Name: Throwgoods Made: 0 Attempts: 0 Percent: 0 Name: Throwgoods Made: 10 Attempts: 16 Percent: 62.5 Name: Throwgoods Made: 22 Attempts: 34 Percent: 64.7059 Displaying team: Name: Throwgoods Made: 28 Attempts: 48 Percent: 58.3333 Displaying dup after assignment: Name: Throwgoods Made: 28 Attempts: 48 Percent: 58.3333 Displaying dup after ill-advised assignment: Name: Whily Looper Made: 5 Attempts: 9 Percent: 55.5556strquote.cpp
// strquote.cpp -- different designs #include#include using namespace std; string version1(const string & s1, const string & s2); const string & version2(string & s1, const string & s2); // has side effect const string & version3(string & s1, const string & s2); // bad design int main() { string input; string copy; string result; cout << "Enter a string: "; getline(cin, input); copy = input; cout << "Your string as entered: " << input << endl; result = version1(input, "***"); cout << "Your string enhanced: " << result << endl; cout << "Your original string: " << input << endl; result = version2(input, "###"); cout << "Your string enhanced: " << result << endl; cout << "Your original string: " << input << endl; cout << "Resetting original string.n"; input = copy; result = version3(input, "@@@");//执行错误,程序试图引用已经释放的内存 cout << "Your string enhanced: " << result << endl; cout << "Your original string: " << input << endl; // cin.get(); // cin.get(); return 0; } string version1(const string & s1, const string & s2) { string temp; temp = s2 + s1 + s2; return temp; } const string & version2(string & s1, const string & s2) // has side effect { s1 = s2 + s1 + s2; // safe to return reference passed to function return s1; } const string & version3(string & s1, const string & s2) // bad design { string temp; temp = s2 + s1 + s2; // unsafe to return reference to local variable return temp; }
执行结果:
Enter a string: It is my fault. Your string as entered: It is my fault. Your string enhanced: ***It is my fault.*** Your original string: It is my fault. Your string enhanced: ###It is my fault.### Your original string: ###It is my fault.### Resetting original string.filefunc.cpp
//filefunc.cpp -- function with ostream & parameter #include#include #include using namespace std; void file_it(ostream & os, double fo, const double fe[], int n); const int LIMIT = 5; int main() { ofstream fout; const char * fn = "ep-data.txt"; fout.open(fn); if (!fout.is_open()) { cout << "Can't open " << fn << ". Bye.n"; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } double objective; cout << "Enter the focal length of your " "telescope objective in mm: "; cin >> objective;//输入1800 double eps[LIMIT]; cout << "Enter the focal lengths, in mm, of " << LIMIT << " eyepieces:n"; for (int i = 0; i < LIMIT; i++) { cout << "Eyepiece #" << i + 1 << ": "; cin >> eps[i]; } file_it(fout, objective, eps, LIMIT);//将目镜数据写入到文件ep-data.txt中 file_it(cout, objective, eps, LIMIT);//将目镜数据打印到屏幕上 cout << "Donen"; // cin.get(); // cin.get(); return 0; } void file_it(ostream & os, double fo, const double fe[], int n) { // save initial formatting state ios_base::fmtflags initial; initial = os.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield); std::streamsize sz = os.precision(0); os << "Focal length of objective: " << fo << " mmn"; os.precision(1); os.width(12); os << "f.l. eyepiece"; os.width(15); os << "magnification" << endl;//f.l. eyepiece magnification //30.0 60 30*60=1800(objective) //19.0 95 19*95=1805(objective) //14.0 129 14*129=1806(objective) //8.8 205 8.8*205=1806(objective) //7.5 240 7.5*240=1800(objective) for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { os.width(12); os << fe[i]; os.width(15); os << int(fo / fe[i] + 0.5) << endl; } // restore initial formatting state os.setf(initial, ios_base::floatfield); os.precision(sz); }
执行结果:
Enter the focal length of your telescope objective in mm: 1800
Enter the focal lengths, in mm, of 5 eyepieces:
Eyepiece #1: 30
Eyepiece #2: 19
Eyepiece #3: 14
Eyepiece #4: 8.8
Eyepiece #5: 7.5
Focal length of objective: 1800 mm
f.l. eyepiece magnification
30.0 60
19.0 95
14.0 129
8.8 205
7.5 240
Done
left.cpp
// left.cpp -- string function with a default argument #includeconst int ArSize = 80; char * left(const char * str, int n = 1); int main() { using namespace std; char sample[ArSize]; cout << "Enter a string:n"; cin.get(sample, ArSize); char *ps = left(sample, 4);//调用left函数 取前四个元素 cout << ps << endl; delete[] ps; // free old string ps = left(sample);//取第一个元素 cout << ps << endl; delete[] ps; // free new string // cin.get(); // cin.get(); return 0; } // This function returns a pointer to a new string // consisting of the first n characters in the str string. char * left(const char * str, int n) { if (n < 0) n = 0; char * p = new char[n + 1]; int i; for (i = 0; i < n && str[i]; i++) p[i] = str[i]; // copy characters while (i <= n) p[i++] = ''; // set rest of string to '' return p; }
执行效果:
Enter a string: forthcoming fort fleftover.cpp
// leftover.cpp -- overloading the left() function #includeunsigned long left(unsigned long num, unsigned ct); char * left(const char * str, int n = 1); int main() { using namespace std; const char * trip = "Hawaii!!"; // test value 源代码在这里有错误 //需要加上const 否则会报错 unsigned long n = 12345678; // test value int i; char * temp; for (i = 1; i < 10; i++) { cout << left(n, i) << endl; temp = left(trip, i); cout << temp << endl; delete[] temp; // point to temporary storage } // cin.get(); return 0; } // This function returns the first ct digits of the number num. unsigned long left(unsigned long num, unsigned ct) { unsigned digits = 1; unsigned long n = num; if (ct == 0 || num == 0) return 0; // return 0 if no digits while (n /= 10)//12345678/10=1234567 digits++;//2 if (digits > ct) { ct = digits - ct; while (ct--) num /= 10;//1234567/10=123456 return num; // return left ct digits 123456 } else // if ct >= number of digits return num; // return the whole number } // This function returns a pointer to a new string // consisting of the first n characters in the str string. char * left(const char * str, int n) { if (n < 0) n = 0; char * p = new char[n + 1]; int i; for (i = 0; i < n && str[i]; i++) p[i] = str[i]; // copy characters while (i <= n) p[i++] = ''; // set rest of string to '' return p; }
执行结果:
1 H 12 Ha 123 Haw 1234 Hawa 12345 Hawai 123456 Hawaii 1234567 Hawaii! 12345678 Hawaii!! 12345678 Hawaii!!funtemp.cpp
// funtemp.cpp -- using a function template #include// function template prototype template // or class T void Swap(T &a, T &b); int main() { using namespace std; int i = 10; int j = 20; cout << "i, j = " << i << ", " << j << ".n"; cout << "Using compiler-generated int swapper:n"; Swap(i, j); // generates void Swap(int &, int &) cout << "Now i, j = " << i << ", " << j << ".n"; double x = 24.5; double y = 81.7; cout << "x, y = " << x << ", " << y << ".n"; cout << "Using compiler-generated double swapper:n"; Swap(x, y); // generates void Swap(double &, double &) cout << "Now x, y = " << x << ", " << y << ".n"; // cin.get(); return 0; } // function template definition template // or class T void Swap(T &a, T &b) { T temp; // temp a variable of type T temp = a; a = b; b = temp; }
执行结果:
i, j = 10, 20. Using compiler-generated int swapper: Now i, j = 20, 10. x, y = 24.5, 81.7. Using compiler-generated double swapper: Now x, y = 81.7, 24.5.twotemps.cpp
// twotemps.cpp -- using overloaded template functions #includetemplate // original template void Swap(T &a, T &b); template // new template void Swap(T *a, T *b, int n); void Show(int a[]); const int Lim = 8; int main() { using namespace std; int i = 10, j = 20; cout << "i, j = " << i << ", " << j << ".n"; cout << "Using compiler-generated int swapper:n"; Swap(i, j); // matches original template cout << "Now i, j = " << i << ", " << j << ".n"; int d1[Lim] = { 0,7,0,4,1,7,7,6 }; int d2[Lim] = { 0,7,2,0,1,9,6,9 }; cout << "Original arrays:n"; Show(d1);//07/04/1776 Show(d2);//07/20/1969 Swap(d1, d2, Lim); // matches new template cout << "Swapped arrays:n"; Show(d1);//07/20/1969 Show(d2);//07/04/1776 // cin.get(); return 0; } template void Swap(T &a, T &b) { T temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } template void Swap(T a[], T b[], int n) { T temp; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { temp = a[i]; a[i] = b[i]; b[i] = temp; } } void Show(int a[]) { using namespace std; cout << a[0] << a[1] << "/";//a[0]=0 a[1]=7 cout << a[2] << a[3] << "/";//a[2]=0 a[3]=4 for (int i = 4; i < Lim; i++) cout << a[i];//输出a[4]至a[7] cout << endl; }
执行结果:
i, j = 10, 20. Using compiler-generated int swapper: Now i, j = 20, 10. Original arrays: 07/04/1776 07/20/1969 Swapped arrays: 07/20/1969 07/04/1776twoswap.cpp
// twoswap.cpp -- specialization overrides a template #includetemplate void Swap(T &a, T &b); struct job { char name[40]; double salary; int floor; }; // explicit specialization template <> void Swap (job &j1, job &j2); void Show(job &j); int main() { using namespace std; cout.precision(2); cout.setf(ios::fixed, ios::floatfield); int i = 10, j = 20; cout << "i, j = " << i << ", " << j << ".n"; cout << "Using compiler-generated int swapper:n"; Swap(i,j); // generates void Swap(int &, int &) cout << "Now i, j = " << i << ", " << j << ".n"; job sue = {"Susan Yaffee", 73000.60, 7};//struct job //char name[40]; //double salary; //int floor; job sidney = {"Sidney Taffee", 78060.72, 9}; cout << "Before job swapping:n"; Show(sue); Show(sidney); Swap(sue, sidney); // uses void Swap(job &, job &) cout << "After job swapping:n"; Show(sue); Show(sidney); // cin.get(); return 0; } template void Swap(T &a, T &b) // general version { T temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } // swaps just the salary and floor fields of a job structure template <> void Swap (job &j1, job &j2) // specialization { double t1; int t2; t1 = j1.salary; j1.salary = j2.salary; j2.salary = t1;//交换salary t2 = j1.floor; j1.floor = j2.floor; j2.floor = t2;//交换floor } void Show(job &j) { using namespace std; cout << j.name << ": $" << j.salary << " on floor " << j.floor << endl; }
执行结果:
i, j = 10, 20. Using compiler-generated int swapper: Now i, j = 20, 10. Original arrays: 07/04/1776 07/20/1969 Swapped arrays: 07/20/1969 07/04/1776tempover.cpp
// tempover.cpp --- template overloading #includetemplate // template A void ShowArray(T arr[], int n); template // template B void ShowArray(T * arr[], int n); struct debts { char name[50]; double amount; }; int main() { using namespace std; int things[6] = { 13, 31, 103, 301, 310, 130 }; struct debts mr_E[3] = { {"Ima Wolfe", 2400.0}, {"Ura Foxe", 1300.0}, {"Iby Stout", 1800.0} }; double * pd[3]; // set pointers to the amount members of the structures in mr_E for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount; cout << "Listing Mr. E's counts of things:n"; // things is an array of int ShowArray(things, 6); // uses template A cout << "Listing Mr. E's debts:n"; // pd is an array of pointers to double ShowArray(pd, 3); // uses template B (more specialized) // cin.get(); return 0; } template void ShowArray(T arr[], int n) { using namespace std; cout << "template An"; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << arr[i] << ' '; cout << endl; } template void ShowArray(T * arr[], int n) { using namespace std; cout << "template Bn"; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << *arr[i] << ' '; cout << endl; }
执行结果:
删去template B后,得到的结果是:Listing Mr. E's counts of things: template A 13 31 103 301 310 130 Listing Mr. E's debts: template B 2400 1300 1800
// tempover.cpp --- template overloading #includetemplate // template A void ShowArray(T arr[], int n); //template // template B //void ShowArray(T * arr[], int n); struct debts { char name[50]; double amount; }; int main() { using namespace std; int things[6] = { 13, 31, 103, 301, 310, 130 }; struct debts mr_E[3] = { {"Ima Wolfe", 2400.0}, {"Ura Foxe", 1300.0}, {"Iby Stout", 1800.0} }; double * pd[3]; // set pointers to the amount members of the structures in mr_E for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount; cout << "Listing Mr. E's counts of things:n"; // things is an array of int ShowArray(things, 6); // uses template A cout << "Listing Mr. E's debts:n"; // pd is an array of pointers to double ShowArray(pd, 3); // uses template B (more specialized) // cin.get(); return 0; } template void ShowArray(T arr[], int n) { using namespace std; cout << "template An"; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << arr[i] << ' '; cout << endl; } //template //void ShowArray(T * arr[], int n) //{ // using namespace std; // cout << "template Bn"; // for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // cout << *arr[i] << ' '; // cout << endl; //}
执行结果:
Listing Mr. E's counts of things: template A 13 31 103 301 310 130 Listing Mr. E's debts: template A 0093F75C 0093F79C 0093F7DCchoices.cpp
// choices.cpp -- choosing a template #includetemplate T lesser(T a, T b) // #1 { return a < b ? a : b; } int lesser(int a, int b) // #2 { a = a < 0 ? -a : a; b = b < 0 ? -b : b; return a < b ? a : b; } int main() { using namespace std; int m = 20; int n = -30; double x = 15.5; double y = 25.9; cout << lesser(m, n) << endl; // use #2 //该函数调用与模板函数和非模板函数都匹配,所以选择非模板函数 cout << lesser(x, y) << endl; // use #1 with double //函数调用与模板匹配(T为double) cout << lesser<>(m, n) << endl; // use #1 with int //lesser<>(m, n)中<>指出,编译器一个选择模板匹配函数,而不是非模板函数 cout << lesser (x, y) << endl; // use #1 with int //进行显式实例化(使用int替代T)将显式实例化得到的函数。x和y被强制转换为int // cin.get(); return 0; }
执行结果:
20 15.5 -30 15
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)