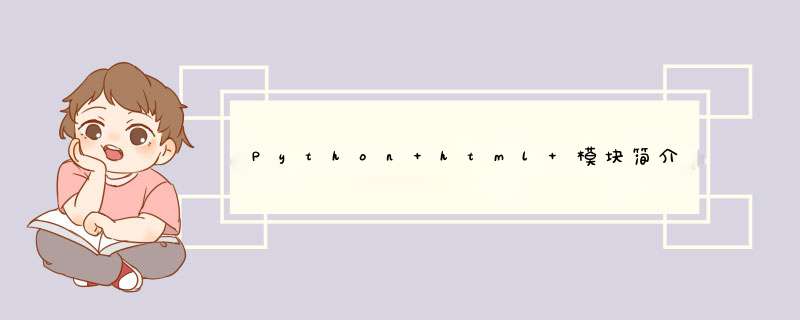
比如,数学符号 , ,可以直接获得:
escape 将特殊字符 & , < 和 > 替换为HTML安全序列。如果可选的 flags quote 为 True (默认值),则还会翻译引号字符,包括双引号( " )和单引号( ' )字符。
将字符串 s 中的所有命名和数字字符引用 (例如 >, >, >) 转换为相应的 Unicode 字符。此函数使用 HTML 5 标准为有效和无效字符引用定义的规则,以及 HTML 5 命名字符引用列表 。
这个模块定义了一个 HTMLParser 类,为 HTML(超文本标记语言)和 XHTML 文本文件解析提供基础。
class html.parser.HTMLParser(*, convert_charrefs=True) 创建一个能解析无效标记的解析器实例。查找标签(tags)和其他标记(markup)并调用 handler 函数。
用法:
通过调用 self.handle_starttag 处理开始标签,或通过调用 self.handle_startendtag 处理结束标签。标签之间的数据通过以 data 为参数调用 self.handle_data 从解析器传递到派生类(数据可以分成任意块)。如果 convert_charrefs 为 True ,则将字符引用自动转换为相应的 Unicode 字符(并且 self.handle_data 不再拆分成块),否则通过调用带有字符串的 self.handle_entityref 或 self.handle_charref 来传递它们以分别包含命名或数字引用作为参数。如果 convert_charrefs 为 True (默认值),则所有字符引用( script / style 元素中的除外)都会自动转换为相应的 Unicode 字符。
一个 HTMLParser 类的实例用来接受 HTML 数据,并在标记开始、标记结束、文本、注释和其他元素标记出现的时候调用对应的方法。要实现具体的行为,请使用 HTMLParser 的子类并重载其方法。
这个解析器不检查结束标记是否与开始标记匹配,也不会因外层元素完毕而隐式关闭了的元素引发结束标记处理。
下面是简单的 HTML 解析器的一个基本示例,使用 HTMLParser 类,当遇到开始标记、结束标记以及数据的时候将内容打印出来。
输出:
HTMLParser.reset() 重置实例。丢失所有未处理的数据。在实例化阶段被隐式调用。
HTMLParser.feed(data) 填充一些文本到解析器中。如果包含完整的元素,则被处理;如果数据不完整,将被缓冲直到更多的数据被填充,或者 close() 被调用。 data 必须为 str 类型。
HTMLParser.close() 如同后面跟着一个文件结束标记一样,强制处理所有缓冲数据。这个方法能被派生类重新定义,用于在输入的末尾定义附加处理,但是重定义的版本应当始终调用基类 HTMLParser 的 close() 方法。
HTMLParser.getpos() 返回当前行号和偏移值。
HTMLParser.get_starttag_text() 返回最近打开的开始标记中的文本。结构化处理时通常应该不需要这个,但在处理“已部署”的 HTML 或是在以最小改变来重新生成输入时可能会有用处(例如可以保留属性间的空格等)。
下列方法将在遇到数据或者标记元素的时候被调用。他们需要在子类中重载。基类的实现中没有任何实际 *** 作(除了 handle_startendtag() ):
HTMLParser.handle_starttag 这个方法在标签开始的时候被调用(例如: <div id="main">)。 tag 参数是小写的标签名。 attrs 参数是一个 (name, value) 形式的列表,包含了所有在标记的 <> 括号中找到的属性。 name 转换为小写, value 的引号被去除,字符和实体引用都会被替换。比如,对于标签 <a href="https://www.cwi.nl/">,这个方法将以下列形式被调用 handle_starttag('a', [('href', 'https://www.cwi.nl/')]) 。 html.entities 中的所有实体引用,会被替换为属性值。
HTMLParser.handle_endtag(tag) 此方法被用来处理元素的结束标记(例如: </div>)。 tag 参数是小写的标签名。
HTMLParser.handle_startendtag(tag, attrs) 类似于 handle_starttag() , 只是在解析器遇到 XHTML 样式的空标记时被调用( <tag ... />)。这个方法能被需要这种特殊词法信息的子类重载;默认实现仅简单调用 handle_starttag() 和 handle_endtag() 。
HTMLParser.handle_data(data) 这个方法被用来处理任意数据(例如:文本节点和 <script>...</script> 以及 <style>...</style> 中的内容)。
HTMLParser.handle_entityref(name) 这个方法被用于处理 &name 形式的命名字符引用(例如 >),其中 name 是通用的实体引用(例如: 'gt' )。如果 convert_charrefs 为 True,该方法永远不会被调用。
HTMLParser.handle_charref(name) 这个方法被用来处理 NNN 和 NNN 形式的十进制和十六进制字符引用。例如, > 等效的十进制形式为 >,而十六进制形式为 > ;在这种情况下,方法将收到 '62' 或 'x3E' 。如果 convert_charrefs 为 True ,则该方法永远不会被调用。
HTMLParser.handle_comment(data) 这个方法在遇到注释的时候被调用(例如: )。例如, 这个注释会用 ' comment ' 作为参数调用此方法。
Internet Explorer 条件注释(condcoms)的内容也被发送到这个方法,因此,对于 ``,这个方法将接收到 '[if IE 9]>IE9-specific content<![endif]' 。
HTMLParser.handle_decl(decl) 这个方法用来处理 HTML doctype 申明(例如 <!DOCTYPE html>)。 decl 形参为 <!...> 标记中的所有内容(例如: 'DOCTYPE html' )。
HTMLParser.handle_pi(data) 此方法在遇到处理指令的时候被调用。 data 形参将包含整个处理指令。例如,对于处理指令 <?proc color='red'>,这个方法将以 handle_pi("proc color='red'") 形式被调用。它旨在被派生类重载;基类实现中无任何实际 *** 作。
注解: HTMLParser 类使用 SGML 语法规则处理指令。使用 '?' 结尾的 XHTML 处理指令将导致 '?' 包含在 data 中。
HTMLParser.unknown_decl(data) 当解析器读到无法识别的声明时,此方法被调用。 data 形参为 <![...]> 标记中的所有内容。某些时候对派生类的重载很有用。基类实现中无任何实际 *** 作。
因此,我们可以如此定义:
下面介绍如何解析 HTML 文档。
解析一个文档类型声明:
解析一个具有一些属性和标题的元素:
script 和 style 元素中的内容原样返回,无需进一步解析:
解析注释:
解析命名或数字形式的字符引用,并把他们转换到正确的字符(注意:这 3 种转义都是 '>' ):
填充不完整的块给 feed() 执行, handle_data() 可能会多次调用(除非 convert_charrefs 被设置为 True ):
解析无效的 HTML (例如:未引用的属性)也能正常运行:
第一种方法:
用System.Net.WebClient下载Web Page存到本地文件或者String中,用正则表达式来分析。这个方法可以用在Web Crawler等需要分析很多Web Page的应用中。
using Systemusing System.Net
using System.Text
using System.Text.RegularExpressions
namespace HttpGet
{
class Class1
{
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
System.Net.WebClient client = new WebClient()
byte[] page = client.DownloadData("http://www.google.com")
string content = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(page)
string regex = "href=[\\\"\\\'](http:\\/\\/|\\.\\/|\\/)?\\w+(\\.\\w+)*(\\/\\w+(\\.\\w+)?)*(\\/|\\?\\w*=\\w*(&\\w*=\\w*)*)?[\\\"\\\']"
Regex re = new Regex(regex)
MatchCollection matches = re.Matches(content)
System.Collections.IEnumerator enu = matches.GetEnumerator()
while (enu.MoveNext() && enu.Current != null)
{
Match match = (Match)(enu.Current)
Console.Write(match.Value + "\r\n")
}
}
}
}
第二种方法:
利用Winista.Htmlparser.Net 解析Html。这是.NET平台下解析Html的开源代码,网上有源码下载
using Systemusing System.Collections.Generic
using System.ComponentModel
using System.Data
using System.Drawing
using System.Linq
using System.Text
using System.Windows.Forms
using Winista.Text.HtmlParser
using Winista.Text.HtmlParser.Lex
using Winista.Text.HtmlParser.Util
using Winista.Text.HtmlParser.Tags
using Winista.Text.HtmlParser.Filters
namespace HTMLParser
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent()
AddUrl()
}
private void btnParser_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
#region 获得网页的html
try
{
txtHtmlWhole.Text = ""
string url = CBUrl.SelectedItem.ToString().Trim()
System.Net.WebClient aWebClient = new System.Net.WebClient()
aWebClient.Encoding = System.Text.Encoding.Default
string html = aWebClient.DownloadString(url)
txtHtmlWhole.Text = html
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message)
}
#endregion
#region 分析网页html节点
Lexer lexer = new Lexer(this.txtHtmlWhole.Text)
Parser parser = new Parser(lexer)
NodeList htmlNodes = parser.Parse(null)
this.treeView1.Nodes.Clear()
this.treeView1.Nodes.Add("root")
TreeNode treeRoot = this.treeView1.Nodes[0]
for (int i = 0 i < htmlNodes.Count i++)
{
this.RecursionHtmlNode(treeRoot, htmlNodes[i], false)
}
#endregion
}
private void RecursionHtmlNode(TreeNode treeNode, INode htmlNode, bool siblingRequired)
{
if (htmlNode == null || treeNode == null) return
TreeNode current = treeNode
TreeNode content
//current node
if (htmlNode is ITag)
{
ITag tag = (htmlNode as ITag)
if (!tag.IsEndTag())
{
string nodeString = tag.TagName
if (tag.Attributes != null && tag.Attributes.Count > 0)
{
if (tag.Attributes["ID"] != null)
{
nodeString = nodeString + " { id=\"" + tag.Attributes["ID"].ToString() + "\" }"
}
if (tag.Attributes["HREF"] != null)
{
nodeString = nodeString + " { href=\"" + tag.Attributes["HREF"].ToString() + "\" }"
}
}
current = new TreeNode(nodeString)
treeNode.Nodes.Add(current)
}
}
//获取节点间的内容
if (htmlNode.Children != null && htmlNode.Children.Count > 0)
{
this.RecursionHtmlNode(current, htmlNode.FirstChild, true)
content = new TreeNode(htmlNode.FirstChild.GetText())
treeNode.Nodes.Add(content)
}
//the sibling nodes
if (siblingRequired)
{
INode sibling = htmlNode.NextSibling
while (sibling != null)
{
this.RecursionHtmlNode(treeNode, sibling, false)
sibling = sibling.NextSibling
}
}
}
private void AddUrl()
{
CBUrl.Items.Add("http://www.xxx.com")
}
}
}
解析HTML最好的类还是微软自己的在站内搜索的项目要进行HTML的解析,发现程序运行非常慢,一开始以为是lucene的问题,一测试大吃一惊,每一步lucene中AddDocument等只用了几十毫秒,而HTML解析竟然用了9秒。
日志如下:
2010-06-26 15:51:25,171 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - DownloadString:00:00:00.0482329
2010-06-26 15:51:34,187 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - ThreadParser:00:00:09.0236490
2010-06-26 15:51:34,187 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - DeleteDocuments:00:00:00.0000069
2010-06-26 15:51:34,203 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - AddDocument:00:00:00.0191071
我使用的是Winista.HtmlParser这块网上找到的HTML解析器。遂准备更换解析器,但是用“.Net HTML Parser”在google上寻找,一直没找到合适的解析器,不是太难用,就是性能比Winista.HtmlParser还差,我才想到,微软的MSHTML不就是用来解析HTML的吗?折腾这么一圈却忘了微软自家的东西,微软的东西性能肯定差不了。
添加对Microsoft.mshtml这个程序集的引用,然后编写如下代码:
IHTMLDocument2 doc = new HTMLDocumentClass()
doc.write(new object[]{pageSource})
doc.close()
Title = doc.title
Body = doc.body.innerText
再测试,哇咔咔,快的要命,只有几十毫秒,2000个帖子一会儿就爬完了。
日志如下:
2010-06-26 16:26:35,546 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - DownloadString:00:00:00.0400263
2010-06-26 16:26:35,562 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - ThreadParser:00:00:00.0257731
2010-06-26 16:26:35,562 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - DeleteDocuments:00:00:00.0001913
2010-06-26 16:26:35,578 [8] DEBUG SearchSite.StartIndex - AddDocument:00:00:00.0010881
HTMLDocumentClass的方法比任何一个网上找到的HTML解析器都丰富,想怎么搞就怎么搞,而且调用方法就是 *** 作Dom的方法,完全不用再去学,哇咔咔,爽呆了。
在使用的过程中遇到两个问题:
1、VS2010中引用Microsoft.mshtml之后,要修改这个引用的“嵌入互 *** 作类型”为False。
2、调用doc.write方法的时候必须通过IHTMLDocument2接口来调用,否则报错“错误的类型”,在google上搜“type mismatch HTMLDocument write”
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)