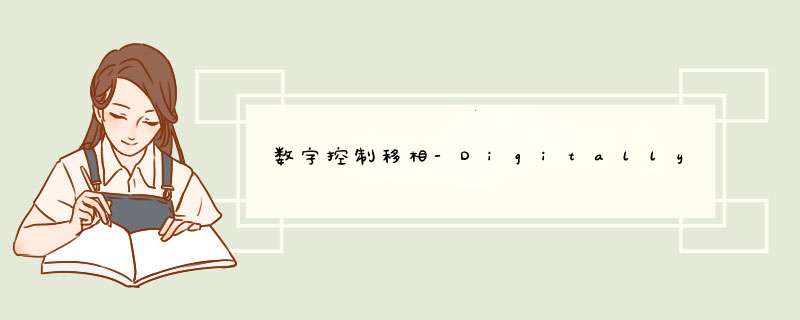
IntroductionAltering the phase response of a signal without changing its amplitude characteristics is commonly performed using an allpass filter, as in Figure 1. The response of this circuit is given by
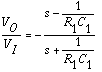
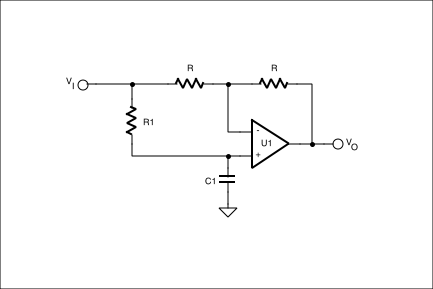
Figure 1. A simple phase shift circuit can be implemented using an allpass filter.
As the signal frequency varies from DC to infinity, the phase shift will vary from 0 to +180 degrees. You can also see that by varying R1, the phase shift at a given frequency will vary likewise. If the position of R1 and C1 are reversed, as in Figure 2, the transfer function becomes
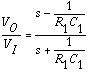
and the phase then varies from -180 to 0 degrees. The phase shift this circuit realizes at any given frequency can be found by
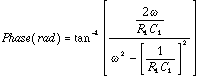
where w is the frequencies in rad/s, or 2×pi×f, when f is in Hertz. As a practical matter, most circuits of this type can comfortably cover a phase range of about 120 degrees with real op amps and components.
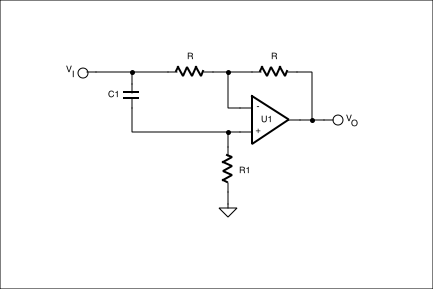
Figure 2. This allpass filter circuit swaps the location of R1 and C1.
Controlling the Phase Shift DigitallyThis circuit implementation is well suited to using digital potentiometers in place of R1, as shown in Figure 3. With this circuit, optimized for phase-shifting over the audio range, the phase at a given frequency is now under control of a digital signal. The DS1669 used here can have its wiper position set by using a single digital control line to cause the wiper position to increment upon each low-going pulse, until it reaches the upper end of the pot, when it will reverse direction and decrement. Supplying a clock to this digital control input will cause the phase to constantly sweep, an effect commonly used in popular recordings today. Note that since this is a single supply circuit, the digital potentiometer is biased at ½V
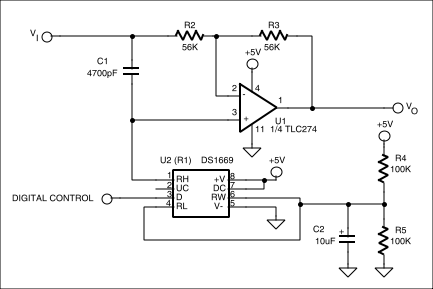
Figure 3. Replacing R1 with a digital potentiometer causes the phase shift the circuit realizes to be under digital control.
A Complete Audio Phase Shift EffectSeveral of these phase shift sections can be cascaded to realize greater phase shifts. Dual, quad, or hex digital potentiometers can be used to control all sections under control of a microprocessor, as shown in the phase shifter/stereo synthesizer example of Figures 4-8. The DS1806 hex digital potentiometers' wiper positions are under control of a simple three-wire digital interface, which clocks the wiper position settings into the device over its DQ line, while the /RST line is high. When /RST goes low, the wiper is positioned at the new setting.
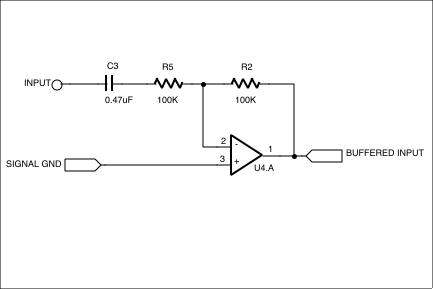
Figure 4. The input stage to the phase shifter provides a buffered, AC coupled signal.
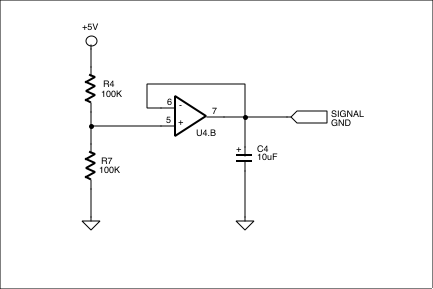
Figure 5. Since this is a single-supply circuit, this circuitry creates a virtual, or signal, ground for the rest of the circuitry. U4 is a TLC274 single-supply op amp.
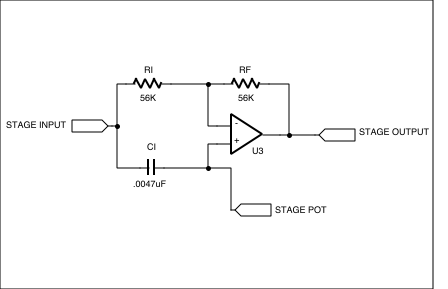
Figure 6. One stage (of four) which implements the phase shift. This is the same circuit as Figure 3, but R1 of that circuit is replaced by a section of a hex potentiometer, referred to here as the "stage pot".
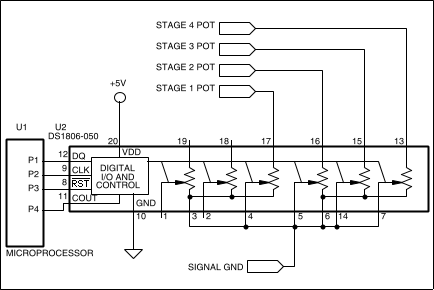
Figure 7. Four sections of the DS1806 are used to control the phase shift of each stage under microprocessor control. Note that two pot sections are left over, available perhaps for use as level controls.
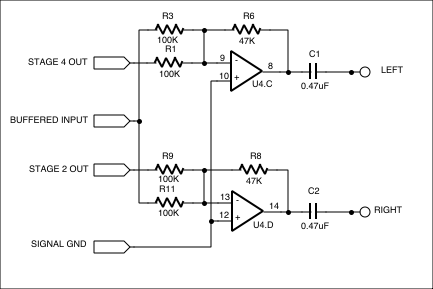
Figure 8. The final output stage consists of a mixer which combines the outputs from the various stages to provide the familiar "phasor" effect, as well as a psuedo-stereo output.
This circuit appeared in EDN Magazine's Design Ideas, February 15, 1996, pp.114-116.
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)