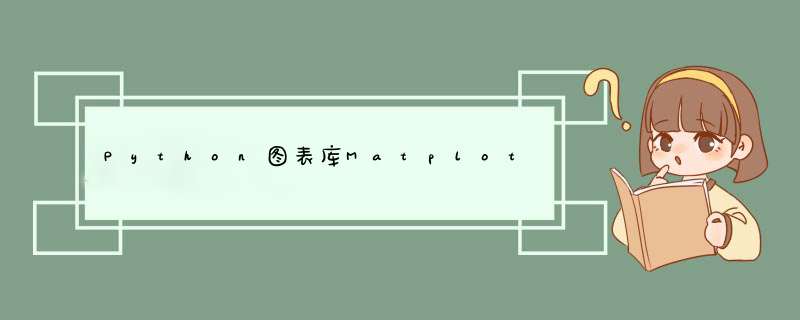
图表有很多个组成部分,例如标题、x/y轴名称、大刻度小刻度、线条、数据点、注释说明等等。
我们来看官方给的图,图中标出了各个部分的英文名称
Matplotlib提供了很多API,开发者可根据需求定制图表的样式。
前面我们设置了标题和x/y轴的名称,本文介绍更多设置其他部分的方法。
先绘制一个事例图。然后以此为基础进行定制。
def demo2(): x_List = [] y_List = [] for i in range(0,365): x_List.append(i) y_List.append(math.sin(i * 0.1)) ax = plt.gca() ax.set_Title('rustfisher.com mapplotlib example') ax.set_xlabel('x') ax.set_ylabel('y = sin(x)') ax.grID() plt.plot(x_List,y_List) plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__': print('rustfisher 图表讲解') demo2()运行得到
红色框框里的是figure;绿色框框里的叫做ax。
代码中ax = plt.gca()获取到的就是绿色框框里的部分(对象)。
figure代表整张图,暂时称为“全图”或者“大图”。一张图里可以有多个子图表。最少必须要有一个图表。像上面那样。
Axes 数据图一张张的图,图里显示着数据,暂称为“数据图”。一个大图里可以有多个数据图。但单个数据图对象只能在1个大图里。
多张数据图 subplots例如同时存在2个数据图
def demo_subplot(): x_List = [] y_List = [] y2_List = [] for i in range(0,365): x_List.append(i) y_List.append(math.sin(i * 0.1)) y2_List.append(math.cos(i * 0.1)) fig,(ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(2) ax1.set_Title('rustfisher.com 1') ax2.set_Title('rustfisher.com 2') ax1.set_xlabel('x') ax1.set_ylabel('y = sin(x)') ax2.set_xlabel('x') ax2.set_ylabel('y = cos(x)') ax1.plot(x_List,y_List) ax2.plot(x_List,y2_List) plt.show()调用subplots()接口,传入数字指定要多少张数据图。
返回的多张图要用括号括起来。每个数据图可以绘制(plot)不同的数据。
标题用set_Title()来设置。
可以看到上下两张图太挤了,有重叠部分。可以在plt.show()之前加一个fig.tight_layout()让它们拉开一点距离。
对于2维数据图,它有2个坐标,横坐标和纵坐标。有一些接口可以设置参数。
例如控制坐标轴的名字set_xlabel() set_ylabel;
set_xlim方法可以控制x轴数据显示范围。同理y轴用set_ylim来控制。
对于显示范围,set_xlim方法主要参数为left和right;或者用xmin xmax。这两套不能同时使用。set_ylim主要参数是top bottom;或者ymin ymax。这两套不能同时使用。
增加显示范围控制的代码
def demo3(): x_List = [] y_List = [] y2_List = [] for i in range(0,ax2) = plt.subplots(2) ax1.set_Title('rustfisher.com 1') ax1.set_xlabel('x') ax1.set_ylabel('y = sin(x)') ax2.set_Title('rustfisher.com 2') ax2.set_xlabel('x') ax2.set_ylabel('y = cos(x)') ax1.set_xlim(left=50,right=200.6) # 控制x轴显示范围 ax1.set_ylim(top=1,bottom=0.3) # 控制y轴显示范围 ax2.set_xlim(xmin=1,xmax=156.6) # 控制x轴显示范围 ax2.set_ylim(ymin=-0.3,ymax=0.3) # 控制y轴显示范围 ax1.plot(x_List,y2_List) fig.tight_layout() plt.show()运行结果
tick意思是标记。在坐标轴上的是刻度。Major tick暂称为大刻度,minor tick暂称为小刻度。
使用set_xticks方法控制刻度显示。传入的列表是我们希望显示的刻度。minor参数默认为False,不显示小刻度。
关键代码如下
ax1.set_xticks([50,60,70,150])ax1.set_yticks([0.1,0.2,0.3,0.7,0.9])ax1.grID() # 显示格子ax2.set_xticks([1,150],minor=True)ax2.set_yticks([-0.1,0.1,0.3],minor=True)ax2.grID()可见当minor=True,传入的刻度列表有可能不显示。
也可以控制大刻度上的文字旋转
plt.setp(ax1.xaxis.get_majorticklabels(),rotation=-45) plt.setp(ax2.xaxis.get_majorticklabels(),rotation=-60)spine是脊柱的意思,这里我们先称为边线。有上下左右4条边线。名称是top bottom left right
可以直接从图表对象获取它的边线,比如右边线ax1.spines.right。
一些简单的 *** 作,例如
set_visible 显示和隐藏set_ticks_position 刻度显示的位置set_bounds 边线显示范围set_linewidth 线的宽度隐藏右边线和上边线
ax1.spines.right.set_visible(False)ax1.spines.top.set_visible(False)让刻度显示在右边和上方
ax2.yaxis.set_ticks_position('right')ax2.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')设置边线显示范围
ax3.spines.left.set_bounds(-0.5,0.5)ax3.spines.top.set_bounds(340,400)设置线的宽度
ax3.spines.bottom.set_linewidth(2)完整代码如下
import mathimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef demo_spine(): x_List = [] y_List = [] for i in range(0,365): x_List.append(i) y_List.append(math.sin(i * 0.1)) fig,ax2,ax3) = plt.subplots(3) ax_List = [ax1,ax3] for i in range(0,3): cur_ax = ax_List[i] cur_ax.set_Title('rustfisher.com ' + str(i)) cur_ax.plot(x_List,y_List) cur_ax.set_xlabel('x') cur_ax.set_ylabel('y = sin(x)') ax1.spines.right.set_visible(False) ax1.spines.top.set_visible(False) ax2.spines.bottom.set_visible(False) ax2.spines.left.set_visible(False) ax2.yaxis.set_ticks_position('right') ax2.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top') ax3.spines.left.set_bounds(-0.5,0.5) ax3.spines.top.set_bounds(340,400) ax3.spines.bottom.set_linewidth(2) fig.tight_layout() plt.show()运行截图
数据点控制数据点的样式。下面我们在一张图表里绘制多条数据线。
def demo_line(): x_List = [] y_List = [] y2_List = [] y3_List = [] for i in range(0,20): x_List.append(i) y_List.append(math.sin(i) * 2 - 4) y2_List.append(math.sin(i) * 2) y3_List.append(math.cos(i) * 1.3 + 3) plt.plot(x_List,y_List,color='blue',linestyle='-.',linewidth=2,markersize=4) plt.plot(x_List,y2_List,'go',linewidth=1) plt.plot(x_List,y3_List,'r+') plt.show()plot()方法中,支持多种选项。
linestyle支持的选项
'-','--','-.',':','None',' ','','solID','dashed','dashdot','dotted'
添加注释,调用lengend()方法。
在前面代码基础上添加
plt.plot(x_List,'r+') plt.legend(['math.sin(i) * 2 - 4','math.sin(i) * 2','math.cos(i) * 1.3 + 3'])控制注释显示的地方,添加bBox_to_anchor和bBox_transform属性
plt.legend(['math.sin(i) * 2 - 4','math.cos(i) * 1.3 + 3'],bBox_to_anchor=(1,1),bBox_transform=plt.gcf().transfigure)在设置标题用到中文的时候,可能会出现乱码。
可以设置rcParams的字体,解决乱码问题。
plt.rcParams['Font.sans-serif'] = ['Arial Unicode MS']至此,我们把图表中各个部分都简要介绍了一下。
参考本例环境
macOSPyCharm CE@R_419_4729@参考资料
【运营的Python指南】绘制图表Matplotlib快速入门https://rustfisher.com/2021/07/16/Python/operation/matplotlib-intro1Python笔记 https://rustfisher.com/categories/Python/matplotlib https://matplotlib.org/ 总结以上是内存溢出为你收集整理的Python图表库Matplotlib 组成部分介绍全部内容,希望文章能够帮你解决Python图表库Matplotlib 组成部分介绍所遇到的程序开发问题。
如果觉得内存溢出网站内容还不错,欢迎将内存溢出网站推荐给程序员好友。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)