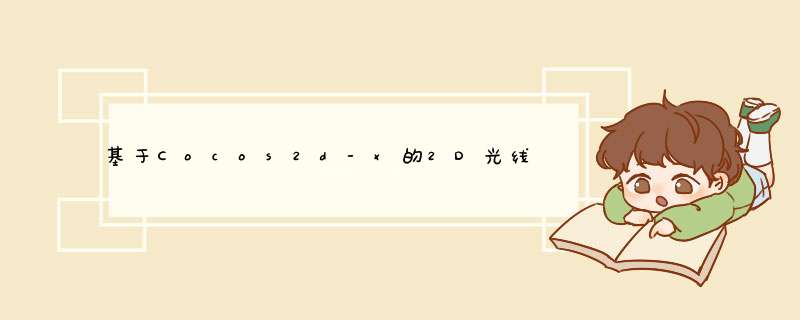
首先,在 .h 里面定义一下需要的结构体:
typedef struct liGHTliNE{ Point segA; // 光线的起始点 Point segB; // 光线的终止点 float t1;}lightline; typedefstruct POINTANDANGLE{ Point point; // 光源打在墙上的点 float angle; // 相对于光源的角度}PointAndAngle; 是的,我们只需要这些。再来 .cpp 里面,现在初始化下多边形的顶点:
boolHelloWorld::InitSegments(){ int subX =60; int subY =0; lightline tmp; // border tmp.segA = Vec2( origin.x,origin.y); tmp.segB = Vec2( origin.x,origin.y +visibleSize.height ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA = Point( origin.x,origin.y ); tmp.segB = Point( origin.x +visibleSize.wIDth,origin.y ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA = Point( origin.x,origin.y +visibleSize.height ); tmp.segB = Point( origin.x +visibleSize.wIDth,origin.y + visibleSize.height ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA = Point( origin.x +visibleSize.wIDth,origin.y + visibleSize.height ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); // polygon #1 tmp.segA =Point(100-subX,150-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(120-subX,50-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(120-subX,50-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(200-subX,80-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(200-subX,80-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(140-subX,210-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(140-subX,210-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(100-subX,150-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); // polygon #2 tmp.segA =Point(100-subX,200-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(120-subX,250-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(120-subX,250-subY ); tmp.segB =Point( 60-subX,300-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(60-subX,300-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(100-subX,200-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); // polygon #3 tmp.segA =Point(200-subX,260-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(220-subX,150-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(220-subX,150-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(300-subX,200-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(300-subX,200-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(350-subX,320-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(350-subX,320-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(200-subX,260-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); // polygon #4 tmp.segA =Point(340-subX,60-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(360-subX,40-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(360-subX,40-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(370-subX,70-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(370-subX,70-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(340-subX,60-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); // polygon #5 tmp.segA =Point(450-subX,190-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(560-subX,170-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(560-subX,170-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(540-subX,270-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(540-subX,270-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(430-subX,290-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(430-subX,290-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(450-subX,190-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); // polygon #6 tmp.segA =Point(400-subX,95-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(580-subX,50-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(580-subX,50-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(480-subX,150-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); tmp.segA =Point(480-subX,150-subY ); tmp.segB =Point(400-subX,95-subY ); m_segments.push_back(tmp); if(0 < m_segments.size() ) { vector<lightline>::iterator it =m_segments.begin(); for( ; it !=m_segments.end(); it++ ) { drawNode->drawline(it->segA,it->segB,color4F(1,1,1) ); } } return true;} 效果:
接下来添加光源,其实就是添加一个随便的精灵即可,这里我使用了自带的资源,Closenormal.png,然后添加下触摸事件,你就可以移动这个光源了,这部分省略吧。
刚才初始化多边形的时候,已经将所有的线段保存在类成员m_segments里面了,下面要去除下重复的点,因为一个点连接2条线段:
voID HelloWorld::GetEachPointAngle(){ vector<Point> tmpPoint; vector<lightline>::iterator it =m_segments.begin(); vector<Point>::iterator isFind; // 获得线段唯一点 for( ; it !=m_segments.end(); it++ ) { isFind =find( tmpPoint.begin(),tmpPoint.end(),it->segA); if( isFind == tmpPoint.end() ) { tmpPoint.push_back(it->segA); } isFind =find( tmpPoint.begin(),it->segB); if( isFind == tmpPoint.end() ) { tmpPoint.push_back(it->segB); } } // ......} 现在获得了唯一点,不需要了很多重复的计算,接下来计算当前光源静止的位置到各个点的角度,并且额外增加两条 0.00001 角度的线,为了能让光源打在后面的墙上。
voID HelloWorld::GetEachPointAngle(){ // ....... //获得唯一点的角度,额外增加 2条射线 vector<Point>::iterator it_point = tmpPoint.begin(); for( ; it_point != tmpPoint.end(); it_point++ ) { float angle =atan2(it_point->y -light->getpositionY(),it_point->x -light->getpositionX()); m_angle.push_back(angle -0.00001); m_angle.push_back(angle); m_angle.push_back(angle +0.00001); } // .......}
接下来开始计算打到墙上的点。将光源点分别与线段计算.公式看下原文。
voID HelloWorld::GetEachPointAngle(){ // ......... //循环个角度,找出最近的交点 vector<float>::iterator it_angle =m_angle.begin(); for( ; it_angle !=m_angle.end(); it_angle++ ) { float dx =cos(*it_angle); float dy =sin(*it_angle); //cclOG("%f,%f,%f",*it_angle,dx,dy); lightline l; l.segA =Point(light->getpositionX(),light->getpositionY() ); l.segB =Point(light->getpositionX() + dx,light->getpositionY() + dy ); float minT1 =0; it =m_segments.begin(); for( ; it !=m_segments.end(); it++ ) { float tmpT1 =GetIntersection( l,*it ); if( -1 == tmpT1 ) { continue; } if(0 == minT1 || minT1 > tmpT1 ) { minT1 = tmpT1; } } PointAndAngle p; p.point =Point(light->getpositionX() + minT1 * dx,light->getpositionY() + minT1 * dy ); p.angle = *it_angle; m_intersects.push_back(p); //cclOG("%f,p.point.x,p.point.y,*it_angle); } sort(m_intersects.begin(),m_intersects.end(),SortAngle ); }floatHelloWorld::GetIntersection(lightline ray,lightline seg ){ //cclOG("%f,ray.segA.x,ray.segA.y,ray.segB.x,ray.segB.y); int r_px = ray.segA.x; int r_py = ray.segA.y; float r_dx = ray.segB.x - ray.segA.x; float r_dy = ray.segB.y - ray.segA.y; int s_px = seg.segA.x; int s_py = seg.segA.y; float s_dx = seg.segB.x - seg.segA.x; float s_dy = seg.segB.y - seg.segA.y; float r_mag =sqrt( r_dx * r_dx + r_dy * r_dy ); float s_mag =sqrt( s_dx * s_dx + s_dy * s_dy ); if( ( r_dx / r_mag ) == ( s_dx / s_mag ) && ( r_dy / r_mag ) == ( s_dy / s_mag) ) { return -1; } float t2 = ( r_dx * (s_py-r_py) + r_dy * (r_px - s_px)) / (s_dx*r_dy - s_dy*r_dx); float t1 = ( s_px + s_dx * t2 - r_px )/ r_dx; if( t1 <0 || t2 <0 || t2 >1 ) { return -1; } cclOG("%d,%d,r_px,r_py,r_dx,r_dy,s_px,s_py,s_dx,s_dy,t1); return t1;} 最后对所有与光源配对的点根据角度进行排序,效果:
最后循环填充三角形即可。
这里说下的是,光线和多边形不在一个layer上,因为在你每次移动的过程中,需要清楚旧光线,来画新光线,所以进行了分层,并且对旧数据进行清除,每次移动,重新计算再绘制。
这里可能会出现不准确的情况,效果:
个人认为是移动时候,数值之间计算的误差导致。并非整数,所以我在 ontouchmoved 这样处理的:
/*********************************************************** * 移动触摸会有误差值,不是整数,所以会出现三角形连接错误 * 根据小数大小,取整运算 ***********************************************************/subP.x = ( ( subP.x - (int)subP.x ) > 0.5 ) ? ceil(subP.x) : floor(subP.x);subP.y = ( ( subP.y - (int)subP.y ) > 0.5 ) ? ceil(subP.y) : floor(subP.y);
效果有所改善:
大神们勿喷,谢谢,谢谢。 总结
以上是内存溢出为你收集整理的基于Cocos2d-x的2D光线效果雏形全部内容,希望文章能够帮你解决基于Cocos2d-x的2D光线效果雏形所遇到的程序开发问题。
如果觉得内存溢出网站内容还不错,欢迎将内存溢出网站推荐给程序员好友。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)