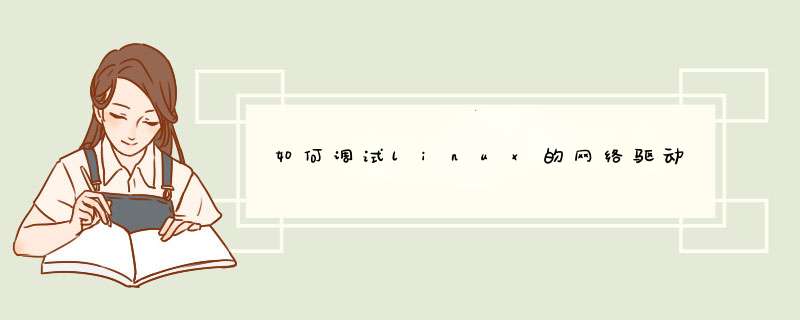
我们借用linux设备驱动第二篇:构造和运行模块里面的hello world程序来演示出错的情况,含有错误代码的hello world如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL")
static int hello_init(void)
{
char *p = NULL
memcpy(p, "test", 4)
printk(KERN_ALERT "Hello, world\n")
return 0
}
static void hello_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "Goodbye, cruel world\n")
}
module_init(hello_init)
module_exit(hello_exit)
Makefile文件如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := helloworld.o
else
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
default:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
endif
clean:
rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend .*.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions modules.order Module.symvers
很明显,以上代码的第8行是一个空指针错误。insmod后会出现下面的oops信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
[ 459.516441] BUG: unable to handle kernel NULL pointer dereference at (null)
[ 459.516445]
[ 459.516448] PGD 0
[ 459.516450] Oops: 0002 [#1] SMP
[ 459.516452] Modules linked in: helloworld(OE+) vmw_vsock_vmci_transport vsock coretemp crct10dif_pclmul crc32_pclmul ghash_clmulni_intel aesni_intel vmw_balloon snd_ens1371 aes_x86_64 lrw snd_ac97_codec gf128mul glue_helper ablk_helper cryptd ac97_bus gameport snd_pcm serio_raw snd_seq_midi snd_seq_midi_event snd_rawmidi snd_seq snd_seq_device snd_timer vmwgfx btusb ttm snd drm_kms_helper drm soundcore shpchp vmw_vmci i2c_piix4 rfcomm bnep bluetooth 6lowpan_iphc parport_pc ppdev mac_hid lp parport hid_generic usbhid hid psmouse ahci libahci floppy e1000 vmw_pvscsi vmxnet3 mptspi mptscsih mptbase scsi_transport_spi pata_acpi [last unloaded: helloworld]
[ 459.516476] CPU: 0 PID: 4531 Comm: insmod Tainted: G OE 3.16.0-33-generic #44~14.04.1-Ubuntu
[ 459.516478] Hardware name: VMware, Inc. VMware Virtual Platform/440BX Desktop Reference Platform, BIOS 6.00 05/20/2014
[ 459.516479] task: ffff88003821f010 ti: ffff880038fa0000 task.ti: ffff880038fa0000
[ 459.516480] RIP: 0010:[<ffffffffc061400d>] [<ffffffffc061400d>] hello_init+0xd/0x30 [helloworld]
[ 459.516483] RSP: 0018:ffff880038fa3d40 EFLAGS: 00010246
[ 459.516484] RAX: ffff88000c31d901 RBX: ffffffff81c1a020 RCX: 000000000004b29f
[ 459.516485] RDX: 000000000004b29e RSI: 0000000000000017 RDI: ffffffffc0615024
[ 459.516485] RBP: ffff880038fa3db8 R08: 0000000000015e80 R09: ffff88003d615e80
[ 459.516486] R10: ffffea000030c740 R11: ffffffff81002138 R12: ffff88000c31d0c0
[ 459.516487] R13: 0000000000000000 R14: ffffffffc0614000 R15: ffffffffc0616000
[ 459.516488] FS: 00007f8a6fa86740(0000) GS:ffff88003d600000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000
[ 459.516489] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033
[ 459.516490] CR2: 0000000000000000 CR3: 0000000038760000 CR4: 00000000003407f0
[ 459.516522] DR0: 0000000000000000 DR1: 0000000000000000 DR2: 0000000000000000
[ 459.516524] DR3: 0000000000000000 DR6: 00000000fffe0ff0 DR7: 0000000000000400
[ 459.516524] Stack:
[ 459.516537] ffff880038fa3db8 ffffffff81002144 0000000000000001 0000000000000001
[ 459.516540] 0000000000000001 ffff880028ab5040 0000000000000001 ffff880038fa3da0
[ 459.516541] ffffffff8119d0b2 ffffffffc0616018 00000000bd1141ac ffffffffc0616018
[ 459.516543] Call Trace:
[ 459.516548] [<ffffffff81002144>] ? do_one_initcall+0xd4/0x210
[ 459.516550] [<ffffffff8119d0b2>] ? __vunmap+0xb2/0x100
[ 459.516554] [<ffffffff810ed9b1>] load_module+0x13c1/0x1b80
[ 459.516557] [<ffffffff810e9560>] ? store_uevent+0x40/0x40
[ 459.516560] [<ffffffff810ee2e6>] SyS_finit_module+0x86/0xb0
[ 459.516563] [<ffffffff8176be6d>] system_call_fastpath+0x1a/0x1f
[ 459.516564] Code: <c7>04 25 00 00 00 00 74 65 73 74 31 c0 48 89 e5 e8 a2 86 14 c1 31
[ 459.516573] RIP [<ffffffffc061400d>] hello_init+0xd/0x30 [helloworld]
[ 459.516575] RSP <ffff880038fa3d40>
[ 459.516576] CR2: 0000000000000000
[ 459.516578] ---[ end trace 7c52cc8624b7ea60 ]---
下面简单分析下oops信息的内容。
由BUG: unable to handle kernel NULL pointer dereference at (null)知道出错的原因是使用了空指针。标红的部分确定了具体出错的函数。Modules linked in: helloworld表明了引起oops问题的具体模块。call trace列出了函数的调用信息。这些信息中其中标红的部分是最有用的,我们可以根据其信息找到具体出错的代码行。下面就来说下,如何定位到具体出错的代码行。
第一步我们需要使用objdump把编译生成的bin文件反汇编,我们这里就是helloworld.o,如下命令把反汇编信息保存到err.txt文件中:
1
objdump helloworld.o -D >err.txt
err.txt内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
helloworld.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
<span style="color:#ff0000">0000000000000000 <init_module>:</span>
0: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 5 <init_module+0x5>
5: 55 push %rbp
6: 48 c7 c7 00 00 00 00mov$0x0,%rdi
d: c7 04 25 00 00 00 00movl $0x74736574,0x0
14: 74 65 73 74
18: 31 c0 xor%eax,%eax
1a: 48 89 e5mov%rsp,%rbp
1d: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 22 <init_module+0x22>
22: 31 c0 xor%eax,%eax
24: 5d pop%rbp
25: c3 retq
26: 66 2e 0f 1f 84 00 00nopw %cs:0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
2d: 00 00 00
0000000000000030 <cleanup_module>:
30: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 35 <cleanup_module+0x5>
35: 55 push %rbp
36: 48 c7 c7 00 00 00 00mov$0x0,%rdi
3d: 31 c0 xor%eax,%eax
3f: 48 89 e5mov%rsp,%rbp
42: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 47 <cleanup_module+0x17>
47: 5d pop%rbp
48: c3 retq
Disassembly of section .rodata.str1.1:
0000000000000000 <.rodata.str1.1>:
0: 01 31 add%esi,(%rcx)
2: 48 rex.W
3: 65 gs
4: 6c insb (%dx),%es:(%rdi)
5: 6c insb (%dx),%es:(%rdi)
6: 6f outsl %ds:(%rsi),(%dx)
7: 2c 20 sub$0x20,%al
9: 77 6f ja 7a <cleanup_module+0x4a>
b: 72 6c jb 79 <cleanup_module+0x49>
d: 64 0a 00or %fs:(%rax),%al
10: 01 31 add%esi,(%rcx)
12: 47 6f rex.RXB outsl %ds:(%rsi),(%dx)
14: 6f outsl %ds:(%rsi),(%dx)
15: 64 fs
16: 62 (bad)
17: 79 65 jns7e <cleanup_module+0x4e>
19: 2c 20 sub$0x20,%al
1b: 63 72 75movslq 0x75(%rdx),%esi
1e: 65 gs
1f: 6c insb (%dx),%es:(%rdi)
20: 20 77 6fand%dh,0x6f(%rdi)
23: 72 6c jb 91 <cleanup_module+0x61>
25: 64 0a 00or %fs:(%rax),%al
Disassembly of section .modinfo:
0000000000000000 <__UNIQUE_ID_license0>:
0: 6c insb (%dx),%es:(%rdi)
1: 69 63 65 6e 73 65 3dimul $0x3d65736e,0x65(%rbx),%esp
8: 44 75 61rex.R jne 6c <cleanup_module+0x3c>
b: 6c insb (%dx),%es:(%rdi)
c: 20 42 53and%al,0x53(%rdx)
f: 44 2f rex.R (bad)
11: 47 50 rex.RXB push %r8
13: 4c rex.WR
...
Disassembly of section .comment:
0000000000000000 <.comment>:
0: 00 47 43add%al,0x43(%rdi)
3: 43 3a 20rex.XB cmp (%r8),%spl
6: 28 55 62sub%dl,0x62(%rbp)
9: 75 6e jne79 <cleanup_module+0x49>
b: 74 75 je 82 <cleanup_module+0x52>
d: 20 34 2eand%dh,(%rsi,%rbp,1)
10: 38 2e cmp%ch,(%rsi)
12: 32 2d 31 39 75 62 xor0x62753931(%rip),%ch# 62753949 <cleanup_module+0x62753919>
18: 75 6e jne88 <cleanup_module+0x58>
1a: 74 75 je 91 <cleanup_module+0x61>
1c: 31 29 xor%ebp,(%rcx)
1e: 20 34 2eand%dh,(%rsi,%rbp,1)
21: 38 2e cmp%ch,(%rsi)
23: 32 00 xor(%rax),%al
Disassembly of section __mcount_loc:
0000000000000000 <__mcount_loc>:
由oops信息我们知道出错的地方是hello_init的地址偏移0xd。而有dump信息知道,hello_init的地址即init_module的地址,因为hello_init即本模块的初始化入口,如果在其他函数中出错,dump信息中就会有相应符号的地址。由此我们得到出错的地址是0xd,下一步我们就可以使用addr2line来定位具体的代码行:
addr2line -C -f -e helloworld.o d
此命令就可以得到行号了。以上就是通过oops信息来定位驱动崩溃的行号。
其他调试手段
以上就是通过oops信息来获取具体的导致崩溃的代码行,这种情况都是用在遇到比较严重的错误导致内核挂掉的情况下使用的,另外比较常用的调试手段就是使用printk来输出打印信息。printk的使用方法类似printf,只是要注意一下打印级别,详细介绍在linux设备驱动第二篇:构造和运行模块中已有描述,另外需要注意的是大量使用printk会严重拖慢系统,所以使用过程中也要注意。
以上两种调试手段是我工作中最常用的,还有一些其他的调试手段,例如使用/proc文件系统,使用trace等用户空间程序,使用gdb,kgdb等,这些调试手段一般不太容易使用或者不太方便使用,所以这里就不在介绍了。
linux下编译运行驱动嵌入式linux下设备驱动的运行和linux x86 pc下运行设备驱动是类似的,由于手头没有嵌入式linux设备,先在vmware上的linux上学习驱动开发。
按照如下方法就可以成功编译出hello world模块驱动。
1、首先确定本机linux版本
怎么查看Linux的内核kernel版本?
'uname'是Linux/unix系统中用来查看系统信息的命令,适用于所有Linux发行版。配合使用'uname'参数可以查看当前服务器内核运行的各个状态。
#uname -a
Linux whh 3.5.0-19-generic #30-Ubuntu SMPTue Nov 13 17:49:53 UTC 2012 i686 i686 i686 GNU/Linux
只打印内核版本,以及主要和次要版本:
#uname -r
3.5.0-19-generic
要打印系统的体系架构类型,即的机器是32位还是64位,使用:
#uname -p
i686
/proc/version 文件也包含系统内核信息:
# cat /proc/version
Linux version 3.5.0-19-generic(buildd@aatxe) (gcc version 4.7.2 (Ubuntu/Linaro 4.7.2-2ubuntu1) ) #30-UbuntuSMP Tue Nov 13 17:49:53 UTC 2012
发现自己的机器linux版本是:3.5.0-19-generic
2、下载机器内核对应linux源码
到下面网站可以下载各个版本linux源码https://www.kernel.org/
如我的机器3.5.0版本源码下载地址为:https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v3.x/linux-3.5.tar.bz2
下载完后,找一个路径解压,如我解压到/linux-3.5/
然后很重要的一步是:执行命令uname -r,可以看到Ubuntu的版本信息是3.5.0-19-generic
。进入linux源码目录,编辑Makefile,将EXTRAVERSION = 修改为EXTRAVERSION= -19-generic。
这些都是要配置源码的版本号与系统版本号,如果源码版本号和系统版本号不一致,在加载模块的时候会出现如下错误:insmod: error inserting 'hello.ko': -1 Invalid module format。
原因很明确:编译时用的hello.ko的kenerl 不是我的pc的kenerl版本。
执行命令cp /boot/config-3.5.0-19-generic ./config,覆盖原有配置文件。
进入linux源码目录,执行make menuconfig配置内核,执行make编译内核。
3、写一个最简单的linux驱动代码hello.c
/*======================================================================
Asimple kernel module: "hello world"
======================================================================*/
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("zeroboundaryBSD/GPL")
static int hello_init(void)
{
printk(KERN_INFO"Hello World enter\n")
return0
}
static void hello_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_INFO"Hello World exit\n ")
}
module_init(hello_init)
module_exit(hello_exit)
MODULE_AUTHOR("zeroboundary")
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A simple HelloWorld Module")
MODULE_ALIAS("a simplestmodule")
4、写一个Makefile对源码进行编译
KERN_DIR = /linux-3.5
all:
make-C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
clean:
make-C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` clean
obj-m += hello.o
5、模块加载卸载测试
insmod hello.ko
rmmod hello.ko
然后dmesg|tail就可以看见结果了
最后,再次编译驱动程序hello.c得到hello.ko。执行insmod ./hello.ko,即可正确insert模块。
使用insmod hello.ko 将该Module加入内核中。在这里需要注意的是要用 su 命令切换到root用户,否则会显示如下的错误:insmod: error inserting 'hello.ko': -1 Operation not permitted
内核模块版本信息的命令为modinfo hello.ko
通过lsmod命令可以查看驱动是否成功加载到内核中
通过insmod命令加载刚编译成功的time.ko模块后,似乎系统没有反应,也没看到打印信息。而事实上,内核模块的打印信息一般不会打印在终端上。驱动的打印都在内核日志中,我们可以使用dmesg命令查看内核日志信息。dmesg|tail
可能还会遇到这种问题insmod: error inserting 'hello.ko': -1 Invalid module format
用dmesg|tail查看内核日志详细错误
disagrees about version of symbolmodule_layout,详细看这里。
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-kernelmodules/index.html
在X86上我的办法是:
make -C/usr/src/linux-headers-3.5.0-19-generic SUBDIRS=$PWD modules
驱动最终以*.ko的形式生成,insmod的本质就是将ko文件与运行的内核进行链接的过程。类似于编译helloworld的链接过程。链接必然需要先进行编译,以便确定所需的外部符号(EXPORT_SYMBOLS)是否存在,因为有些符号(函数或全局变量)在内核中,在驱动中如果使用到这些符号,必须预留一个位置,insmod时进一步确定这些符号的具体位置(符号绑定)。如果内核都没有编译过,怎么知道这些符号有没有编入内核中?
关于这方面的知识可参照IBM developerworks上面的《Linux 可加载内核模块剖析》及相关文章。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)