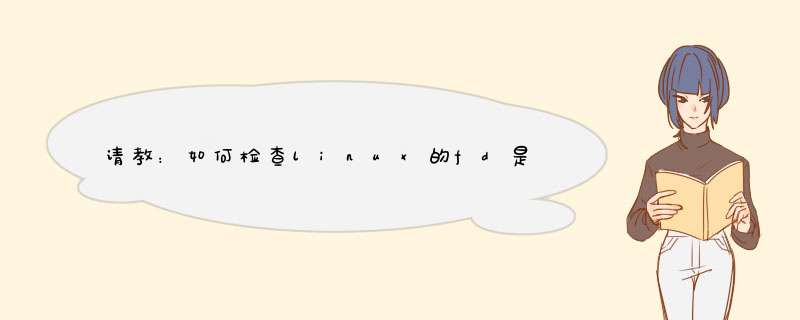
ls -l /proc/进程PID/fd/
会列出当前进程所有的fd.
或者
写代码的时候最好写个open就写个close
写个malloc就写个free
在Linux下,系统全部能够打开的fd总数为:/proc/sys/fs/file-max,取决于内存
The file-max file /proc/sys/fs/file-max sets the maximum number of file-handles that the Linux kernel will allocate. We generally tune this file to improve the number of open files by increasing the value of /proc/sys/fs/file-max to something reasonable like 256 for every 4M of RAM we have: i.e. for a machine with 128 MB of RAM, set it to 8192 - 128/4=32 32*256=8192.
/proc/sys/fs/file-nr 记录系统中fd的使用情况,已分配文件句柄的数目
已使用文件句柄的数目
文件句柄的最大数目 ,
单个进程能够打开的最大fd数量为 ulimit -n, 可以通过sysconf(_SC_OPEN_MAX)获取默认的进程fd打开数量。
修改fd限制可以先修改shell的ulimit -n,
或者通过setrlimit函数进行修改:
void modifyfdlimit()
{
rlimit fdLimit
fdLimit.rlim_cur = 30000
fdLimit.rlim_max = 30000
if (-1 == setrlimit (RLIMIT_NOFILE, &fdLimit))
{
printf ("Set max fd open count fai. /nl")
char cmdBuffer [64]
sprintf (cmdBuffer, "ulimit -n %d", 30000)
if (-1 == system (cmdBuffer))
{
printf("%s failed. /n", cmdBuffer)
exit(0)
}
if (-1 == getrlimit (RLIMIT_NOFILE, &fdLimit))
{
printf("Ulimit fd number failed.")
exit(0)
}
}
//printf("Hard limit: %d. Soft limit: %d", fdLimit.rlim_max, fdLimit.rlim_cur)
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)