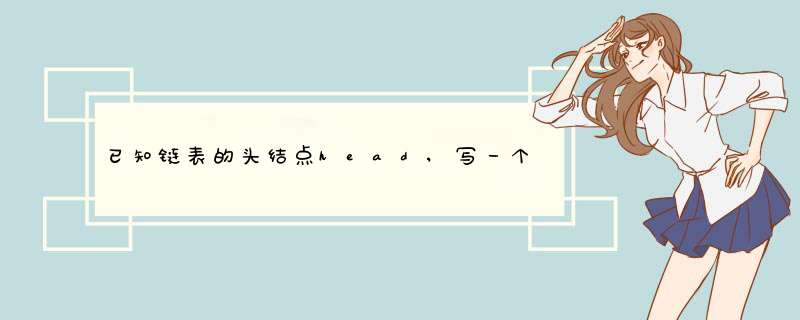
这个程序的原理就是:假如本来有0-10数(0是头结点,不考虑逆置)按正常顺序排列,现在我把1后面的数断开,这样链表只剩下0->1了。接下来,我把2插入到链表中,就变成了0->2->1,然后在插入3,就变成0->3->2->1,类推,实现1-10的逆置。程序中的p2和p3都是过渡用的结点,你再仔细理解下。
如果要不使用新空间,应该就是使用递归的方法。
下面是我的代码,关键是Reverse方法。其他的代码都是生成测试数据和输出结果用的。
class Program
{
class Node
{
public string data;
public Node next;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node first,current;
first = current = new Node {data = "0"};
for(var i=1;i<100;i++)
{
var c = new Node {data = iToString()};
currentnext = c;
current = c;
}
PrintLinkList(first);
first = Reverse(first);
PrintLinkList(first);
ConsoleReadLine();
}
static Node Reverse(Node cur)
{
if (curnext != null)
{
var next = curnext;
var n = Reverse(curnext);
nextnext = cur;
curnext = null;
return n;
}
return cur;
}
static void PrintLinkList(Node first)
{
while(first!=null)
{
ConsoleWriteLine(firstdata);
first = firstnext;
}
}
}
Node ReverseList(Node head)
{
if ( head == NULL || head->next == NULL )
return head; // 如果链表空,或只有一个元素,则直接返回,无需处理。
Node p1 = head ; // 建立三个指针分别指向当前元素、当前位置的下一个元素,以及下一个元素的下一个元素。可分别认为是s1,s2,s3
Node p2 = p1->next ;
Node p3 = p2->next ;
p1->next = NULL ; // 将首元素的next指针置空,也就是头变尾
while ( p3 != NULL ) // 在第三个元素不为空的情况下
{
p2->next = p1 ; // 让第二个元素的next指针指向第一个元素(逆序的关键)
p1 = p2 ; // 将当前指针指向第二个元素,
p2 = p3 ; // 将当前位置的下一个指针指向第三元素
p3 = p3->next ; // 将下一个元素的下一个指针指向第三个元素的下一个
}
p2->next = p1 ; // 如果最后一个元素不存在,还是要把第二个元素的next指针指向第一个元素。
head = p2 ; // 第二元素置为链头
return head ;
}
不知道你是否是链表倒置还是排序的逆序,如果你是想链表倒置的话一般使用3个指针,前两个指针用来使链表节点倒置,而最后一个指针用来指向断开出,例如:node
r,p,q;//申明三个指针;r=q=NULL;p=head;while(p!=NULL){r=q;q=p;p=p->next;//p指向断开处后的节点q->next=r;//将后一个节点指向前一个节点
}画张图的话会比较好理解
#include <stdioh>
#include <stdlibh>
typedef struct Node
{
int num;
struct Node nextptr;
}Node;
void printList(Node head)
{
Node cptr= headnextptr;
while(cptr!=NULL)
{
//printf("%x: %d|%x->\n",cptr, cptr->num, cptr->nextptr);
printf("%d ",cptr->num);
cptr= cptr->nextptr;
}
printf("\n");
}
void freeList(Node head)
{
Node nptr, cptr= headnextptr;
while(cptr != NULL)
{
nptr= cptr->nextptr;
free(cptr);
cptr= nptr;
}
}
Node newNode(const int ipt_num)
{
static Node newptr;
newptr=(Node)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newptr->num= ipt_num;
newptr->nextptr= NULL;
return newptr;
}
Node merger(Node la, Node lb)
{
Node lc, cptr= &lc;
Node aptr= lanextptr;
Node bptr= lbnextptr;
while(aptr!=NULL || bptr!=NULL)
{
if(aptr!=NULL && bptr!=NULL)
{
if(aptr->num < bptr->num)
{
cptr->nextptr= newNode(aptr->num);
aptr= aptr->nextptr;
}
else if(aptr->num > bptr->num)
{
cptr->nextptr= newNode(bptr->num);
bptr= bptr->nextptr;
}
else{
cptr->nextptr= newNode(aptr->num);
aptr= aptr->nextptr;
bptr= bptr->nextptr;
}
}
else{
if(aptr==NULL)
{
cptr->nextptr= newNode(bptr->num);
bptr= bptr->nextptr;
}
else{//bptr==NULL
cptr->nextptr= newNode(aptr->num);
aptr= aptr->nextptr;
}
}
cptr= cptr->nextptr;
cptr->nextptr= NULL;
}
return lc;
}
void inverted(Node& la, Node& lb)
{
Node newnode, cutptr;
newnodenextptr=NULL;
while(lanextptr!=NULL || lbnextptr!=NULL)
{
if(lanextptr!=NULL && lbnextptr!=NULL)
{
if(lanextptr->num < lbnextptr->num)
{
cutptr= lanextptr;
lanextptr= lanextptr->nextptr;
}
else{
cutptr= lbnextptr;
lbnextptr= lbnextptr->nextptr;
}
}
else{
if(lanextptr!=NULL)
{
cutptr= lanextptr;
lanextptr= lanextptr->nextptr;
}
else{
cutptr= lbnextptr;
lbnextptr= lbnextptr->nextptr;
}
}
cutptr->nextptr= newnodenextptr;
newnodenextptr= cutptr;
}
la= newnode;
}
int main(void)
{
Node la, lb, lc;
Node curptr;
curptr= &la;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(3);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(5);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(8);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(11);
curptr= &lb;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(2);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(6);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(8);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(9);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(11);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(15);
curptr= curptr->nextptr;
curptr->nextptr= newNode(20);
printList(la);
printList(lb);
lc= merger(la,lb);
printList(lc);
inverted(la,lb);
printList(la);
freeList(la);
freeList(lb);
freeList(lc);
printf("end");
return 0;
}
可以用递归,如果没到链表尾,则递归查询,否则输出当前值。下面只是算法表示,不能直接放到程序里编译执行。
int outlink(node p)
{
if(p->next!=null)
outlink(p->next);
printf(p->data);
return 0;
}
List_ptr InvertList(List_ptr head) //原地逆转单链表head
{
List_ptr p=head,q=NULL,listend=head;
while(listend->next!=NULL) listend=listend->next;
while(p!=listend)
{
head=p->next;
listend->next=p;
if(q==NULL) p->next=NULL;
else p->next=q;
q=p;
p=head;
}
return head;
}
void
Inverse(LinkList
&L)
/
对带头结点的单链表L实现就地逆置
/
{
if
(L->next
!=
NULL)
{
if
(L->next->next
==
NULL)
{
}
else
if
(L->next->next->next
==
NULL)
{
LNode
p
;
p=L->next;
L->next->next->next=L->next;
L->next=L->next->next;
p->next=NULL;
}
else
{
LNode
p,
q,
r;
p
=
L->next;
q
=
p->next;
r
=
q->next;
p->next
=
NULL;
while
(r->next
!=
NULL)
{
q->next
=
p;
p
=
q;
q
=
r;
r
=
r->next;
}
q->next
=
p;
r->next
=
q;
L->next
=
r;
}
}
}
请给分
!!!
以上就是关于已知链表的头结点head,写一个函数把这个链表逆序。C++ 代码不是看得很懂。全部的内容,包括:已知链表的头结点head,写一个函数把这个链表逆序。C++ 代码不是看得很懂。、C# 求单链表逆序的算法,要能测试通过的,谢谢、关于链表的逆序问题等相关内容解答,如果想了解更多相关内容,可以关注我们,你们的支持是我们更新的动力!
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)