DS31256 HDLC控制器的配置步骤—桥接模式
本应用笔记提供了怎样配置桥接模式下DS31256 HDLC控制器T1端口的例子。文章提供了一个实际例程,以方便最终用户使用,帮助他们理解怎样在环回模式下配置器件,构建数据包,并进行传送、接收和检查。
- PCI桥接模式
- 配置模式
利用PCI桥接模式,PCI总线上的主机可以访问本地总线。PCI总线用于控制并监视DS31256,发送分组数据。DS31256将数据从PCI总线映射到本地总线(请参考DS31256数据资料的11.1.1节,了解详细信息)。
关于使用配置模式的详细信息,请参考应用笔记2871:“DS31256 HDLC控制器的配置步骤—配置模式”。 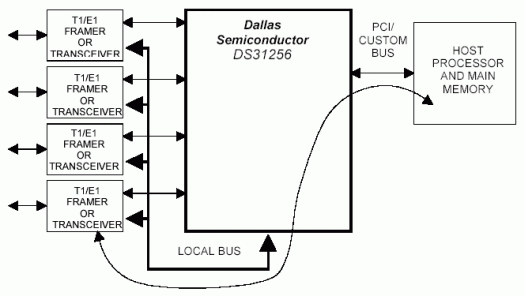
图1.
为提高可读性,这个例子中的代码使用了几个函数调用。这些函数的定义如下:
将指定的数据写入指定的DS31256寄存器地址
输入:- read_reg(address, data)
地址 = 数据要写入的寄存器地址 数据 = 要写入到指定寄存器中的数据 输出:无
读取DS31256指定地址寄存器中的内容
输入:- write_reg_IS(address, data)
地址 = 要读取的寄存器地址 输出:
数据 = 来自寄存器的数值
将指定的数据写入指定的DS31256间接选择寄存器,然后,在返回前,等待该寄存器的忙比特被清位。
输入:- wr_dword(address, data)
地址 = 数据要写入的间接选择寄存器 数据 = 要写入到指定寄存器的数据 输出:无
函数代码:
write_reg(address, data)
bit_check = 0x8000;
while(bit_check & 0x8000)
read_reg(address, bit_check);
将指定的32位数据写入指定的32位主机存储器地址
输入:- rd_dword(address, data)
地址 = 数据要写入的主机存储器地址 数据 = 要写入到指定存储器地址的数据 输出:无
从指定的32位主机存储器地址读取的32位数据
输入:- frame_wait(count)
地址 = 要读取的主机存储器地址 输出:
数据 = 从主机存储器读取的32位数据
提供等于帧周期数的延时,帧周期为125微秒。
输入:T1配置模式代码实例
计数 = 要等待的帧周期数 输出:无
这一代码实例包括以下步骤:
- 复位DS31256
- 配置DS31256
- 使能HDLC通道
- 使HDLC通道处于环回模式
- 排列、发送、接收、检查数据包
下面几节提供简要说明和代码实例,详细介绍了这些步骤。采用了寄存器名称而不是地址,以提高可读性。DS31256内部器件配置寄存器对应的地址/偏移列在相应的表格中。此外,缩写Tx和Rx分别用于表示发送侧和接收侧。请参考DS31256数据资料,了解详细信息。
复位DS31256包括三步。首先,必须复位DS31256内部寄存器,然后,DS31256内部RAM必须置零,最后,再次复位DS31256内部寄存器。
使用主复位寄存器(MRID)可以对DS31256中的所有寄存器进行软件复位。当MRID寄存器的比特0被设置为1时,所有内部寄存器将被置为默认值0。在设置器件正常工作之前,主机必须将该位置回0。
//Reset DS31256 using MRID registers master reset bit.
write_reg(MRID, 0x0001);
write_reg(MRID, 0x0000);
将DS31256内部RAM置零
复位芯片时,DS31256内部配置RAM并没有被清零,因此,必须手动清零。使用适当的数据和DS31256间接选择寄存器,对DS31256的每一内部RAM进行一系列写 *** 作,完成该任务。本节详细介绍完成该任务的过程。
// Zero Rx configuraTIon and Tx configuraTIon RAM's for all ports
for(port = 0; port < 16; port = port + 1)
{
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, 0x0000);
for(ds0 = 0; ds0 < 128; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
{
// Set bits 9-8 = 01 to select Rx Configuration RAM
// Set bits 9-8 = 10 to select Tx Configuration RAM
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, (0x0100 + ds0));
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, (0x0200 + ds0));
}
}
// Zero the Rx HDLC channel definition RAM
write_reg(RHCD, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RHCDIS, channel);
// Zero the Tx HDLC channel definition RAM
write_reg(THCD, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(THCDIS, channel);
// Zero the Rx FIFO Starting Block Pointer RAM
write_reg(RFSBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RFSBPIS, channel);
// Zero the Rx FIFO Block Pointer RAM
write_reg(RFBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RFBPIS, channel);
// Zero the Rx FIFO High Watermark RAM
write_reg(RFHWM, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RFHWMIS, channel);
// Zero the Tx FIFO Starting Block Pointer registers
write_reg(TFSBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TFSBPIS, channel);
// Zero the Tx FIFO Block Pointer RAM
write_reg(TFBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TFBPIS, channel);
// Zero the Tx FIFO Low Watermark RAM
write_reg(TFLWM, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TFLWMIS, channel);
// Zero the Rx DMA configuration RAM
write_reg(RDMAC, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x0400 + channel);
// Zero the Tx DMA configuration RAM
write_reg(TDMAC, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x0200 + channel);
复位DS31256内部寄存器
使用主复位寄存器(MRID)可以对DS31256中的所有寄存器进行软件复位。当MRID寄存器的比特0被设置为1时,所有内部寄存器将被置为默认值0。在设置器件正常工作之前,主机必须将该位置回0。
// Reset DS31256 using MRID registers master reset bit.
write_reg(MRID, 0x0001);
write_reg(MRID, 0x0000);
配置DS31256
配置DS31256包括以下步骤:
- 配置PCI寄存器
- 配置1层寄存器
- 配置HDLC寄存器
- 配置FIFO寄存器
- 配置DMA寄存器
下面几节详细介绍了配置这些寄存器设置。采用了几个变量来提高可读性,提供计算能力更强的代码结构。下面的代码对这些变量进行初始化:
// This example uses port 1 channel 3
port = 1;
channel = 3;
// Rx free queue base address
rfq_base_addr = 0x10000000;
// Rx free queue end address
// Rx free queue size = 16
rfq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Rx done queue base address
rdq_base_addr = 0x10000100;
// Rx done queue end address
// Rx done queue size = 16
rdq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Rx descriptor base address
// Rx descriptor table size = 256
rdscr_base_addr = 0x10000200;
// Rx data buffer base address
rx_buf_base_addr = 0x10001000;
// Tx pending queue base address
tpq_base_addr = 0x10000300;
// Tx pending queue end address
// Tx pending queue size = 16
tpq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Tx done queue base address
tdq_base_addr = 0x10000400;
// Tx done queue end address
// Tx done queue size = 16
tdq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Tx descriptor base address
// Tx descriptor table size = 256
tdscr_base_addr = 0x10000500;
// Tx data buffer base address
tx_buf_base_addr = 0x10002000;
PCI桥接模式支持PCI总线上的主机对本地总线进行访问。PCI总线用于控制和监视DS31256,传送分组数据。DS31256将数据从PCI总线映射到本地总线(请参考DS31256数据资料第10节)。
// Map DS31256 Configuration Registers to a PCI bus base address
write_reg(PDCM, 32'h80000000);
// PCI command/status register 0 - controls DS31256 DMA functionality
// Set Bit 1 = 1 to enable accesses to internal device configuration registers through PCI bus
//(required for Bridge mode)
// Set Bit 2 = 1 to allow the device operation as bus master on PCI bus (required for DMA)
// Set Bit 6 = 1 to act on parity errors
// Set Bit 8 = 1 to enable the PSERR pin
write_reg(PCMD0, 32'h00000146);
配置1层寄存器
DS31256的每一端口都含有1层控制器,完成以下几项功能,包括:
- 为输入和输出数据分配HDLC通道号
- 通道化本地和网络环回
- 64kps、56kps、或者没有数据通道化选择
- 通道化发送DS0通道填充全1
- 向BERT发送和接收数据
- 将数据送入V.54环路码型探测器
通过RP[n]CR、TP[n]CR、CP[n]RD和CP[n]RDIS寄存器,在端口上完成1层配置,其中,n是要配置的端口。
// Set RX Port Control Register
// Set bits 2-0 = 000 for clock, data and sync are not inverted
// Set bits 5-4 = 00 for sync pulse 0 clocks early
// Set bits 7-6 = 00 for T1 mode
// Set bit 10 = 0 to disable local loopback
write_reg(RP[0]CR + 4 * port, 0x0000);
// Set Tx Port Control Register
// Set bit 2-0 = 000 for clock, data and sync are not inverted
// Set bit 3 = 0 to force all data at TD to be 1
// Set bits 5-4 = 00 for sync pulse 0 clocks early
// Set bits 7-6 = 0 for T1 mode
write_reg(TP[0]CR + 4 * port, 0x0000);
// RX Port Configuration Registers
// DS0's 0-3 disabled, assigned to HDLC channel
// CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 01 for Receive Configuration
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, 0x0000 + channel);
for(ds0 = 0; ds0 < 4; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x0100 + ds0);
// Tx Port Configuration Registers
// DS0's 0-3 disabled, assigned to HDLC channel
// CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 10 for Transmit Configuration
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, 0x0000 + channel);
for(ds0 = 0; ds0 < 4; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x0200 + ds0);
配置HDLC寄存器
DS31256含有一个256通道HDLC控制器,完成2层功能。该控制器完成的功能包括:
- 零填充和去填充
- 标志探测和字节对齐
- CRC产生和校验
- 数据置反和位反转
通过RHCD、RHCDIS、THCD和THCDIS寄存器,在通道上配置HDLC控制器。
// RX HDLC configuration
// Set bits 3-2 = 10 for 32-bit CRC
write_reg(RHCD, 0x0008);
write_reg_IS(RHCDIS, channel);
// Tx HDLC configuration
// Set bit 1= 0 to select an interfill byte of 7E
// Set bits 3-2 = 10 for 32-bit CRC
// Set bits 11-8 = 1000 for closing flag/no interfill bytes/opening flag
write_reg(THCD, 0x0108);
write_reg_IS(THCDIS, channel);
配置FIFO寄存器
DS31256含有一个16kB发送FIFO和一个16kB接收FIFO。每一FIFO按照4 dword或者16字节被分成1024个模块。在HDLC通道基础上分配FIFO存储器。可以设置分配给每一HDLC通道的FIFO存储器的数量,最少是4个模块,最多为1024个模块。建立圆形链表,列出一组模块,每一模块指向链中的下一模块,最后一个模块指向第一个,这样,将FIFO存储器分配给HDLC通道。链表中的一个模块分配给该通道的FIFO起始模块指针,将FIFO模块链表分配给指定的HDLC通道。
在这个例子中,4个Tx FIFO模块和4个Rx FIFO模块被分配给HDLC通道。这个例子还使用了一个Rx FIFO高水线3,以及Tx FIFO低水线1。Rx FHFO高水线指示HDLC引擎在DMA开始向PCI总线发送数据之前,应该将多少模块写入Rx FIFO。高水线设置必须在一个模块以及相关某一通道链表模块之间。Tx FIFO低水线指示在DMA开始从PCI总线获取大量数据之前,有多少模块应留在Tx FIFO中。HDLC通道用于防止出现传送下溢以及接收上溢所需要的FIFO存储器、Rx FIFO高水线和Tx FIFO低水线数量取决于应用程序。通过下表列出的寄存器,在HDLC通道基础上,单独配置DS31256的Tx FIFO和Rx FIFO。
// Build the Rx FIFO block linked list
// 0->1->2->3->0
for (block = 0; block < 4; block = block + 1)
{
// Bits 9-0 in RFBP register indicate which block is next in the linked list
write_reg(RFBP, block + 1);
write_reg_IS(RFBPIS, block);
}
// The last block points to the first block to create a circular linked list
write_reg(RFBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(RFBPIS, 0x0003);
// Assign the circular linked list to a specific channel
write_reg(RFSBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(RFSBPIS, channel);
// Set RX FIFO high watermark for channel to 3
write_reg(RFHWM, 0x0003);
write_reg_IS(RFHWMIS, channel);
// Tx FIFO block linked list
// 0->1->2->3->0
for (block = 0; block < 4; block = block + 1)
{
// Bits 9-0 in TFBP register indicate which block is next in the linked list
write_reg(TFBP, block + 1);
write_reg_IS(TFBPIS, block);
}
// The last block points to the first block to create a circular linked list
write_reg(TFBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(TFBPIS, 0x0003);
// Assign the circular linked list to a specific channel
write_reg(TFSBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(TFSBPIS, channel);
// Set Tx FIFO low watermark for channel to 1
write_reg(TFLWM, 0x0001);
write_reg_IS(TFLWMIS, channel);
配置DMA寄存器
DMA模块处理分组数据在FIFO模块和PCI模块之间的传送。PCI模块控制数据在DS31256和外部PCI总线之间的传送。主机定义为CPU或者位于PCI总线上的智能控制器,由它指示DS31256怎样处理输入输出数据。
这通过使用描述符来实现,描述符定义为从主机传送给DMA模块以及由DMA模块传送给主机并经过格式化预处理的消息。通过这些描述符,主机告知DMA要传送的分组数据的位置和状态,把接收到的分组数据放到哪里。DMA使用这些描述符告知主机,已经传送的分组数据的状态,以及接收到的分组数据的状态和位置。
在接收侧,主机写入自由队列描述符,告知DMA在哪里可以放置到达分组数据。与每一自由队列输入相关的是接收数据缓冲位置和数据包描述符。DS31256使用接收自由队列输入来将接收到的分组数据写入主机存储器,它在Rx完成队列中建立输入。这些Rx完成队列输入告知主机接收到的数据的位置和状态。请参考DS31256数据资料,了解详细信息。主机必须通过写入下表列出的所有寄存器来配置Rx DMA:
// Rx large buffer size = 256 bytes
write_reg(RLBS, 0x0100);
// Rx free queue base address
write_reg(RFQBA0, rfq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(RFQBA1, (rfq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Rx free queue large buffer read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(RFQLBRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(RFQLBWP, 0x0000);
// Rx free queue small buffer start address = 16
write_reg(RFQSBSA, rfq_end_idx);
// Rx free queue small buffer read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(RFQSBRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(RFQSBWP, 0x0000);
// Rx free queue end address
write_reg(RFQEA, rfq_end_idx);
// Rx done queue base address
write_reg(RDQBA0, rdq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(RDQBA1, (rdq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Rx done queue read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(RDQRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(RDQWP, 0x0000);
// Rx done queue end address
write_reg(RDQEA, rdq_end_idx);
// Rx descriptor base address
write_reg(RDBA0, rdscr_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(RDBA1, (rdscr_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Rx DMA Channel Configuration
// The data in RDMAC register is written to or read from the Receive Configuration RAM
// Set bit 0 = 0 to disable the HDLC Channel
// Set bit 201 = 00 for large buffers only
// Set bit 6-3 = 0000 for 0 byte offset from the data buffer address of the first data buffer
// Set Bit 9-7 = 000 for DMA write to the Done Queue only after packet reception is complete
// Set the HDLC Channel Number by RDMACIS register
write_reg(RDMAC, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x0400 + channel);
在发送侧,主机将写入未决队列,告知DMA哪一通道有准备要发送的分组数据。与每一未决队列描述符相关的是一个或者多个发送数据包描述符链表,由它描述了分组数据。每一发送数据包描述符还有一个发送数据缓冲指针,含有HDLC数据包的实际数据负载。
DS31256处理发送未决队列描述符输入时,它建立发送完成队列描述符队列输入。完成发送一个完整的数据包或者DS31256所配置的数据缓冲后,DMA将写入完成队列。通过这些完成队列描述符,DMA告知主机关于输出分组数据的状态。请参考DS31256数据资料,了解详细信息。主机必须通过写入下表列出的所有寄存器来配置Tx DMA:
// Tx pending queue base address
write_reg(TPQBA0, tpq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(TPQBA1, (tpq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Tx pending queue read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(TPQRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(TPQWP, 0x0000);
// Tx pending queue end address
write_reg(TPQEA, tpq_end_idx);
// Tx done queue base address
write_reg(TDQBA0, tdq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(TDQBA1, (tdq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Tx done queue read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(TDQRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(TDQWP, 0x0000);
// Tx done queue end address
write_reg(TDQEA, tdq_end_idx);
// Tx descriptor base address
write_reg(TDBA0, tdscr_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(TDBA1, (tdscr_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Tx DMA Channel Configuration
// The data in TDMAC register is written to or read from the Transmit Configuration RAM
// Set bit 0 = 0 to disable HDLC Channel
// Set bit 1 = 0 for write done queue after packet transmitted
// Set the HDLC Channel Number by TDMACIS register
write_reg(TDMAC, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x0200 + channel);
使能HDLC通道
DS31256初始化后,下一步是使能HDLC通道。除了已经阐述的配置步骤之外,必须完成以下步骤来使能DS31256数据包传送和接收:
- 使能端口Tx和Rx配置RAM中的HDLC通道(使能HDLC通道)
- 初始化Rx自由队列(装入DMA描述符)
- 针对DS31256使能Tx DMA和Rx DMA (使能DMA)
- 使能HDLC通道Tx和Rx DMA
- 使能1层的端口数据传送(打开HDLC通道)
使能端口Tx和Rx配置RAM中的HDLC通道
// Enable packet reception in port layer 1 Rx configuration RAM
for (ds0 = 0; ds0 < 4; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
{
// Read the current data value from the Rx Configuration RAM
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 6-0 = DS0
// Set CP[n]RDIS bit 14 = 1 to read data from the RAM
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 01 to select Rx configuration RAM
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x4100 + ds0);
read_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, data);
// Update memory with new value
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 6-0 = DS0
// Set CP[n]RDIS bit 14 = 0 to write data to the RAM
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 01 to select Rx configuration RAM
// Enable DS0 by setting bit 15 = 1 in CP[0]RD register
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, data | 0x8000);
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x0100 + ds0);
}
初始化Rx自由队列
在DS31256将DMA接收到的数据包从其内部FIFO发送到主机存储器之前,主机必须告知DS31256把数据放到哪里。这通过Rx自由队列完成。Rx自由队列中的每一输入都含有指向Rx数据缓冲和Rx数据包描述符索引的指针。这一例子使用了一个Rx自由队列输入。该输入含有一个Rx自由队列大缓冲和一个Rx数据包描述符。DS31256 Rx大数据缓冲容量被设置为256字节(RLBS = 256)。此外,DS31256被配置为使用4字节CRC,将Rx CRC写入Rx数据缓冲。因此,一个Rx大数据缓冲可以支持252字节的分组数据。
// check for space in Rx large free queue
read_reg(RFQLBWP, wr_ptr);
read_reg(RFQLBRP, rd_ptr);
if (rd_ptr < wr_ptr)
else
// If room in Rx free queue then put 1 entry in the queue
// dword 0 = Rx data buffer address (use Rx data buffer starting at Rx buffer area base address)
// dword 1 = corresponding Rx descriptor index (use Rx descriptor table index 0)
if (cnt < 0)
rx_dscr_idx = 0;
wr_dword(rfq_base_addr + wr_ptr * 8, rx_buf_base_addr);
wr_dword(rfq_base_addr + wr_ptr * 8 + 4, rx_dscr_idx);
// Advance the Rx free queue large buffer write pointer by 1
if (wr_ptr = rfq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(RFQLBWP, wr_ptr);
}
使能DS31256 Tx和Rx DMA
// Enable Tx and Rx DMA in the DS31256 master configuration register
// Set bit 0 = 1 to enable Receive DMA
// Set bits 2-1 = 00 to burst length maximum is 32 dwords
// Set bit 3 = 1 to enable Transmit DMA
// Set bits 6 = 1 for HDLC packet data on PCI bus is big endian
// Set bits 11-7 = 00000 to select Port 0 has the dedicated resources of the BERT
write_reg(MC, 0x0049);
使能HDLC通道Tx和Rx
// Read the current channel value from the Rx DMA Configuration RAM
// Set RDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set RDMACIS bits 10-8 = 100 to read lower word of dword 2
// Set RDMACIS bit 14 = 1 to read from RAM
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x4400 + channel);
read_reg(RDMAC, data);
// Enable channel Rx DMA
// Update RAM with new value
// Set RDMAC bit 0 = 1 to enable the HDLC channel
// Set RDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set RDMACIS bits 10-8 = 100 to read lower word of dword 2
// Set RDMACIS bit 14 = 1 to read from RAM
write_reg(RDMAC, data | 0x0001);
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x0400 + channel);
// Read the current channel value from the Tx DMA Configuration RAM
// Set TDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set TDMACIS bits 11-8 = 0010 to read lower word of dword 1
// Set TDMACIS bit 14 = 1 to read from RAM
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x4200 + channel);
read_reg(TDMAC, data);
// Enable channel Tx DMA
// Update RAM with new value
// Set TDMAC bit 0 = 1 to enable the HDLC channel
// Set TDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set TDMACIS bits 11-8 = 0010 to read lower word of dword 1
// Set TDMACIS bit 14 = 0 to write to RAM
write_reg((TDMAC, data | 0x0001);
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x0200, + channel);
使能1层的端口数据传输
// Tx port control register
// Set Bit 3 TFDA1 = 1 to allow data to be transmitted normally
read_reg(TP[0]CR + 4 * port, data);
write_reg(TP[0]CR + 4 * port, data | 0x0008);
使HDLC通道进入环回模式完成通道配置后,使能它需要大约5个帧周期,即625µs,使DS31256内部逻辑完成向新配置的转换。转换完成后,HDLC通道可以进入环回模式,这样,通道上传送的所有数据也会在该通道上接收到。在5个帧等待周期之前使HDLC通道进入环回模式会导致无用数据写入通道的Rx FIFO。
// Wait for at least 5 frame periods for the internal DS31256 initialization to complete
frame_wait(5);
// Set Bit 10 = 1 to enable loopback - routes transmit data back to the receive port
read_reg(RP[0]CR + 4 * port, data);
write_reg(RP[0]CR + 4 * port, data | 0x0400);
排列、发送、接收、检查数据包完成DS31256初始化之后,可以开始发送和接收数据。由于DS31256处于环回模式,HDLC通道传送的所有数据也会在该通道上接收到。本节将讨论构建主机存储器中数据包的过程,以及数据的发送、接收和结果检查。下面几节详细介绍这一过程。 构建主机存储器中的数据包这一个例子将发送一个16字节数据包。在数据包发送之前,必须在主机存储器中构建它。此外,也必须在主机存储器中构建对应的Tx数据包描述符。下面的代码详细介绍了这些任务。
// Create a 16-byte data packet in memory in a Tx buffer whose start address is the Tx buffer area base
// address
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr, 0x01234567);
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr + 4, 0x89ABCDEF);
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr + 8, 0x02468ACE);
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr + 12, 0x13579BDF);
// Create a Tx descriptor (4 dwords) for the packet at Tx descriptor
// Tx descriptor table index 0
// dword0 = Tx buffer address
// dword1 = EOF, CV, byte count, next descriptor pointer
// dowrd2 = HDLC channel
// dword3 = PV, next pending descriptor pointer (set to 0)
tx_dscr_idx = 0;
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16, tx_buf_base_addr);
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16 + 4, 0x80100000);
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16 + 8, 0x00000000 + channel);
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16 + 12, 0x00000000); 数据包发送和接收为完成数据包发送,Tx描述符必须放在发送未决队列中,然后,必须递增发送未决队列写指针(TPQWP)。当DS31256探测到未决队列不空(TPQWP不等于TPQRP)时,它将开始处理队列输入,并发送数据包。
// Read SDMA register to clear any previously set status bits
read_reg(SDMA, data);
// check free space in Tx pending queue
read_reg(TPQWP, wr_ptr);
read_reg(TPQRP, rd_ptr)
if (rd_ptr < wr_ptr)
else
// If room in the Tx pending queue create an entry for the packet
if (cnt < 0)
{
wr_dword(tpq_base_addr + wr_ptr * 4, 0x0000000 + (channel << 16));
// Advance the Tx pending queue write pointer
if (wr_ptr = tpq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(TPQWP, wr_ptr);
} 检查结果等待足够的时间周期以完成数据包发送和接收后,可以进行几项检查,确定数据包发送和接收是否成功。以下代码详细说明了这几项检查。
// wait 2 frame periods for packet to be transmitted/received
frame_wait(2);
// Check SDMA register
// Expected value = 0x6440, if not, it means there was error
read_reg(SDMA, data);
// Check to see how many entries are in the Tx done queue (distance from TDQRP to TDQWP)
// Expected value is 1 - one entry in the Tx done queue corresponding to the packet that was sent
read_reg(TDQRP, rd_ptr);
read_reg(TDQWP, wr_ptr);
if (wr_ptr >= rd_ptr)
else
// Check Tx done queue descriptor
// Expected value = 0x0003000
// Bits 15-0 indicates the descriptor pointer
// Bits 23-16 indicate the channel number, it should be 3 in this example
// Bits 28-26 indicate the packet status, all 0 means the packet transmission is complete and the
// descriptor pointer field corresponds to the first descriptor in the HDLC packet that has been
// transmitted
rd_dword(tdq_base_addr + rd_ptr*4, tdq_entry);
// Advance the Tx done queue read pointer
if (wr_ptr = tdq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(TDQRP, wr_ptr);
// Check the Rx large free queue to see how many Rx buffers are in the queue (distance from
// RFQLBRP to RFQLBWP)
// Expected number is 0 since the queue had 1 buffer before the packet was received and packet
// reception required 1 buffer
read_reg(RFQLBRP, rd_ptr);
read_reg(RFQLBWP, wr_ptr);
if (wr_ptr >= rd_ptr)
else
// Check Rx done queue to see if any packets were received (distance from RDQRP to RDQWP)
// Expected value is 1 - one entry in the Rx done queue entry corresponding to the one packet that
// should have been received
read_reg(RDQRP, rd_ptr);
read_reg(RDQWP, wr_ptr);
if (wr_ptr >= rd_ptr)
else
// Check the Rx done queue descriptor
// Expected value = 0x40030000,
// Bits 15-0 indicates the descriptor pointer
// Bits 23-16 indicate the channel number, it should be 3 in this example
// Bits 26-24 indicate the buffer count, all 0 means that a complete packet has been received
rd_dword(rdq_base_addr + 8 * rd_ptr, rdq_entry);
// Check the corresponding Rx descriptor (4 dwords)
// dword 0 expected value = 0x10001000 the Rx buffer address
// dword 1 expected value = 0x80140000
// Bits 15-0 is the next descriptor pointer
// Bits 28-16 is the number of bytes stored in the data buffer
// Bits 31-29 indicates buffer status
// dword 2 excepted value = 0x000B7503
// Bits 7-0 indicates HDLC channel number (should match TDQ entry channel)
// Bits 31-8 indicates the timestamp (can vary)
rdscr_idx = rdq_entry & 0x0000FFFF;
rd_dword(rdscr_base_addr + 16 * rdscr_idx, rdscr_dword0);
rd_dword(rdscr_base_addr + 16 * rdscr_idx + 4, rdscr_dword1);
rd_dword(rdscr_base_addr + 16 * rdscr_idx + 8, rdscr_dword2);
// Check the data in the Rx buffer
// 16 bytes of data + 4-byte CRC
// Expected values = 0x01234567
// 0x02468ACE
// 0x13579BDF
// 0x05127B09 (4-byte CRC)
byte_count = (rdscr_dword1 >> 16) & 0x00001FFF;
for (addr = rdscr_dword0, addr < rdscr_dword0 + byte_count; addr = addr + 4)
// Advance the Rx done queue read pointer
if (rd_ptr = rdq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(RDQRP, rd_ptr); 结论本应用笔记介绍了怎样配置桥接模式下DS31256的T1端口。代码实例解释了怎样对DS31256编程(配置),详细说明(按步骤说明)了数据包发送/接收。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)