
步进电机是将电脉冲信号转变为角位移或线位移的开环控制电机,是现代数字程序控制系统中的主要执行元件,应用极为广泛。。在非超载的情况下,电机的转速、停止的位置只取决于脉冲信号的频率和脉冲数,而不受负载变化的影响,当步进驱动器接收到一个脉冲信号,它就驱动步进电机按设定的方向转动一个固定的角度,称为“步距角”,它的旋转是以固定的角度一步一步运行的。可以通过控制脉冲个数来控制角位移量,从而达到准确定位的目的;同时可以通过控制脉冲频率来控制电机转动的速度和加速度,从而达到调速的目的。
步进电机是一种感应电机,它的工作原理是利用电子电路,将直流电变成分时供电的,多相时序控制电流,用这种电流为步进电机供电,步进电机才能正常工作,驱动器就是为步进电机分时供电的,多相时序控制器。
步进电机S型曲线加减速算法与实现
S型曲线的的方程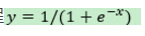 ,在[-5,5]的图形如下图所示:
,在[-5,5]的图形如下图所示:
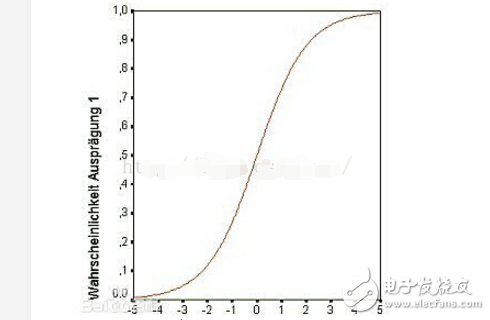
如要将此曲线应用在步进电机的加、减速过程中,需要将方程在XY坐标系进行平移,同时对曲线进行拉升变化:
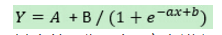
其中的A分量在y方向进行平移,B分量在y方向进行拉伸,ax+b分量在x方向进行平移和拉伸。
项目中加速过程:从5600Hz加速到64000Hz,采用4细分。输出比较模块所用的定时器驱动频率为10M,采用1000个点进行加速处理。最终根据项目的需要,在加速过程中采用的曲线方程为:
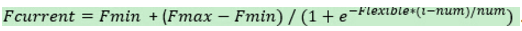 。
。
其中的Fcurrent为length(1000)个点中的单个频率值。Fmin起始频率为5600; Fmax为最大频率64000; -flexible*(i - num)/num是对S型曲线进行拉伸变化,其中flexible代表S曲线区间(越大代表压缩的最厉害,中间(x坐标0点周围)加速度越大;越小越接近匀加速。理想的S曲线的取值为4-6),i是在循环计算过程中的索引,从0开始,num为 length/2 大小(这样可以使得S曲线对称)。在项目中i的区间[0,1000), num=1000/2=500。这些参数均可以修改。提供的计算接口如下。
对应的计算接口code:
/* calculate the Period and Freq array value, fill the Period value into the Period register during the TImer interrupt.
*calculate the acceleraTIon procedure , a totally 1000 elements array.
* parameter fre[]: point to the array that keeps the freq value.
* period[]: point to the array that keeps the TImer period value.
* len: the procedure of acceleraTIon length.it is best thing to set the float number, some compile software maybe transfer error if set it as a int
* fre_max: maximum speed, frequency vale.
* fre_min: start minimum speed, frequency vale. mind : 10000000/65535 = 152, so fre_min can‘t less than 152.
* flexible: flexible value. adjust the S curves
*/
void CalculateSModelLine(float fre[], unsigned short period[], float len, float fre_max, float fre_min, float flexible)
{
int i=0;
float deno ;
float melo ;
float delt = fre_max-fre_min;
for(; i《len; i++)
{
melo = flexible * (i-len/2) / (len/2);
deno = 1.0 / (1 + expf(-melo)); //expf is a library function of exponential(e)
fre[i] = delt * deno + fre_min;
period[i] = (unsigned short)(10000000.0 / fre[i]); // 10000000 is the timer driver frequency
}
return ;
}
// start move motor
void StartPWM()
{
DriverMotorFlag = TRUE;
Index = 0;
MOTOR_EN_DISABLE = ENABLE;
OpenOC4(OC_ON | OC_TIMER_MODE16 | OC_TIMER3_SRC | OC_PWM_FAULT_PIN_DISABLE, 0, 0);
// map rc13 to oc4 output
RPC13R = 11;
// 50 percent duty
OC4RS = OC_PERIOD_MIN / 2;
OpenTimer3(T3_ON | T3_PS_1_8, OC_PERIOD_MIN);
INTSetVectorPriority(INT_TIMER_3_VECTOR, INT_PRIORITY_LEVEL_6);
INTSetVectorSubPriority(INT_TIMER_3_VECTOR, INT_SUB_PRIORITY_LEVEL_1);
EnableIntT3;
}
//stop motor, hereis no deceleration
void StopPWM()
{
DriverMotorFlag = FALSE;
Index = 0;
MOTOR_EN_DISABLE = DISENABLE;
OpenOC4(OC_OFF | OC_TIMER_MODE16 | OC_TIMER3_SRC | OC_PWM_FAULT_PIN_DISABLE, 0, 0);
// map rc13 to oc4 output
RPC13R = 0;
PORTCbits.RC13 = 0;
CloseTimer3();
DisableIntT3;
}
//change the timer Period value in the correspond timer rather than the other place, Or the motor will be stalled occasionally.
// 刚开始我在另外的一个定时器中断中每隔1ms改变 应用在OC模块的timer3 的Period值,结构偶发的造成电机在加速过程中堵转。其实应该是在timer3的中断中修改。
static unsigned short CountForAcc = 0;
void __ISR(_TIMER_3_VECTOR, ipl6) Timer3OutHandler(void)
{
// clear the interrupt flag, or the interrupt will not occur again.
mT3ClearIntFlag();
if(CountForAc++++ 》 2) // here can adjust the totally time of acceleration
{
CountForAcc = 0;
//if(DriverMotorFlag == TRUE && PR3 》 OC_PERIOD_MAX + SPEED_STEP)
if(DriverMotorFlag == TRUE && Index 《 ACC_TIMES)
{
PR3 = Period[Index++];
OC4RS = PR3 / 2;
}
}
}
通过CalculateSModelLine接口得到如下不同的几条加速曲线:
黄色:CalculateSModelLine(Freq, Period, 1000, 56000, 16000, 4);
橙色:CalculateSModelLine(Freq, Period, 1000, 64000, 500, 8);
蓝色:CalculateSModelLine(Freq, Period, 1000, 64000, 500, 15);
灰色:CalculateSModelLine(Freq, Period, 1000, 40000, 500, 5);
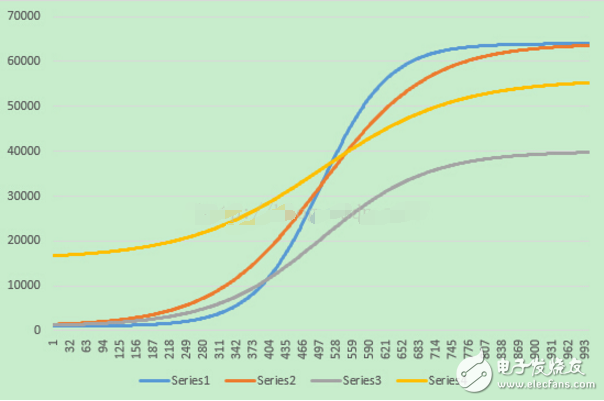
最后可以估算加速过程的时间和角位移,以橙色曲线为例:CalculateSModelLine(Freq, Period, 1000, 64000, 500, 8)为例(假设在中断中没有 if(CountForAcc++ 》 2) 条件限制):
时间:Period第一个点的值为10000000/500 = 20000,最后也点的值 10000000/64000=156,平均值为10000左右,timer中断的平均时间Tn=10000/10000000=1ms, 1000个点,总时间为1s,当然,起始频率大加速时间就越短,比如Fmin=16000Hz,Fmax=64000,则40ms左右即可完成加速过程。
角位移:1.8(单步) * 1000(步数) / 4(细分)= 450°
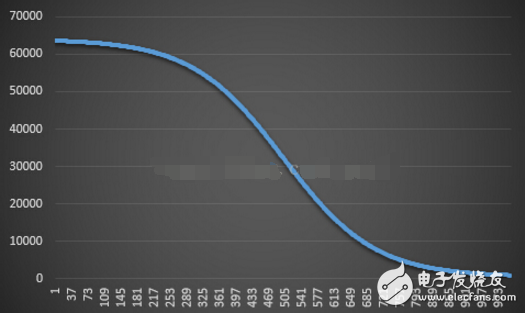
上述为加速过程,减速同样的道理,只要将方程改为:
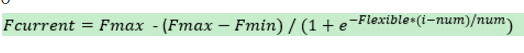
可以得到减速曲线如下所示:
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)