
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is often found to be the root cause of equipment failure on the factory floor and in the field. Such failures can be difficult to track down when they masquerade as other types of failures, as they often do. In manufacturing, for instance, the yield loss at final test might be traced to a bad component or subassembly and then (with further investigation) associated with an OEM manufacturing or test process that subjects the part to ESD.
Early field failures and post-installation problems in industrial equipment are often caused by ESD during installation. The most insidious ESD damage is that which degrades the performance of an instrument but (at least initially) does not affect its operation in an obvious way. Such events can cause erratic or nonlinear operation immediately but may not produce a "hard" failure for months or years.
This article explains how to protect your products from ESD. It outlines the standard test methods required by the electronics industry, offers some common techniques to protect against ESD, and highlights some of Maxim's patented ESD-protected devices. With careful design, these devices can improve product quality while saving money and your company's reputation.
Damage Potential A photomicrograph (Figure 1) shows the damage sustained by a competitor's RS-232 interface IC after exposure to an ESD strike of 15kV (a common test level). The result is a gross failure that is easily visible, because the overstress actually vaporized metalization on the chip. In other cases, the investigation of invisible failures in the gate-oxide layers or buried layers requires careful removal of metalization or other layers. ESD strikes can also find paths into the core of an instrument. Somewhat like a lightning strike, ESD will course through the circuit until its energy is dissipated, often with unexpected effects.
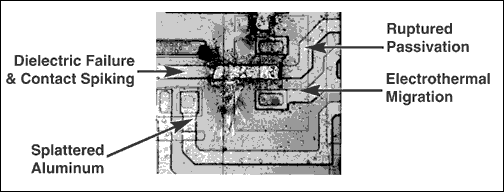
Figure 1. This photomicrograph shows gross ESD damage to an unprotected RS-232 receiver.
Where Does High Voltage Come From? Mechanically separating two materials creates electrostatic charge. The surfaces of these otherwise neutral materials are electrically double-layered to varying degrees, meaning that the outer layer might have a majority of electrons balanced by positive charge in the bulk of the material. Other materials exhibit the opposite surface charge. When materials with opposite surface charges come in contact, a transfer of electrons leaves one material with a net negative charge and the other with a net positive charge. Called triboelectric generation, this effect is the basis of static generation and transfer.
The triboelectric series shown in Table 1 positions materials like glass and nylon at the positive end and silicon and teflon at the negative end. The materials' conductivity also affects their ability to build up a surface charge. For many materials, the conductivity or surface resisitivity is strongly dependent on humidity. Low humidity promotes low conductivity, which maintains the localized charges by preventing them from moving.
Table 1. Triboelectric Series
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出
赞
(0)
打赏
 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
Tech Tips: Getting the Most fr
上一篇
2022-08-05
+12V Input Converter Generates
下一篇
2022-08-05

评论列表(0条)