因为DS1302的接口简单、价格低廉、使用方便,也随着流行的串行时钟电路增多大家对它的兴趣增加不少。DS1302主要就是对年、月、日、周、时、分、秒进行计时,具有闰年补偿等功能,但是有很多人对于如何使用DS1302转换12/24小时还不是很了解,这边文章就是把DS1302的12/24小时制转换程序告诉大家的。
我们来看DS1302的datasheet中关于小时的部分:首先确定地址:读取小时的地址为85H,写入时的地址为84H。
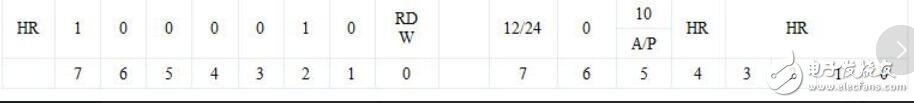
AM-PM/12-24模式选择:小时寄存器的bit7是AM-PM/12-24模式选择选择位,这一位为“1”时,选择了12小时制。因此,这样实现12小时制:Write_DS1302(0x84,80)。小时寄存器的bit5为“1”时,为上午。这样实现12小时制的上午:Write_DS1302(0x84,90)
写入时间后,我们就可以读取了:temp=Read_DS1302(0x83)关键就在于显示,与12小时有关的是bit0—bit4,因此,读到的值需去掉无关的位,可以这样:

左移三位,再右移三位后,temp中就是真正的12小时的16进制码了。下面附完整原代码,将其保存为DS1302.h,然后在main中调用就行。
DS1302的12/24小时制转换程序
系统时钟:89C52 12M时钟频率
#ifndef _DS1302_h
#define _DS1302_h
sbit DS1302_scl=P3^6;
sbit io=P3^4;
sbit rst=P3^5;
unsigned char Read_DS1302(unsigned char Addr) //读取DS1302
{
unsigned char i,Value;
rst=0;
DS1302_scl=0;
rst=1;
for(i=0;i《8;i++)
{
DS1302_scl=0;
io=Addr & 0x01;
DS1302_scl=1;
Addr》》=1;
}
for(i=0;i《8;i++)
{
Value》》=1;
DS1302_scl=0;
if(io) Value|=0x80;
DS1302_scl=1;
}
rst=0;
return Value;
}
void Write_DS1302(unsigned char Addr,unsigned char Value) //写入DS1302
{
unsigned char i;
rst=0;
DS1302_scl=0;
rst=1;
for(i=0;i《8;i++)
{
DS1302_scl=0;
io=Addr & 0x01;
DS1302_scl=1;
Addr》》=1;
}
for(i=0;i《8;i++)
{
DS1302_scl=0;
io=Value & 0x01;
DS1302_scl=1;
Value》》=1;
}
rst=0;
}
void Set_MIN(unsigned char s) //1为分钟加,0为分钟减
{
unsigned char temp;
Write_DS1302(0x8E,0x00);//去除写保护
temp=Read_DS1302(0x83);
if(s)
{
temp+=1;
if(temp》0x59)
temp=0;
if(temp%0x10》0x09)
temp=((temp+0x10) & 0xf0);
}
else
{
if(temp》0)
temp-=1;
else
temp=0x59;
if((temp%0x10)》0x09)
temp=((temp/0x10)*0x10 + 0x09);
}
Write_DS1302(0x82,temp);
Write_DS1302(0x80,0x00);
}
void Set_HR(unsigned char s) //1为小时加,0为小时减
{
unsigned char temp;
Write_DS1302(0x8E,0x00);//去除写保护
temp=Read_DS1302(0x85);//小时数保存在低5位
temp《《=3;
temp》》=3;
if(s)
{
temp+=1;
if(temp==0x0a)
temp=0x10;
if(temp》0x12)
temp=0;
}
else
{
if(temp==0)
temp=0x12;
temp-=1;
if(temp==0x0f)
temp=0x09;
}
temp=temp | 0x80;
Write_DS1302(0x84,temp);
}
#endif
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)