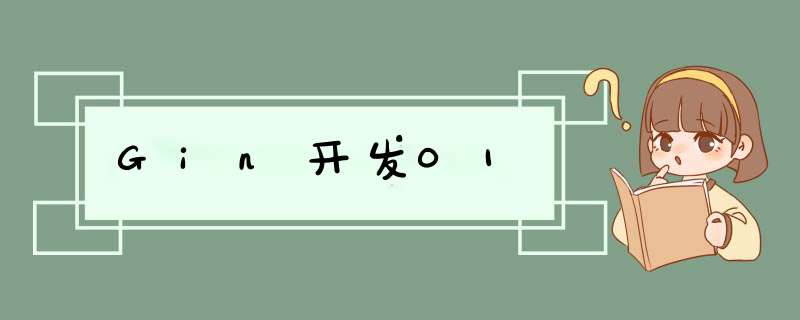
首先配置好go环境,设置好GOPATH环境变量。我的为例,输入go env,输出如下:
C:\Users\Xin>go envset GOARCH=386set GOBIN=C:\go\bin // 必须设置set GOEXE=.exeset GOHOSTARCH=386set GOHOSTOS=windowsset GOOS=windowsset GOPATH=D:\go // 必须设置set GORACE=set GOROOT=C:\go // 必须设置set GOTOolDIR=C:\go\pkg\tool\windows_386set GCCGO=gccgoset GO386=set CC=gccset GOGCCFLAGS=-m32 -mthreads -fmessage-length=0set CXX=g++set CGO_ENABLED=1set PKG_CONfig=pkg-configset CGO_CFLAGS=-g -O2set CGO_CPPFLAGS=set CGO_CXXFLAGS=-g -O2set CGO_FFLAGS=-g -O2set CGO_LDFLAGS=-g -O2
然后,使用go下载gin库,go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin,一般使用需要的依赖:
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"import "net/http"2 Demo和学习记录 2.1 最简单的Demo
首先官方最简单的一个Demo:
// 文件名为 t1.gopackage mainimport "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"func main() { r := gin.Default() r.GET("/Ping",func(c *gin.Context) { c.JsON(200,gin.H{ "message": "pong",}) }) r.Run() // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080}在
%GOPATH%\src文件夹中创建一个自己的项目文件夹,比如 Demo1,然后新建一个go文件,如t1.go。将上述代码复制进入,保存。 新建CMD窗口,进入Demo1所在文件夹,然后输入go run t1.go将我们的代码运行起来。 在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/Ping,浏览器如果有回复,则说明我们代码成功! 2.2 路由与参数获取 路由的几种方式:
- 绝对匹配。对/xxx的GET/POST/DELETE/head…请求的路由。
router.GET("/someGet",getting) router.POST("/somePost",posting) router.PUT("/somePut",putting) router.DELETE("/someDelete",deleting) router.PATCH("/somePatch",patching) router.head("/somehead",head) router.OPTIONS("/someOptions",options) route.Any("/testing",startPage)
/user/:name 对二级名称关联name变量。 /user/:name/*action与上一个的区别是*部分可以有,也可以没有,即可匹配/user/:name/url。 现代化路由形式:
分组的路由:
func main() { router := gin.Default() // Simple group: v1 v1 := router.Group("/v1") { v1.POST("/login",loginEndpoint) v1.POST("/submit",submitEndpoint) v1.POST("/read",readEndpoint) } // Simple group: v2 v2 := router.Group("/v2") { v2.POST("/login",loginEndpoint) v2.POST("/submit",submitEndpoint) v2.POST("/read",readEndpoint) } router.Run(":8080")}
参数获取:
GET请求的参数获取:
func main() { router := gin.Default() // url matching: /welcome?firstname=Jane&lastname=Doe router.GET("/welcome",func(c *gin.Context) { firstname := c.Defaultquery("firstname","Guest") // 带有默认返回值的获取方式 lastname := c.query("lastname") // shortcut for c.Request.URL.query().Get("lastname"),可能为nil c.String(http.StatusOK,"Hello %s %s",firstname,lastname) }) router.Run(":8080")}
Multipart/UrlEncode表单:
func main() { router := gin.Default() router.POST("/form_post",func(c *gin.Context) { message := c.PostForm("message") nick := c.DefaultPostForm("nick","anonymous") c.JsON(200,gin.H{ "status": "posted","message": message,"nick": nick,}) }) router.Run(":8080")}
当两种方式都存在时,可以混合使用。
文件上传:
单个文件:
func main() { router := gin.Default() router.POST("/upload",func(c *gin.Context) { // single file file,_ := c.Formfile("file") log.Println(file.filename) // Upload the file to specific dst. // c.SaveUploadedfile(file,dst) c.String(http.StatusOK,fmt.Sprintf("'%s' uploaded!",file.filename)) }) router.Run(":8080")}
多个文件:
func main() { router := gin.Default() router.POST("/upload",func(c *gin.Context) { // Multipart form form,_ := c.MultipartForm() files := form.file["upload[]"] for _,file := range files { log.Println(file.filename) // Upload the file to specific dst. // c.SaveUploadedfile(file,dst) } c.String(http.StatusOK,fmt.Sprintf("%d files uploaded!",len(files))) }) router.Run(":8080")}2.3 中间件
在上面的代码中,我们创建gin的实例使用的是r := gin.Default()里面开启了很多默认的中间件。如果你想使用一个干净的,没有任何中间件的gin实例,可以使用r := gin.New()。
func main() { // Creates a router without any mIDdleware by default r := gin.New() // Global mIDdleware r.Use(gin.Logger()) r.Use(gin.Recovery()) // Per route mIDdleware,you can add as many as you desire. r.GET("/benchmark",MyBenchLogger(),benchEndpoint) // Authorization group // authorized := r.Group("/",Authrequired()) // exactly the same as: authorized := r.Group("/") // per group mIDdleware! in this case we use the custom created // Authrequired() mIDdleware just in the "authorized" group. authorized.Use(Authrequired()) { authorized.POST("/login",loginEndpoint) authorized.POST("/submit",submitEndpoint) authorized.POST("/read",readEndpoint) // nested group testing := authorized.Group("testing") testing.GET("/analytics",analyticsEndpoint) } // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 r.Run(":8080")}2.4 数据绑定与验证
Gin支持绑定的数据格式为Json,XML,Url Param(foo=bar&boo=baz)。数据验证使用的是go-playground/valIDator.v8。
// Binding from JsONtype Login struct { User string `form:"user" Json:"user" binding:"required"` Password string `form:"password" Json:"password" binding:"required"`}func main() { router := gin.Default() // Example for binding JsON ({"user": "manu","password": "123"}) router.POST("/loginjsON",func(c *gin.Context) { var Json Login if c.BindJsON(&Json) == nil { if Json.User == "manu" && Json.Password == "123" { c.JsON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{"status": "you are logged in"}) } else { c.JsON(http.StatusUnauthorized,gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"}) } } }) // Example for binding a HTML form (user=manu&password=123) router.POST("/loginForm",func(c *gin.Context) { var form Login // This will infer what binder to use depending on the content-type header. if c.Bind(&form) == nil { if form.User == "manu" && form.Password == "123" { c.JsON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"}) } } }) // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 router.Run(":8080")}
如果只绑定URL的字段,可以使用如下:
if c.Bindquery(&person) == nil { log.Println("====== Only Bind By query String ======") log.Println(person.name) log.Println(person.Address)}
如果POST和URL数据都需要:
// If `GET`,only `Form` binding engine (`query`) used.// If `POST`,first checks the `content-type` for `JsON` or `XML`,then uses `Form` (`form-data`).// See more at https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/master/binding/binding.go#L48if c.Bind(&person) == nil { log.Println(person.name) log.Println(person.Address)}
绑定HTML中的checkBoxes:
// HTML部分 <form action="/" method="POST"> <p>Check some colors</p> <label for="red">Red</label> <input type="checkBox" name="colors[]" value="red" ID="red" /> <label for="green">Green</label> <input type="checkBox" name="colors[]" value="green" ID="green" /> <label for="blue">Blue</label> <input type="checkBox" name="colors[]" value="blue" ID="blue" /> <input type="submit" /></form>// go语言部分 type myForm struct { colors []string `form:"colors[]"`}...func formHandler(c *gin.Context) { var fakeForm myForm c.Bind(&fakeForm) c.JsON(200,gin.H{"color": fakeForm.colors})}
Multipart/Urlencoded的绑定:
type LoginForm struct { User string `form:"user" binding:"required"` Password string `form:"password" binding:"required"`}func main() { router := gin.Default() router.POST("/login",func(c *gin.Context) { // you can bind multipart form with explicit binding declaration: // c.MustBinDWith(&form,binding.Form) // or you can simply use autobinding with Bind method: var form LoginForm // in this case proper binding will be automatically selected if c.Bind(&form) == nil { if form.User == "user" && form.Password == "password" { c.JsON(200,gin.H{"status": "you are logged in"}) } else { c.JsON(401,gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"}) } } }) router.Run(":8080")}2.5 数据渲染
XML/JsON/YAML类型数据:
func main() { r := gin.Default() // gin.H is a shortcut for map[string]interface{} r.GET("/someJsON",func(c *gin.Context) { c.JsON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{"message": "hey","status": http.StatusOK}) }) r.GET("/moreJsON",func(c *gin.Context) { // You also can use a struct var msg struct { name string `Json:"user"` Message string Number int } msg.name = "Lena" msg.Message = "hey" msg.Number = 123 // Note that msg.name becomes "user" in the JsON // Will output : {"user": "Lena","Message": "hey","Number": 123} c.JsON(http.StatusOK,msg) }) r.GET("/someXML",func(c *gin.Context) { c.XML(http.StatusOK,"status": http.StatusOK}) }) r.GET("/someYAML",func(c *gin.Context) { c.YAML(http.StatusOK,"status": http.StatusOK}) }) // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 r.Run(":8080")}
SecureJsON:(原始JsON加前缀)
func main() { r := gin.Default() // You can also use your own secure Json prefix r.SecureJsonPrefix("myTitle") // 默认是while(1); r.GET("/someJsON",func(c *gin.Context) { names := []string{"lena","austin","foo"} // Will output : while(1);["lena","austin","foo"] c.SecureJsON(http.StatusOK,names) }) // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 r.Run(":8080")}
静态文件渲染:
func main() { router := gin.Default() router.Static("/assets","./assets") router.StaticFS("/more_static",http.Dir("my_file_system")) router.Staticfile("/favicon.ico","./resources/favicon.ico") // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 router.Run(":8080")}
HTML页面渲染:
func main() { router := gin.Default() router.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*") //router.LoadHTMLfiles("templates/template1.HTML","templates/template2.HTML") router.GET("/index",func(c *gin.Context) { c.HTML(http.StatusOK,"index.tmpl",gin.H{ "Title": "Main website",}) }) router.Run(":8080")}2.6 自定义
自定义模版渲染:
import "HTML/template"func main() { router := gin.Default() HTML := template.Must(template.Parsefiles("file1","file2")) router.SetHTMLTemplate(HTML) router.Run(":8080")}
自定义分隔符:
r := gin.Default()r.Delims("{[{","}]}")r.LoadHTMLGlob("/path/to/templates"))
自定义模版函数:
func formatAsDate(t time.Time) string { year,month,day := t.Date() return fmt.Sprintf("%d%02d/%02d",year,day)}func main() { router := gin.Default() router.Delims("{[{","}]}") router.SetFuncMap(template.FuncMap{ "formatAsDate": formatAsDate,}) router.LoadHTMLfiles("./fixtures/basic/raw.tmpl") router.GET("/raw","raw.tmpl",map[string]interface{}{ "Now": time.Date(2017, 07, 01, 0,time.UTC),}) }) router.Run(":8080")}// taw.tmplDate: {[{.Now | formatAsDate}]}
重定向:
r.GET("/test",func(c *gin.Context) { c.Redirect(http.StatusMovedPermanently,"http://www.Google.com/")})2.7 自定义中间件
func Logger() gin.HandlerFunc { return func(c *gin.Context) { t := time.Now() // Set example variable c.Set("example","12345") // before request c.Next() // after request latency := time.Since(t) log.Print(latency) // access the status we are sending status := c.Writer.Status() log.Println(status) }}func main() { r := gin.New() r.Use(Logger()) r.GET("/test",func(c *gin.Context) { example := c.MustGet("example").(string) // it would print: "12345" log.Println(example) }) // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 r.Run(":8080")}
在定制中间件时,不要直接使用原始context,而要使用一个read-only的copy。
授权验证中间件:
// simulate some private datavar secrets = gin.H{ "foo": gin.H{"email": "foo@bar.com","phone": "123433"},"austin": gin.H{"email": "austin@example.com","phone": "666"},"lena": gin.H{"email": "lena@guapa.com","phone": "523443"},}func main() { r := gin.Default() // Group using gin.BasicAuth() mIDdleware // gin.Accounts is a shortcut for map[string]string authorized := r.Group("/admin",gin.BasicAuth(gin.Accounts{ "foo": "bar","austin": "1234","lena": "hello2","manu": "4321",})) // /admin/secrets endpoint // hit "localhost:8080/admin/secrets authorized.GET("/secrets",func(c *gin.Context) { // get user,it was set by the BasicAuth mIDdleware user := c.MustGet(gin.AuthUserKey).(string) if secret,ok := secrets[user]; ok { c.JsON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{"user": user,"secret": secret}) } else { c.JsON(http.StatusOK,"secret": "NO SECRET :("}) } }) // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 r.Run(":8080")}2.8 定制http服务
func main() { router := gin.Default() s := &http.Server{ Addr: ":8080",Handler: router,ReadTimeout: 10 * time.Second,WriteTimeout: 10 * time.Second,MaxheaderBytes: 1 << 20,} s.ListenAndServe()}2.10 支持加密httpS
最简单的方式:
package mainimport ( "log" "github.com/gin-gonic/autotls" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() { r := gin.Default() // Ping handler r.GET("/Ping",func(c *gin.Context) { c.String(200,"pong") }) log.Fatal(autotls.Run(r,"example1.com","example2.com"))}
自己管理证书的方式:
package mainimport ( "log" "github.com/gin-gonic/autotls" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "golang.org/x/crypto/acme/autocert")func main() { r := gin.Default() // Ping handler r.GET("/Ping","pong") }) m := autocert.Manager{ Prompt: autocert.AcceptTOS,HostPolicy: autocert.HostWhiteList("example1.com","example2.com"),Cache: autocert.DirCache("/var/www/.cache"),} log.Fatal(autotls.RunWithManager(r,&m))}2.11 优雅地关闭服务
// +build go1.8package mainimport ( "context" "log" "net/http" "os" "os/signal" "time" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() { router := gin.Default() router.GET("/",func(c *gin.Context) { time.Sleep(5 * time.Second) c.String(http.StatusOK,"Welcome Gin Server") }) srv := &http.Server{ Addr: ":8080",Handler: router,} go func() { // service connections if err := srv.ListenAndServe(); err != nil { log.Printf("Listen: %s\n",err) } }() // Wait for interrupt signal to gracefully shutdown the server with // a timeout of 5 seconds. quit := make(chan os.Signal) signal.Notify(quit,os.Interrupt) <-quit log.Println("Shutdown Server ...") ctx,cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second) defer cancel() if err := srv.Shutdown(ctx); err != nil { log.Fatal("Server Shutdown:",err) } log.Println("Server exist")}总结
以上是内存溢出为你收集整理的Gin开发01全部内容,希望文章能够帮你解决Gin开发01所遇到的程序开发问题。
如果觉得内存溢出网站内容还不错,欢迎将内存溢出网站推荐给程序员好友。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)