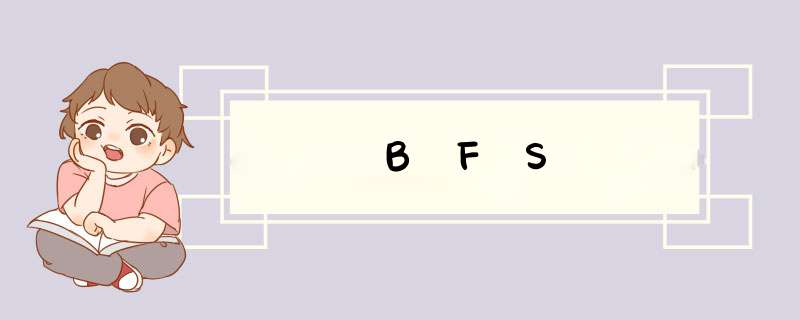
BFS(广度优先搜索算法),搜索过程是从起始点一层一层的访问周围点,没有涉及到代价函数,是一种盲目搜索,搜索周围点的顺序是人为确定的。
一般使用队列(先入先出)这种数据结构实现。
但我的代码中使用链表这个数据结构实现,链表也能完成先入先出的 *** 作。
我的代码中的主要算法过程:
- 创建
OPEN与CLOSED列表,代表已访问的点以未访问的点 - 添加初始节点到
OPEN中 - 判断
OPEN列表是否为空,为空则结束搜索,未找到路径,(循环1)- 取出
OPEN中最前面的点,记为cueent_node,将其从OPEN中删除,并添加到CLOSED中 - 获取
current_node周围点(子节点),并遍历(循环2)- 判断周围点是否在
CLOSED中,在其中则continue。 - 判断周围单是否在
OPEN中,在其中则continue。 - 到此步则说明该子节点是新节点,因此构建子节点与父节点之间关系,并直接将其添加到
OPEN中 - 判断该子节点是否为终点,为终点则直接返回。
- 判断周围点是否在
- 取出
- 返回带有父节点信息的终点。
- 从终点遍历到起点,保存每个点,最终形成路径集合。
地图类:
#ifndef MYMAP_H_
#define MYMAP_H_
#include #include "mymap.h"
namespace mymap {
// 构造函数,构建指定长宽的地图大小
MyMap::MyMap(const int map_xlength, const int map_ylength)
: map_xlength_(map_xlength), map_ylength_(map_ylength) {
map_.resize(map_ylength_);
for (auto &e : map_) {
e.resize(map_xlength_);
}
int x_scale = map_xlength_ / 5;
int y_scale = map_ylength_ /5;
SetObsLineX(0, map_xlength_ - 1, 0);
SetObsLineX(0, map_xlength_ - 1, map_ylength_ - 1);
SetObsLineY(0, map_ylength_ - 1, 0);
SetObsLineY(0, map_ylength_ - 1, map_xlength_ - 1);
SetObsLineX(x_scale, x_scale * 2, y_scale * 3);
SetObsLineX(x_scale * 3, x_scale * 4, y_scale * 2);
SetObsLineX(0, x_scale, y_scale * 2);
SetObsLineX(x_scale * 4, x_scale * 5, y_scale * 3);
SetObsLineY(0, y_scale * 3, x_scale * 2);
SetObsLineY(y_scale * 2, y_scale * 5, x_scale * 3);
}
void MyMap::SetObsLineX(const int x_begin, const int x_end, const int y) {
for (int i = x_begin; i <= x_end; ++i) {
map_[i][y] = unfree;
}
}
void MyMap::SetObsLineY(const int y_begin, const int y_end, const int x) {
for (int i = y_begin; i <= y_end; ++i) {
map_[x][i] = unfree;
}
}
bool MyMap::GetMapPointState(const int x, const int y) const {
return map_[x][y];
}
} // namespace mymap
**Bfs实现:**只要过程在Bfs::search函数中
#ifndef BFS_H_
#define BFS_H_
#include
#include #include "bfs.h"
#include #include 源代码中将整个过程显示成动画了,这里只是最后的结果,从CLOSED(黄色点)中可以看出,搜索是一层一层搜索的。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)