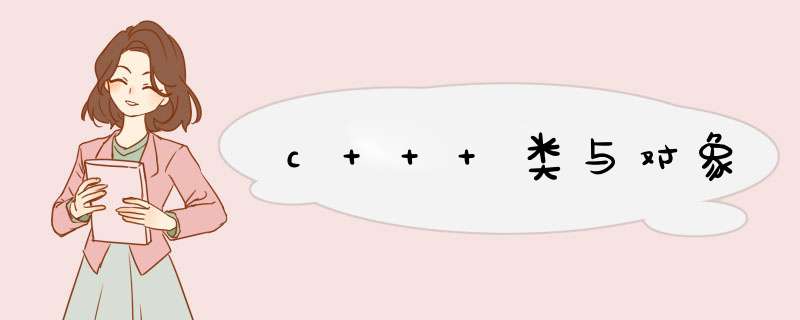
数据抽象:
int a; int b;行为抽象:
//功能抽象
show_perple(); set_number();- 将属性和行为作为一个整体
- 给属性和行为加入权限
类的格式:class 类名{ 权限:行为 属性};
//创建一个类
class person {
//设置权限
public:
//行为
int show_age();
string show_name();
//属性
int age;
string name;
};用类来计算面积:
using namespace std;
class person {
public:
double mianji()
{
return width*height;
}
double width;
double height;
};
int main()
{
//创建一个对象
person p;
//给属性赋值
p.width = 20;
p.height = 30;
cout << p.mianji() << endl;
}| public | 公共权限 |
| protected | 保护权限 |
| private | 私有权限 |
public:类内外都可以访问
protected:类内能访问,类外不能访问
private:类内能访问,类外不能访问
保护类型和私有类型的区别:在继承时继承情况不同
using namespace std;
//创建一个类
class person {
//公共权限
public:
//公共属性
int age;
void show_age() { cout << age << endl; }
void show_name() { cout << name << endl; }
void show_char() { cout << a << endl; }
//保护权限
protected:
string name="name";
//私有权限
private:
char a='b';
};
int main()
{
//创建一个对象
person p;
//可以直接访问公共权限的行为和属性
p.age = 10;
p.show_age();
//不可以直接访问保护和私有权限的行为和属性
//p.name="lllll"; 无法直接访问
//p.a='l'; 无法直接访问
//但可以通过公共行为来修改保护和私有属性
p.show_name();
p.show_char();
return 0;
}class 和struct的区别
| struct | 默认是public |
| class | 默认是private |
一般来所会将 属性设置为私有
- 方便控制读写权限
- 方便检测数据的有效性
1.直接在类中实现
class person {
public:
void show_name()
{
cout << name << endl;
}
int a=10;
string name="ppp";
};2.在类外实现
class person {
public:
//先在类中声明
void show_name();
int a=10;
string name="ppp";
};
//类外实现 因为该函数是在 person类中的
//所以要在函数名前添加 作用域 person::
void person::show_name()
{
cout << name << endl;
}关键词:inline
class person {
public:
inline void show_name()
{
cout << name << endl;
}
int a=10;
string name="ppp";
};欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)