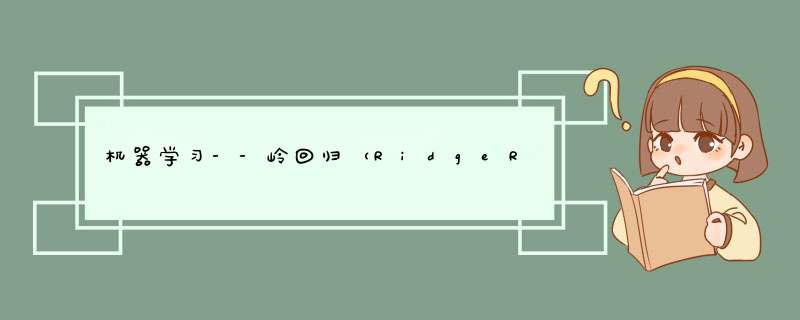
RidgeRegression 通过对系数的大小施加惩罚来解决普通最小二乘法的一些问题。岭系数最小化的是带罚项的残差平方和,优化目标为:
m
i
n
w
∥
w
T
x
−
y
∥
2
2
+
α
∥
w
∥
2
2
\mathop{min}\limits_{w}\Vert w^Tx-y\Vert_2^2+\alpha\Vert w\Vert_2^2
wmin∥wTx−y∥22+α∥w∥22
其中,
α
≥
0
\alpha \geq 0
α≥0 是控制系数收缩量的复杂性参数:
α
\alpha
α 的值越大,收缩量越大,模型对共线性的鲁棒性也更强。
# coding=utf-8
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
线性回归最小化目标是:
min_w ||Xw - y||_2^2 + alpha * ||w||_2^2
"""
all_data = datasets.load_diabetes()
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test =train_test_split(all_data.data, all_data.target, test_size=0.3)
model = Ridge()
x_train = x_train[:, 3].reshape(-1, 1)
x_test = x_test[:, 3].reshape(-1, 1)
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
prediction = model.predict(x_test)
print(f"w = {model.coef_}")
print(f"w_0 = {model.intercept_}")
print(f"default score = {model.score(x_test, y_test)}")
print(f"mean squared error = {mean_squared_error(y_test, prediction)}")
print(f"r2 score = {r2_score(y_test, prediction)}")
# Plot outputs
print(f"x_test.shape = {x_test.shape}, y_test.shape = {y_test.shape}")
plt.scatter(x_test, y_test, marker='v')
plt.plot(x_test, prediction, color="blue", linewidth=3)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)