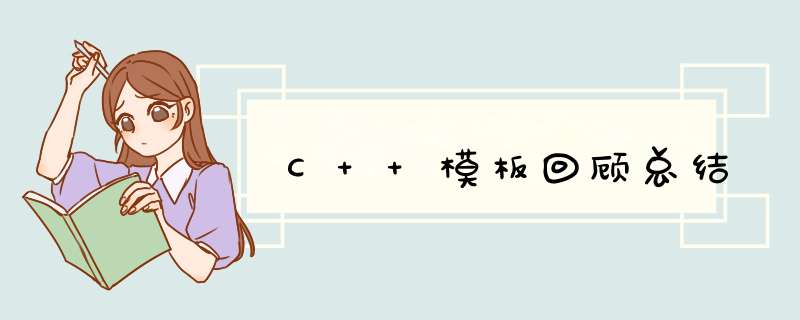
main.cpp
//ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include "myHead.hpp"
using namespace std;
#if 0
template
T Max(T a, T b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
class Student {
public:
Student(string name, int score) :name(name), score(score) {}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Student object) {
out << object.name << "\t" << object.score;
return out;
}
bool operator>(Student object) {
return this->score > object.score;
}
protected:
string name;
int score;
};
//模板的重载
template
void print(T data) {
cout << "一个参数" << endl;
cout << data << endl;
}
template
void print(A first, B second) {
cout << "两个参数" << endl;
cout << first << "\t" << second << endl;
}
void print(char first, char second) {
cout << "普通函数" << endl;
cout << first << "\t" << second << endl;
}
//模板的特化
template
void print(T first, T second) {
cout << "两个一样" << endl;
cout << first << "\t" << second << endl;
}
template <>
void print(int first, int second) {
cout << "函数特化" << endl;
cout << first << "\t" << second << endl;
}
int main() {
//隐式调用
cout << Max(1, 2) << endl;
cout << Max(1.1, 2.2) << endl;
cout << Max(string("I Love YOU"), string("I Miss YOU")) << endl;
//模板的显式调用
cout << Max(2, 3) << endl;
cout << Max(2.2, 3.3) << endl;
//传入自定义类型
//需要重载流运算符
cout << Max(Student("name1", 100), Student("name2", 99)) << endl;
cout << Max(Student("name1", 111), Student("name2", 999)) << endl;
//优先调用的是类型一致的普通函数
print('A', 'B');
//显式调用
print('A', 'B');
print('A','B');
print(1, 2);
print(1);
print(1);
printValue(1, 2);
return 0;
}
#endif+
#if 0
//类模板,只要用template修饰的类就称之为类模板
//类模板必须显示实例化
//类模板不是一个完整的类,所以当我们要使用类名的时候,都需要采用显式方式调用
//类名<类型>
template
class Test {
public:
void print() {
cout << "类模板中的函数" << endl;
}
void printValue();
protected:
};
template
void Test::printValue() {
cout << "Test::printValue" << endl;
}
template
class MM {
public:
MM(T info) :info(info){}
void print() {
cout << info << endl;
}
protected:
T info;
};
template
struct MMinfo
{
A first;
B second;
MMinfo(A first, B second) :first(first), second(second){}
};
template
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, MMinfo object) {
out << object.first << "\t" << object.second;
return out;
}
//类模板的继承
//所产生的子类也是一个模板
template
class Boy :public MM {
public:
//初始化参数列表其实也是调用父类的构造函数,所以必须采用类名<>类型
Boy(T info) :MM(info) {}
protected:
};
//类模板中的静态数据成员
template
class Man {
public:
Man(T info) :info(info) {
count++;
}
void print() {
cout << info << "\t" << count << endl;
}
protected:
T info;
public:
static int count;
};
template
int Man::count = 0;
int main() {
Test testObject;
testObject.print();
Test* testString = new Test;
testString->printValue();
delete testString;
//传入确定类型
MM mm(string("小可爱"));
mm.print();
//类型嵌套的传入
//模板类也可以传入一个模板进去
MM> girl(MMinfo(string("mm"), 18));
girl.print();
Boy boy("帅哥");
boy.print();
/*静态函数*/
Man manObject("帅气大叔");
manObject.print();
cout << Man::count << endl; //1
Man coolMan(18);
coolMan.print();
cout << Man::count << endl;
return 0;
}
#endif
template
class Compare {
public:
static bool compart(T a, T b) {
cout << "原生特化" << endl;
return a > b;
}
protected:
};
template <>
class Compare {
public:
static bool compare(int a, int b) {
cout << "完全特化" << endl;
return a > b;
}
};
/*
template
class Compare {
public:
static bool compare(const T& a, const T& b) {
cout << "局部特化" << endl;
return a > b;
}
};
*/
template
class PrintInfo {
public:
static void print(A first, B second) {
cout << "原生模板" << endl;
cout << first << "\t" << second << endl;
}
};
//两个类型特化成一个类型
template
class PrintValue{
public:
static void print(T first, T second) {
cout << "局部特化" << endl;
cout << first << "\t" << second << endl;
}
};
//注意:类模板多文件的时候,只能在同一个.h文件中,不能分类
int main() {
Compare::compare(1, 2);
const int a = 1;
const int b = 2;
Compare::compare(a,b);
PrintInfo::print(string("小可爱"), 18);
PrintInfo::print(string("帅气大叔"),string("美女"));
return 0;
}
myhead.h
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
template
void printValue(A first, B second) {
cout << "class A , class B" << endl;
cout << first << endl;
cout << seconde << endl;
}
template <>
void printValue(int first, int second) {
cout << "<>" << endl;
cout << first << endl;
cout << second << endl;
}
void printValue(int first, int second) {
cout << "源函数" << endl;
cout << first << endl;
cout << second << endl;
}
template
void printValue(T first, T second) {
cout << "class T" << endl;
cout << first << "\t" << second << endl;
} 欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)