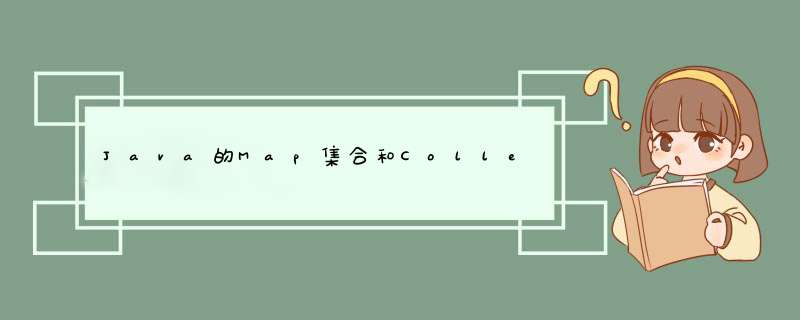
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
//V put(K key, V value) 将指定的值与映射中的指定键值关联
map.put("name","zhangsan");
map.put("age","18");
map.put("age","18");
//输出集合对象
System.out.println(map);
}
}
public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
//V put(K key, V value) 将指定的值与映射中的指定键值关联
map.put("name","lisi");
map.put("age","20");
//V remove(Object key) 根据键值删除键值对元素
System.out.println(map.remove("name"));
//void clear
// map.clear();
//boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合是否包含指定的键
System.out.println(map.containsKey("name"));
System.out.println(map.containsKey("age"));
//boolean containsValue(自己学吧) 判断是否包含指定的值
//boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
//int size() 集合长度,也就是键值的个数
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map);
}
}
public class MapDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","wangwu");
map.put("age","20");
map.put("sex","male");
//V get(Object key) 根据键获取值
System.out.println(map.get("sex"));
System.out.println("------------------");
//Set keySet() 获取所有键的集合
Set<String> key= map.keySet();
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println("---------------");
for (String s: key) {
System.out.println(s);
}
//Collection(V) 获取有值的集合
Collection<String> collection= map.values();
System.out.println(collection);
System.out.println("------------");
for (String s: collection) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
上一个代码中将set方法注释下的代码修改以下为代码即可
//Set keySet() 获取所有键的集合
//遍历键的集合 获取到每一个键 用增强for循环实现
for (String s: key) {
//根据键查找值 用get()方法实现
String s1 = map.get(s);
System.out.println(s+","+s1);
}
public class MapDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap();
map.put("name","maliu");
map.put("age","50");
map.put("sex","female");
//获取所有键值对对象集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
//遍历
for (Map.Entry<String, String> me: entries){
//根据键值对对象获取键和值
String key = me.getKey();
String value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key+","+value);
}
}
}
public class CollectionsDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(30);
list.add(40);
list.add(80);
list.add(230);
list.add(90);
//public static > void sort (List list):将指定的列表升序排序
// Collections.sort(list);
//public static void reverse (List list): 反转指定列表中的元素顺序
// Collections.reverse(list);
//public static void shuffle (List list):使用默认的随机排列指定的列表
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)