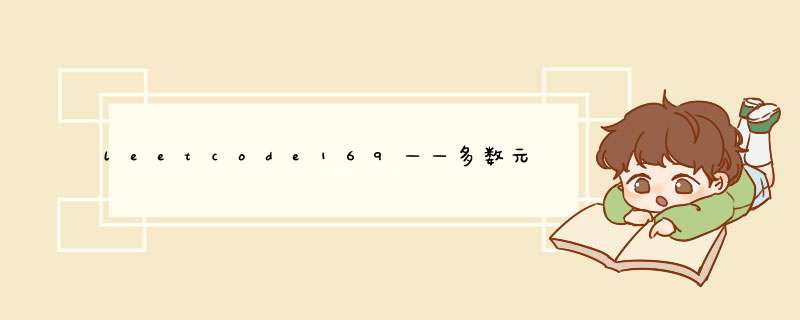
一.C
先排序,下标为 [ n / 2 ] 的元素一定是众数
int Cmp_int(const void* p1, const void* p2)
{
return *(int*)p1 - *(int*)p2;
}
int majorityElement(int* nums, int numsSize)
{
qsort(nums, numsSize, sizeof(int), Cmp_int);
return nums[numsSize / 2];
}
java
/*
s.sort(int[] a):从小到大排序
s.sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex):对数组a的下标从fromIndex到toIndex-1的元素排序
*/
class Solution
{
public int majorityElement(int[] nums)
{
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
}
二.随机化
class Solution
{
private int randRange(Random rand, int min, int max)
{
return rand.nextInt(max - min) + min; //生成一个范围在0~x(不包含X)内的任意正整数
}
private int countOccurences(int[] nums, int num) //数组里有几个和num相等的数字
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
{
if (nums[i] == num)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums)
{
Random rand = new Random();
int majorityCount = nums.length / 2;
while (true)
{
//产生随机下标,将下标指向的数字赋值给candidate
int candidate = nums[randRange(rand, 0, nums.length)];
if (countOccurences(nums, candidate) > majorityCount) //大于半数则为众数
{
return candidate;
}
}
}
}
三.分治
class Solution
{
private int countInRange(int[] nums, int num, int lo, int hi)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
{
if (nums[i] == num)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
private int majorityElementRec(int[] nums, int lo, int hi)
{
// base case; the only element in an array of size 1 is the majority
// element.
if (lo == hi)
{
return nums[lo];
}
// recurse on left and right halves of this slice.
int mid = (hi - lo) / 2 + lo;
int left = majorityElementRec(nums, lo, mid);
int right = majorityElementRec(nums, mid + 1, hi);
// if the two halves agree on the majority element, return it.
if (left == right)
{
return left;
}
// otherwise, count each element and return the "winner".
int leftCount = countInRange(nums, left, lo, hi);
int rightCount = countInRange(nums, right, lo, hi);
return leftCount > rightCount ? left : right;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums)
{
return majorityElementRec(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
}四.Boyer-Moore 投票算法
候选众数:candidate
计数器:count
思路:
假设整个数组的众数记做a,则最初的数组中a的数量大于其余所有数。当采用count计数的时候有两种情况:
1)假设candidate等于a,则当count从1变为0的过程,此区间内a的数量等于其余数的数量,因此以count=0为分界线,数组右端部分的众数仍然为a
2)假设candidate不等于a,则当count从1变为0的过程, 此区间内a的数量小于等于其余数的数量,因此以count=0为分界线,数组右端部分的众数仍然为a
因此,以count=0可以将整个原始数组分为若干部分,count=0右端部分的数组中的众数永远是a,最终必然会筛选出a
class Solution
{
public int majorityElement(int[] nums)
{
int count = 0;
Integer candidate = null;
for (int num : nums)
{
if (count == 0)
{
candidate = num;
}
count += (num == candidate) ? 1 : -1;
}
return candidate;
}
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)