说在最前:下面把主要代码都已经附上,如果有人想要完整的工程文件(包括ESP-IDF和KEIL5和STM32CUBEMX的工程)请移步下载链接:
完整资源下载
如果你自己写的,有bug无法解决,请参考,下面的文章:
含泪Debug:STM32与ESP32 SPI通信避坑
我先极其粗浅的介绍一下SPI通信:
四线SPI通信:SPI_SCLK用于传递时钟信号,SPI_CS用于传递片选信号(低有效),MOSI为主机的输出、从机的输入,MISO为主机的输入、从机的输出。
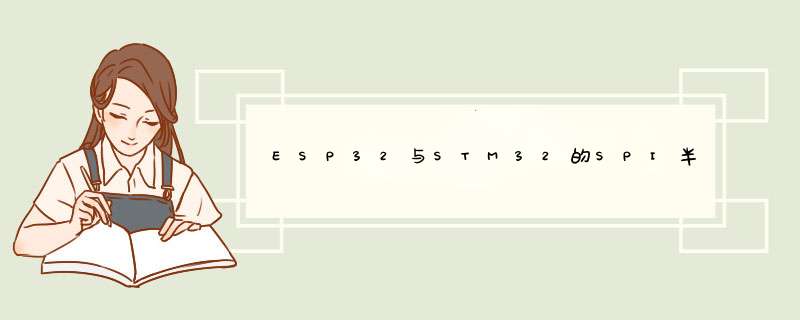
四线SPI的数据交换:CS片选信号,用于使能从设备接收数据;主从设备在SPI_SCLK时钟信号的驱动下,如下图的方式交换数据。
实现的时候,STM32与ESP32是轮询式的:
HAL_SPI_Transmit(&hspi5,ptr,128,0xffff);ret=spi_slave_transmit(RCV_HOST, &t, portMAX_DELAY);所以,为了保证二者能够转备好在同一时刻进行数据的交换,就需要握手协议。
(以半双工,STM32做master为例)如何握手呢?ESP32-IDF例程中的代码如下:
//Called after a transaction is queued and ready for pickup by master. We use this to set the handshake line high.
void my_post_setup_cb(spi_slave_transaction_t *trans) {
WRITE_PERI_REG(GPIO_OUT_W1TS_REG, (1<也就是说,ESP32每次请求数据前,先把HANDSHAKE引脚拉高,请求后把HANDSHAKE拉低。如果STM32想给ESP32发送数据的话,就要检测ESP32是否准备好,也就是检测HANDSHAKE的电平值,如果为高电平才可以发送。
话不多说直接上代码:
ESP-IDF版本为v4.0.1(如果不能编译可能你们的版本太高了),在例程的基础上略微改动
/* SPI Slave example, receiver (uses SPI Slave driver to communicate with sender)
This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, this
software is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "freertos/semphr.h"
#include "freertos/queue.h"
#include "lwip/sockets.h"
#include "lwip/dns.h"
#include "lwip/netdb.h"
#include "lwip/igmp.h"
#include "esp_wifi.h"
#include "esp_system.h"
#include "esp_event.h"
#include "nvs_flash.h"
#include "soc/rtc_periph.h"
#include "driver/spi_slave.h"
#include "esp_log.h"
#include "esp_spi_flash.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
/*
SPI receiver (slave) example.
This example is supposed to work together with the SPI sender. It uses the standard SPI pins (MISO, MOSI, SCLK, CS) to
transmit data over in a full-duplex fashion, that is, while the master puts data on the MOSI pin, the slave puts its own
data on the MISO pin.
This example uses one extra pin: GPIO_HANDSHAKE is used as a handshake pin. After a transmission has been set up and we're
ready to send/receive data, this code uses a callback to set the handshake pin high. The sender will detect this and start
sending a transaction. As soon as the transaction is done, the line gets set low again.
*/
/*
Pins in use. The SPI Master can use the GPIO mux, so feel free to change these if needed.
*/
#define GPIO_HANDSHAKE 2
#define GPIO_MOSI 5
#define GPIO_MISO 17
#define GPIO_SCLK 16
#define GPIO_CS 4
#ifdef CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32
#define RCV_HOST HSPI_HOST
#define DMA_CHAN 2
#elif defined CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S2
#define RCV_HOST SPI2_HOST
#define DMA_CHAN RCV_HOST
#endif
//Called after a transaction is queued and ready for pickup by master. We use this to set the handshake line high.
void my_post_setup_cb(spi_slave_transaction_t *trans) {
WRITE_PERI_REG(GPIO_OUT_W1TS_REG, (1< STM32的版本为STM32F446,只发配置的主要部分:spi.c
/**
******************************************************************************
* File Name : SPI.c
* Description : This file provides code for the configuration
* of the SPI instances.
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* © Copyright (c) 2021 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software component is licensed by ST under BSD 3-Clause license,
* the "License"; You may not use this file except in compliance with the
* License. You may obtain a copy of the License at:
* opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "spi.h"
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
/* USER CODE END 0 */
SPI_HandleTypeDef hspi2;
/* SPI2 init function */
void MX_SPI2_Init(void)
{
hspi2.Instance = SPI2;
hspi2.Init.Mode = SPI_MODE_MASTER;
hspi2.Init.Direction = SPI_DIRECTION_2LINES;
hspi2.Init.DataSize = SPI_DATASIZE_8BIT;
hspi2.Init.CLKPolarity = SPI_POLARITY_LOW;
hspi2.Init.CLKPhase = SPI_PHASE_1EDGE;
hspi2.Init.NSS = SPI_NSS_SOFT;
hspi2.Init.BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BAUDRATEPRESCALER_2;
hspi2.Init.FirstBit = SPI_FIRSTBIT_MSB;
hspi2.Init.TIMode = SPI_TIMODE_DISABLE;
hspi2.Init.CRCCalculation = SPI_CRCCALCULATION_DISABLE;
hspi2.Init.CRCPolynomial = 10;
if (HAL_SPI_Init(&hspi2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
void HAL_SPI_MspInit(SPI_HandleTypeDef* spiHandle)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
if(spiHandle->Instance==SPI2)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI2_MspInit 0 */
/* USER CODE END SPI2_MspInit 0 */
/* SPI2 clock enable */
__HAL_RCC_SPI2_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
/**SPI2 GPIO Configuration
PB13 ------> SPI2_SCK
PB15 ------> SPI2_MOSI
*/
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = SPI_SCLK_Pin|SPI_MOSI_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_AF_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;
GPIO_InitStruct.Alternate = GPIO_AF5_SPI2;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI2_MspInit 1 */
/* USER CODE END SPI2_MspInit 1 */
}
}
void HAL_SPI_MspDeInit(SPI_HandleTypeDef* spiHandle)
{
if(spiHandle->Instance==SPI2)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI2_MspDeInit 0 */
/* USER CODE END SPI2_MspDeInit 0 */
/* Peripheral clock disable */
__HAL_RCC_SPI2_CLK_DISABLE();
/**SPI2 GPIO Configuration
PB13 ------> SPI2_SCK
PB15 ------> SPI2_MOSI
*/
HAL_GPIO_DeInit(GPIOB, SPI_SCLK_Pin|SPI_MOSI_Pin);
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI2_MspDeInit 1 */
/* USER CODE END SPI2_MspDeInit 1 */
}
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/************************ (C) COPYRIGHT STMicroelectronics *****END OF FILE****/
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
__HAL_UART_ENABLE(&huart3);
hspi2.Instance->CR1 |= (1<<6); // 打开SPE
GPIOB->ODR|=1UL<<0;
int count=0;
unsigned char wr_buff[128]={0};
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
GPIOB->ODR^=1UL<<0;
snprintf((char *)wr_buff,128,"THIS_IS_STM32_SENDING_NUM:%d\n",count);
spi_send_128(wr_buff);
count++;
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)