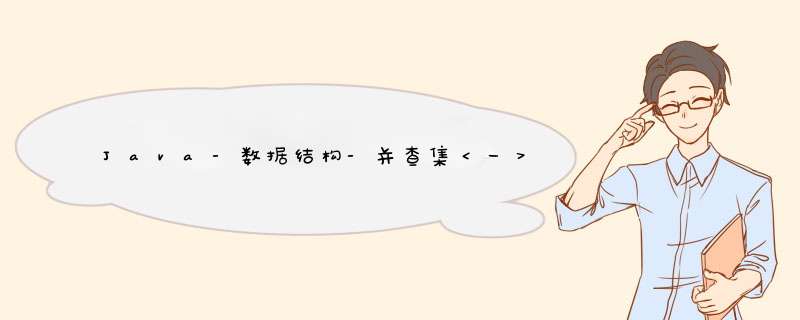
并查集的精髓在于,两块集合(区域)有没有相交,以及要不要联通两块区域(集合)。参考树的结构,把元素挂到父节点下,若两个元素的父节点相同,则是同一块区域,两个元素的父节点不相同,则不是同一块区域。
以上图为例,1和2是同一片区域,3和4是同一片区域,5自己是一片区域,那么以上总共有三个区域。
二. 并查集的主要构成和实现方式 1. 主要构成(0) 元素添加的过程
以用HashMap的方式实现为例,那么添加一个新的元素时,它的父节点是null
public void add(int x){
if(!father.containsKey(x)){//从来没有在father中出现过
father.put(x,null);
numOfSets++;//联通区域需要加1
}
}(1)查找父节点过程find()
while(father.get(root) != null){//在father中一致循环找到它的父节点,层层往上
root = father.get(root);
}(2)缩减层数的过程
方法一. 层层递归向上,写个while循环或者递归就可以了
while(x != root){
int original_father = father.get(x);//先保留父节点
father.put(x,root);//把x直接挂到父节点下
x = original_father;//x变成原来的父节点,然后循环
}方法二. 一路压到栈中,然后层层出栈,把沿路的都挂到父节点上
Stack> path = new Stack<>();
while (element != fatherMap.get(element)) {
path.push(element);
element = fatherMap.get(element);
}
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
fatherMap.put(path.pop(), element);
} (3)并的过程merge()
merge的本质是把两个节点的父节点合并
public void merge(int x,int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY){
father.put(rootX,rootY);
numOfSets--;
}
}模板代码(源自左神)
public class Code04_UnionFind {
public static class Element {
public V value;
public Element(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static class UnionFindSet {
public HashMap> elementMap;
public HashMap, Element> fatherMap;
public HashMap, Integer> rankMap;
public UnionFindSet(List list) {
elementMap = new HashMap<>();
fatherMap = new HashMap<>();
rankMap = new HashMap<>();
for (V value : list) {
Element element = new Element(value);
elementMap.put(value, element);
fatherMap.put(element, element);
rankMap.put(element, 1);
}
}
private Element findHead(Element element) {
Stack> path = new Stack<>();
while (element != fatherMap.get(element)) {
path.push(element);
element = fatherMap.get(element);
}
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
fatherMap.put(path.pop(), element);
}
return element;
}
public boolean isSameSet(V a, V b) {
if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) {
return findHead(elementMap.get(a)) == findHead(elementMap.get(b));
}
return false;
}
public void union(V a, V b) {
if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) {
Element aF = findHead(elementMap.get(a));
Element bF = findHead(elementMap.get(b));
if (aF != bF) {
Element big = rankMap.get(aF) >= rankMap.get(bF) ? aF : bF;
Element small = big == aF ? bF : aF;
fatherMap.put(small, big);
rankMap.put(big, rankMap.get(aF) + rankMap.get(bF));
rankMap.remove(small);
}
}
}
}
} 模板代码(源自leetcode)
class UnionFind {
private Map father;
public UnionFind() {
father = new HashMap();
}
public void add(int x) {
if (!father.containsKey(x)) {
father.put(x, null);
}
}
public void merge(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX != rootY){
father.put(rootX,rootY);
}
}
public int find(int x) {
int root = x;
while(father.get(root) != null){
root = father.get(root);
}
while(x != root){
int original_father = father.get(x);
father.put(x,root);
x = original_father;
}
return root;
}
public boolean isConnected(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
}
作者:musiala
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-provinces/solution/python-duo-tu-xiang-jie-bing-cha-ji-by-m-vjdr/ 有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。返回矩阵中 省份 的数量.
class Solution {
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind();
for(int i = 0; i < isConnected.length;i++){
uf.add(i);
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1){
uf.merge(i,j);
}
}
}
return uf.numOfSets;
}
}
//首先我们需要一个class结构,来实现并查集结构
class UnionFind{
//HashMap存放每个结点和它的父节点
HashMap father;
//存放联通的区域
int numOfSets = 0;
//初始化
public UnionFind(){
father = new HashMap<>();
numOfSets = 0;
}
//添加结点的过程
public void add(int x){
if(!father.containsKey(x)){//从来没有在father中出现过
father.put(x,null);
numOfSets++;//联通区域需要加1
}
}
//查找的过程
public int find(int x){
int root = x;
while(father.get(root) != null){//在father中一致循环找到它的父节点,层层往上
root = father.get(root);
}
//减层的 *** 作
while(x != root){
int original_father = father.get(x);//先保留父节点
father.put(x,root);//把x直接挂到父节点下
x = original_father;//x变成原来的父节点,然后循环
}
return root;
}
//把两个结点合成一个结点,若父节点一样则不同合了
public void merge(int x,int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY){
father.put(rootX,rootY);
numOfSets--;
}
}
//x和y是否是联通的,找有没有共同的父节点就可以了
public boolean isConnected(int x, int y){
return find(x) == find(y);
}
//返回联通区域的数量
public int getNumOfSets(){
return numOfSets;
}
}
树可以看成是一个连通且 无环 的 无向 图。
给定往一棵 n 个节点 (节点值 1~n) 的树中添加一条边后的图。添加的边的两个顶点包含在 1 到 n 中间,且这条附加的边不属于树中已存在的边。图的信息记录于长度为 n 的二维数组 edges ,edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示图中在 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。请找出一条可以删去的边,删除后可使得剩余部分是一个有着 n 个节点的树。如果有多个答案,则返回数组 edges 中最后出现的边。
class UnionFind{
HashMap father;
int numset;
public UnionFind(){
numset = 0;
father = new HashMap<>();
}
public void add(int x){
if(!father.containsKey(x)){
father.put(x,null);
numset++;
}
}
public int find(int x){
int root = x;
while(father.get(root) != null){
root = father.get(root);
}
//压缩
while(father.get(x) != null){
int ori_father = father.get(x);
father.put(x,root);
x = ori_father;
}
return root;
}
public void merge(int x, int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY){
father.put(rootX,rootY);
numset--;
}
}
public boolean isConnected(int x, int y){
return find(x) == find(y);
}
public int getnumset(){
return numset;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind();
for(int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++){
if(uf.isConnected(edges[i][0],edges[i][1])){
return edges[i];
}
else{
uf.add(edges[i][0]);
uf.add(edges[i][1]);
uf.merge(edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);
}
}
return edges[0];
}
} 欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)