今天实现toDataArrays方法,用于将链式存储的二叉树转为顺序存储。
1.二叉树的顺序存储1. 如何进行二叉树的顺序存储?
- 完全二叉树
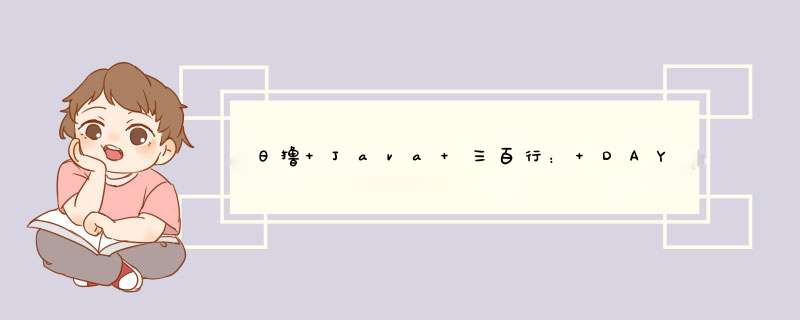
对于一棵完全二叉树,如果将它的结点由上自下、由左到右的从0开始编号,那么编号为 i \textit{i} i的结点,如果它的左右孩子存在的话,那么左孩子的编号为 2 i + 1 2 \textit{i}+1 2i+1,右孩子的编号为 2 i + 2 2 \textit{i}+2 2i+2。正如下图所示:
显然,可以很自然的想到一种顺序存储的方式,即将数组的下标与结点的编号关联起来,编号为 i \textit{i} i的结点存储在数组下标为 i \textit{i} i的位置,这种表示方法非常高效。 - 更普遍的二叉树
如果要存储的二叉树不是一棵完全二叉树,那么它将不再具备上述性质,如果还要用上述方法进行顺序储存的话,则必须使用许多的虚结点来将其补充成一棵完全二叉树。在数组中存储这些并不存在的虚结点的信息,是十分浪费空间资源的,因此考虑另一种压缩存储的方式。
我们仍将二叉树用虚结点补充成完全二叉树,但只存储实际存在的结点信息,用两个数组分别记录结点的值和它的编号。
2. 如何将链式存储的二叉树转为顺序存储?
从上文图片中可以看出,结点的编号顺序恰恰也是对二叉树进行层序遍历的顺序。因此我们可以层序遍历二叉树,对每一个实际存在的结点记录它的值与编号即可。
层序遍历二叉树的步骤如下:
- 初始化:将根结点入队
- 从队列中出队一个结点并访问,并将该结点的左右孩子入队( 如果存在的话 )
- 重复步骤2至队列为空则遍历结束
我们的算法要做的就是在层序遍历的基础上,将访问 *** 作细化为记录结点的值与编号,在这个程序中,选择在结点入队时或出队时进行处理都是可以的。
2.程序1. toDataArrays
/**
***********************
* Convert the tree to data arrays, including a char array and an int array.
* The results are stored in two member variables.
*
* @see #valuesArray
* @see #indicesArray
***********************
*/
public void toDataArrays( ) {
// Initialize arrays.
int tempLength = getNumNodes( );
valuesArray = new char[ tempLength ];
indicesArray = new int[ tempLength ];
int i = 0;
// Traverse and convert at the same time.
CircleObjectQueue tempQueue = new CircleObjectQueue( );
tempQueue.enqueue( this );
CircleIntQueue tempIntQueue = new CircleIntQueue( );
tempIntQueue.enqueue( 0 );
BinaryCharTree tempTree = ( BinaryCharTree ) tempQueue.dequeue( );
int tempIndex = tempIntQueue.dequeue( );
while( tempTree != null ) {
valuesArray[ i ] = tempTree.value;
indicesArray[ i ] = tempIndex;
i++;
if( tempTree.leftChild != null ) {
tempQueue.enqueue( tempTree.leftChild );
tempIntQueue.enqueue( tempIndex * 2 + 1 );
} // Of if
if( tempTree.rightChild != null ) {
tempQueue.enqueue( tempTree.rightChild );
tempIntQueue.enqueue( tempIndex * 2 + 2 );
} // Of if
tempTree = ( BinaryCharTree ) tempQueue.dequeue( );
tempIndex = tempIntQueue.dequeue( );
} // Of while
} // Of toDataArrays
2. 测试
/**
***********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
***********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
BinaryCharTree tempTree = manualConstructTree();
System.out.println("\r\nPreorder visit:");
tempTree.preOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\nIn-order visit:");
tempTree.inOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\nPost-order visit:");
tempTree.postOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\n\r\nThe depth is: " + tempTree.getDepth());
System.out.println("The number of nodes is: " + tempTree.getNumNodes());
tempTree.toDataArrays( );
System.out.println("The values are: " + Arrays.toString( tempTree.valuesArray ) );
System.out.println("The indices are: " + Arrays.toString( tempTree.indicesArray ) );
}// Of main
执行结果如下:
- 引用 (指针) 是无法存储到文件里面的,因此二叉树的顺序储存也很有必要。
- 在进行程序实现时,小细节很重要。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)