上回使用Q-Learning实现了一维环境里的寻宝问题,接下来将其扩展到二维环境。与一维环境中仅能左右移动不同,探索者可以在二维环境里进行上下左右四个方向移动。
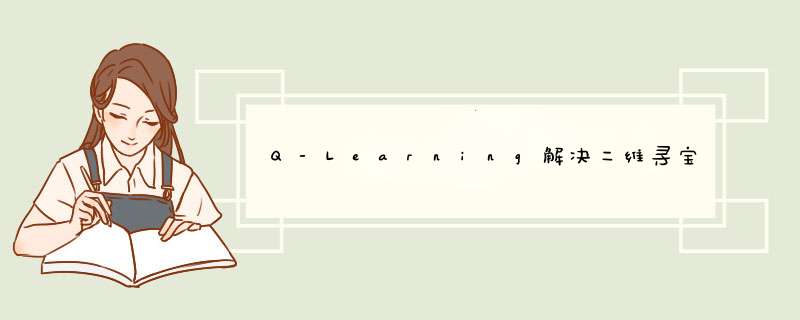
环境说明二维寻宝问题的环境如下图,探索者能够在5x5的位置中移动,起点位置为绿色方块,宝藏位置为红色方块,每一个位置对应相应的奖励。探索者从起点开始,在上下左右中选择移动方向,直至到达红色区域并获得宝藏。
实现流程:(1)设置初始状态;(2)选择动作;(3)获取状态反馈;(4)更新Q表;(5)更新状态;(6)设置终止条件
状态动作说明状态(state):探索者所处的位置,使用(X,Y)表示。例如(0,0)表示探索者处于第一行第一列。
动作(action):探索者能够选择的移动方向,分为上、下、左、右。
初始化时需要设置环境状态,动作列表以及算法的参数。
class TwoDimensionQTable:
def __init__(self, states,actions,rewords,learningRate=0.01, rewarddecay=0.9, eGreedy=0.9,episode=200):
#状态列表
self.states=states
#动作列表
self.actions = actions
#奖励列表
self.rewords=rewords
#学习率
self.lr = learningRate
#奖励衰减率
self.gamma = rewarddecay
#贪婪策略
self.epsilon = eGreedy
#训练次数
self.episode=episode
#空Q表
self.qTable = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.float64)
由于初始设置Q表为空,在算法进行过程中需要将探索得到的新状态添加进入Q表并更新Q表的行列。
#遇到新状态后添加到Q表,行索引:状态;列索引:动作
def stateExist(self, state):
if str(state) not in self.qTable.index:
self.qTable = self.qTable.append(
pd.Series(
[0]*len(self.actions),
index=self.qTable.columns,
name=str(state),
)
)
在动作选择部分,算法根据当前状态(state)选择动作(action)。选择动作过程中的策略是:90%的概率根据Q表最优值进行选择;10%的概率随机选择;
在动作选择过程中,由于二维环境存在边界限制,选择的动作时需要考虑边界条件。例如,处于第一行时,探索者无法选择向上的动作。
#根据状态从qTable选择动作
def chooseAction(self,state):
#判断状态是否存在Q表中
self.stateExist(str(state))
#选择采取的动作
#90%的概率按照Q表最优进行选择
if np.random.uniform()<self.epsilon:
#动作限制
if state[0]==0:
if state[1]==0:
actionLimits=['right','down']
elif state[1]==len(self.rewords[0])-1:
actionLimits=['left','down']
else:
actionLimits=['left','right','down']
elif state[0]==len(self.rewords)-1:
if state[1]==0:
actionLimits=['up','right']
elif state[1]==len(self.rewords[0])-1:
actionLimits=['left','up']
else:
actionLimits=['left','right','up']
elif state[1]==0:
if state[0]==0:
actionLimits=['down','right']
elif state[0]==len(self.rewords)-1:
actionLimits=['right','up']
else:
actionLimits=['down','right','up']
elif state[1]==len(self.rewords[0])-1:
if state[0]==0:
actionLimits=['down','left']
elif state[0]==len(self.rewords)-1:
actionLimits=['left','up']
else:
actionLimits=['down','left','up']
else:
actionLimits=self.actions
stateActionList=self.qTable.loc[str(state),:][actionLimits]
#print("stateActionList:",stateActionList)
#若存在多个最好动作,则随机选择其中一个
action=np.random.choice(stateActionList[stateActionList==np.max(stateActionList)].index)
#10%的概率随机选择一个动作
else:
if state[0]==0:
if state[1]==0:
action=np.random.choice(['right','down'])
elif state[1]==len(self.rewords[0])-1:
action=np.random.choice(['left','down'])
else:
action=np.random.choice(['left','right','down'])
elif state[0]==len(self.rewords)-1:
if state[1]==0:
action=np.random.choice(['up','right'])
elif state[1]==len(self.rewords[0])-1:
action=np.random.choice(['left','up'])
else:
action=np.random.choice(['left','right','up'])
elif state[1]==0:
if state[0]==0:
action=np.random.choice(['down','right'])
elif state[0]==len(self.rewords)-1:
action=np.random.choice(['right','up'])
else:
action=np.random.choice(['down','right','up'])
elif state[1]==len(self.rewords[0])-1:
if state[0]==0:
action=np.random.choice(['down','left'])
elif state[0]==len(self.rewords)-1:
action=np.random.choice(['left','up'])
else:
action=np.random.choice(['down','left','up'])
else:
action=np.random.choice(self.actions)
return action
在探索环境中,宝藏位置的奖励为1,陷阱位置设定为-1,其余位置设定为0。
#根据状态和动作返回下一个状态和当前的奖励
def feedBack(self,state,action):
#向上移动
if action=='up':
nextState=(state[0]-1,state[1])
elif action=='down':
nextState=(state[0]+1,state[1])
elif action=='left':
nextState=(state[0],state[1]-1)
else:
nextState=(state[0],state[1]+1)
reword=self.rewords[nextState[0]][nextState[1]]
return nextState,reword
#根据当前状态、动作、下一状态、奖励更新Q表
def updateTable(self,state,action,nextState,reword):
#判断状态是否存在Q表中
self.stateExist(str(nextState))
#当前状态值
qPredict=self.qTable.loc[str(state),action]
#下一状态值
if nextState==(3,4):
qTarget=reword
else:
qTarget=reword+self.gamma*self.qTable.loc[str(nextState),:].max()
#更新
self.qTable.loc[str(state),action]+=self.lr*(qTarget-qPredict)
#主循环
def mainCycle(self):
for episode in range(self.episode):
#初始状态
state=(0,0)
actionStr=""
while True:
#选择动作
action=self.chooseAction(state)
if episode==self.episode-1:
actionStr+=str(state)+"->"
#状态反馈
nextState,reword=self.feedBack(state,action)
#更新Q表
self.updateTable(state,action,nextState,reword)
#更新状态
state=nextState
#终止条件
if state==(3,4):
if episode==self.episode-1:
print(actionStr)
break
可以发现,算法的实现流程与一维寻宝的实现流程一致,其区别是二维环境的设置以及增加了边界条件限制,其余 *** 作的代码基本未改变。
因而,使用Q-Learning算法的统一实现流程模板:(1)设置初始状态;(2)选择动作;(3)获取状态反馈;(4)更新Q表;(5)更新状态;(6)设置终止条件。
===========================================
今天到此为止,后续记录其他强化学习技术的学习过程。
以上学习笔记,如有侵犯,请立即联系并删除!
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)