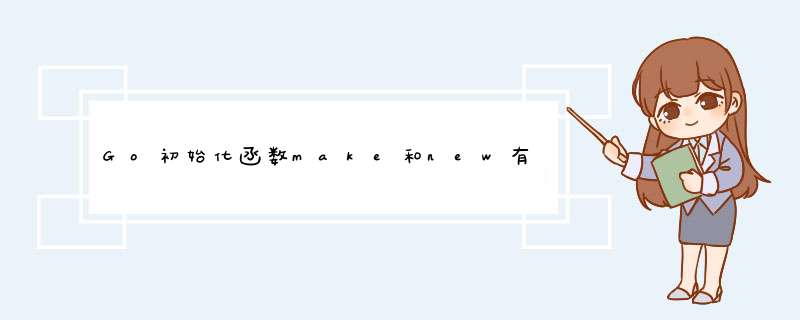
代码演示:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
testMap()
fmt.Println("--------")
testSlice()
fmt.Println("--------")
testChannel()
}
func testMap() {
mmap := make(map[string]int64)
nmap := new(map[string]int64)
fmt.Println("&mmap = ", &mmap, "------ mmap = ", mmap)
fmt.Println("&nmap = ", &nmap, "------ nmap = ", nmap)
mmap = map[string]int64{"key": 100}
nmap = &map[string]int64{"key": 100}
fmt.Println("&mmap = ", &mmap, "------ mmap = ", mmap)
fmt.Println("&nmap = ", &nmap, "------ nmap = ", nmap)
}
func testSlice() {
mslice := make([]int, 0, 10)
mslice2 := make([]int, 0)
nslice := new([]int)
fmt.Println("&mslice = ", &mslice, "------ mslice = ", mslice)
fmt.Println("&mslice2 = ", &mslice2, "------ mslice2 = ", mslice2)
fmt.Println("&nslice = ", &nslice, "------ nmap = ", nslice)
mslice = append(mslice, 111)
mslice2 = append(mslice2, 222)
*nslice = append(*nslice, 333)
fmt.Println("&mslice = ", &mslice, "------ mslice = ", mslice)
fmt.Println("&mslice2 = ", &mslice2, "------ mslice2 = ", mslice2)
fmt.Println("&nslice = ", &nslice, "------ nmap = ", nslice)
}
func testChannel() {
mchan := make(chan int, 1)
mchan2 := make(chan int, 10)
nchan := new(chan int)
fmt.Println("&mchan = ", &mchan, "------ mchan = ", mchan)
fmt.Println("&mchan2 = ", &mchan2, "------ mchan2 = ", mchan2)
fmt.Println("&nchan = ", &nchan, "------ nchan = ", nchan)
mchan <- 10
mchan2 <- 20
*nchan = make(chan int, 1)
*nchan <- 30
fmt.Println("&mchan = ", &mchan, "------ mchan = ", <-mchan)
fmt.Println("&mchan2 = ", &mchan2, "------ mchan2 = ", <-mchan2)
fmt.Println("&nchan = ", &nchan, "------ nchan = ", <-*nchan)
}
运行结果:
&mmap = &map[] ------ mmap = map[]
&nmap = 0xc1200ac020 ------ nmap = &map[]
&mmap = &map[key:100] ------ mmap = map[key:100]
&nmap = 0xc1200ac020 ------ nmap = &map[key:100]
--------
&mslice = &[] ------ mslice = []
&mslice2 = &[] ------ mslice2 = []
&nslice = 0xc1200ac040 ------ nmap = &[]
&mslice = &[111] ------ mslice = [111]
&mslice2 = &[222] ------ mslice2 = [222]
&nslice = 0xc1200ac040 ------ nmap = &[333]
--------
&mchan = 0xc1200ac048 ------ mchan = 0xc1200c6000
&mchan2 = 0xc1200ac050 ------ mchan2 = 0xc1200c8000
&nchan = 0xc1200ac058 ------ nchan = 0xc1200ac060
&mchan = 0xc1200ac048 ------ mchan = 10
&mchan2 = 0xc1200ac050 ------ mchan2 = 20
&nchan = 0xc1200ac058 ------ nchan = 30
源码:
// The make built-in function allocates and initializes an object of type
// slice, map, or chan (only). Like new, the first argument is a type, not a
// value. Unlike new, make's return type is the same as the type of its
// argument, not a pointer to it. The specification of the result depends on
// the type:
// Slice: The size specifies the length. The capacity of the slice is
// equal to its length. A second integer argument may be provided to
// specify a different capacity; it must be no smaller than the
// length. For example, make([]int, 0, 10) allocates an underlying array
// of size 10 and returns a slice of length 0 and capacity 10 that is
// backed by this underlying array.
// Map: An empty map is allocated with enough space to hold the
// specified number of elements. The size may be omitted, in which case
// a small starting size is allocated.
// Channel: The channel's buffer is initialized with the specified
// buffer capacity. If zero, or the size is omitted, the channel is
// unbuffered.
func make(t Type, size ...IntegerType) Type
// The new built-in function allocates memory. The first argument is a type,
// not a value, and the value returned is a pointer to a newly
// allocated zero value of that type.
func new(Type) *Type
简单翻译下:
//make内置函数分配并初始化一个类型对象切片、映射或chan(仅这三个)。像new一样,第一个参数是一个类型,而不是value。与new不同,make的返回类型与他的参数类型相同,而不是指向它的指针。结果的规格取决于类型:
//- Slice:大小指定长度。切片的容量为等于它的长度。可以提供第二个整数参数指定不同的容量;它必须不小于长度。例如,make([]int, 0,10)分配一个底层数组的大小为10,返回长度为0,容量为10的切片由此基础数组支持。
//- Map:为空映射分配足够的空间来容纳指定的元素数。在这种情况下,可以省略字号分配一个小的起始大小。
//- Channel:通道的缓冲区用指定的参数初始化缓冲能力。如果为零,或者省略了大小,则通道为无缓冲的。
func make(t Type, size ...IntegerType) Type
//new的内置函数分配内存。第一个参数是一个类型,不是一个value,返回的值是一个指向new的指针分配该类型的零值。
func new(Type) *Type
Go语言中的 new 和 make 主要区别如下:
make 只能用来分配及初始化类型为 slice、map、chan 的数据。new 可以分配任意类型的数据;new 分配返回的是指针,即类型 *Type。make 返回引用,即 Type;new 分配的空间被清零。make 分配空间后,会进行初始化;最后,简单总结一下Go语言中 make 和 new 关键字的实现原理,make 关键字的主要作用是创建 slice、map 和 Channel 等内置的数据结构,而 new 的主要作用是为类型申请一片内存空间,并返回指向这片内存的指针。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)