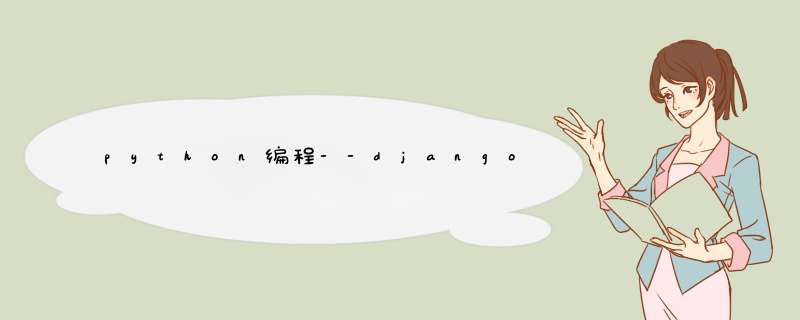
代码部分:
from djangodb import models
class Student(modelsModel):
name = modelsCharField(max_length=30)
grade = modelsIntegerField()
执行部分 :
python managepy makemigrations
python managepy migrate
Django教程——01安装使用
在上面一篇文章里,介绍了安装Django的方法,这里说说连接数据库吧
这篇主要介绍踩的坑和解决办法
正常连接和初始化数据库的命令是
执行这个命令的时候,出现了如下报错
经过一段排查,是我配置数据库的时候,多嵌套了一层default,修改为如下即可
然后继续执行migrate时,会报如下错误
本机环境是mac电脑,按官方教程 *** 作的时候,发现安装mysqlclient的python包会依赖本机安装mysql或者mysql-client,但在装mysql和mysql-client的时候,发现一直报错。后面发现解决办法是,在settingspy文件里,加下如下代码,即改用pymsql连接即可。
或者在settingspy同目录的__init__py里加如上代码也可以
然后再执行python managepy migrate命令会发现表顺利创建。新增表,不影响原有库的其他表。
1 创建项目
运行面命令创建 django 项目项目名称叫 mysite :
$ django-adminpy startproject mysite
创建项目目录:
mysite
├── managepy
└── mysite
├── __init__py
├── settingspy
├── urlspy
└── wsgipy
1 directory, 5 files
说明:
__init__py :让 Python 该目录发包 (即组模块)所需文件 空文件般需要修改
managepy :种命令行工具允许种式与该 Django 项目进行交互 键入python managepy help看能做 应需要编辑文件;目录纯便
settingspy :该 Django 项目设置或配置
urlspy:Django项目URL路由设置目前空
wsgipy:WSGI web 应用服务器配置文件更细节查看 How to deploy with WSGI
接修改 settingspy 文件例:修改 LANGUAGE_CODE、设置区 TIME_ZONE
SITE_ID = 1
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'zh_CN'
TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai'
USE_TZ = True
面启 [Time zone]() 特性需要安装 pytz:
$ sudo pip install pytz
2 运行项目
运行项目前我需要创建数据库表结构我使用默认数据库:
$ python managepy migrate
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, contenttypes, auth, sessions
Running migrations:
Applying contenttypes0001_initial OK
Applying auth0001_initial OK
Applying admin0001_initial OK
Applying sessions0001_initial OK
启服务:
$ python managepy runserver
看面输:
Performing system checks
System check identified no issues (0 silenced)
January 28, 2015 - 02:08:33
Django version 171, using settings 'mysitesettings'
Starting development server at
Quit the server with CONTROL-C
端口8000启本服务器, 并且能台电脑连接访问 既服务器已经运行起现用网页浏览器访问 应该看令赏悦目淡蓝色 Django 欢迎页面始工作
指定启端口:
$ python managepy runserver 8080
及指定 ip:
$ python managepy runserver 0000:8000
3 创建 app
前面创建项目并且功运行现创建 app app 相于项目模块
项目目录创建 app:
$ python managepy startapp polls
*** 作功 mysite 文件夹看已经叫 polls 文件夹目录结构:
polls
├── __init__py
├── adminpy
├── migrations
│ └── __init__py
├── modelspy
├── testspy
└── viewspy
1 directory, 6 files
4 创建模型
每 Django Model 都继承自 djangodbmodelsModel
Model 每属性 attribute 都代表 database field
通 Django Model API 执行数据库增删改查, 需要写些数据库查询语句
打 polls 文件夹 modelspy 文件创建两模型:
import datetime
from djangodb import models
from djangoutils import timezone
class Question(modelsModel):
question_text = modelsCharField(max_length=200)
pub_date = modelsDateTimeField('date published')
def was_published_recently(self):
return selfpub_date >= timezonenow() - datetimetimedelta(days=1)
class Choice(modelsModel):
question = modelsForeignKey(Question)
choice_text = modelsCharField(max_length=200)
votes = modelsIntegerField(default=0)
mysite/settingspy 修改 INSTALLED_APPS 添加 polls:
INSTALLED_APPS = (
'djangocontribadmin',
'djangocontribauth',
'djangocontribcontenttypes',
'djangocontribsessions',
'djangocontribmessages',
'djangocontribstaticfiles',
'polls',
)
添加新 app 我需要运行面命令告诉 Django 模型做改变需要迁移数据库:
$ python managepy makemigrations polls
看面输志:
Migrations for 'polls':
0001_initialpy:
- Create model Choice
- Create model Question
- Add field question to choice
polls/migrations/0001_initialpy 查看迁移语句
运行面语句查看迁移 sql 语句:
$ python managepy sqlmigrate polls 0001
输结:
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE "polls_choice" ("id" integer NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, "choice_text" varchar(200) NOT NULL, "votes" integer NOT NULL);
CREATE TABLE "polls_question" ("id" integer NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, "question_text" varchar(200) NOT NULL, "pub_date" datetime NOT NULL);
CREATE TABLE "polls_choice__new" ("id" integer NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, "choice_text" varchar(200) NOT NULL, "votes" integer NOT NULL, "question_id" integer NOT NULL REFERENCES "polls_question" ("id"));
INSERT INTO "polls_choice__new" ("choice_text", "votes", "id") SELECT "choice_text", "votes", "id" FROM "polls_choice";
DROP TABLE "polls_choice";
ALTER TABLE "polls_choice__new" RENAME TO "polls_choice";
CREATE INDEX polls_choice_7aa0f6ee ON "polls_choice" ("question_id");
COMMIT;
运行面命令检查数据库否问题:
$ python managepy check
再运行面命令创建新添加模型:
$ python managepy migrate
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, contenttypes, polls, auth, sessions
Running migrations:
Applying polls0001_initial OK
总结修改模型需要做几步骤:
修改 modelspy 文件
运行 python managepy makemigrations 创建迁移语句
运行 python managepy migrate模型改变迁移数据库
阅读 django-adminpy documentation查看更 managepy 用
创建模型我通 Django 提供 API 做测试运行面命令进入 python shell 交互模式:
$ python managepy shell
面些测试:
>>> from pollsmodels import Question, Choice # Import the model classes we just wrote
# No questions are in the system yet
>>> Questionobjectsall()
[]
# Create a new Question
# Support for time zones is enabled in the default settings file, so
# Django expects a datetime with tzinfo for pub_date Use timezonenow()
# instead of datetimedatetimenow() and it will do the right thing
>>> from djangoutils import timezone
>>> q = Question(question_text="What's new", pub_date=timezonenow())
# Save the object into the database You have to call save() explicitly
>>> qsave()
# Now it has an ID Note that this might say "1L" instead of "1", depending
# on which database you're using That's no biggie; it just means your
# database backend prefers to return integers as Python long integer
# objects
>>> qid
1
# Access model field values via Python attributes
>>> qquestion_text
"What's new"
>>> qpub_date
datetimedatetime(2012, 2, 26, 13, 0, 0, 775217, tzinfo=)
# Change values by changing the attributes, then calling save()
>>> qquestion_text = "What's up"
>>> qsave()
# objectsall() displays all the questions in the database
>>> Questionobjectsall()
[]
打印所 Question 输结 []我修改模型类使其输更易懂描述修改模型类:
from djangodb import models
class Question(modelsModel):
#
def __str__(self): # __unicode__ on Python 2
return selfquestion_text
class Choice(modelsModel):
#
def __str__(self): # __unicode__ on Python 2
return selfchoice_text
接继续测试:
>>> from pollsmodels import Question, Choice
# Make sure our __str__() addition worked
>>> Questionobjectsall()
[]
# Django provides a rich database lookup API that's entirely driven by
# keyword arguments
>>> Questionobjectsfilter(id=1)
[]
>>> Questionobjectsfilter(question_text__startswith='What')
[]
# Get the question that was published this year
>>> from djangoutils import timezone
>>> current_year = timezonenow()year
>>> Questionobjectsget(pub_date__year=current_year)
# Request an ID that doesn't exist, this will raise an exception
>>> Questionobjectsget(id=2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
DoesNotExist: Question matching query does not exist
# Lookup by a primary key is the most common case, so Django provides a
# shortcut for primary-key exact lookups
# The following is identical to Questionobjectsget(id=1)
>>> Questionobjectsget(pk=1)
# Make sure our custom method worked
>>> q = Questionobjectsget(pk=1)
# Give the Question a couple of Choices The create call constructs a new
# Choice object, does the INSERT statement, adds the choice to the set
# of available choices and returns the new Choice object Django creates
# a set to hold the "other side" of a ForeignKey relation
# (eg a question's choice) which can be accessed via the API
>>> q = Questionobjectsget(pk=1)
# Display any choices from the related object set -- none so far
>>> qchoice_setall()
[]
# Create three choices
>>> qchoice_setcreate(choice_text='Not much', votes=0)
>>> qchoice_setcreate(choice_text='The sky', votes=0)
>>> c = qchoice_setcreate(choice_text='Just hacking again', votes=0)
# Choice objects have API access to their related Question objects
>>> cquestion
# And vice versa: Question objects get access to Choice objects
>>> qchoice_setall()
[, , ]
>>> qchoice_setcount()
3
# The API automatically follows relationships as far as you need
# Use double underscores to separate relationships
# This works as many levels deep as you want; there's no limit
# Find all Choices for any question whose pub_date is in this year
# (reusing the 'current_year' variable we created above)
>>> Choiceobjectsfilter(question__pub_date__year=current_year)
[, , ]
# Let's delete one of the choices Use delete() for that
>>> c = qchoice_setfilter(choice_text__startswith='Just hacking')
>>> cdelete()
>>>
面部测试涉及 django orm 相关知识详细说明参考 DjangoORM
5 管理 admin
Django优秀特性, 内置Django admin台管理界面, 便管理者进行添加删除网站内容
新建项目系统已经我设置台管理功能见 mysite/settingspy:
INSTALLED_APPS = (
'djangocontribadmin', #默认添加台管理功能
'djangocontribauth',
'djangocontribcontenttypes',
'djangocontribsessions',
'djangocontribmessages',
'djangocontribstaticfiles',
'mysite',
)
同已经添加进入台管理 url, mysite/urlspy 查看:
url(r'^admin/', include(adminsiteurls)), #使用设置url进入网站台
接我需要创建管理用户登录 admin 台管理界面:
$ python managepy createsuperuser
Username (leave blank to use 'june'): admin
Email address:
Password:
Password (again):
Superuser created successfully
总结
看项目目录结构:
mysite
├── dbsqlite3
├── managepy
├── mysite
│ ├── __init__py
│ ├── settingspy
│ ├── urlspy
│ ├── wsgipy
├── polls
│ ├── __init__py
│ ├── adminpy
│ ├── migrations
│ │ ├── 0001_initialpy
│ │ ├── __init__py
│ ├── modelspy
│ ├── templates
│ │ └── polls
│ │ ├── detailhtml
│ │ ├── indexhtml
│ │ └── resultshtml
│ ├── testspy
│ ├── urlspy
│ ├── viewspy
└── templates
└── admin
└── base_sitehtm
通面介绍 django 安装、运行及何创建视 图模型清晰认识接深入习 django 自化测试、持久化、间件、 际 化等知识
以上就是关于python编程--django框架,想要添加一个表进到数据库里全部的内容,包括:python编程--django框架,想要添加一个表进到数据库里、Django教程-02连接初始化数据库、如何在django上自动创建createuperuser等相关内容解答,如果想了解更多相关内容,可以关注我们,你们的支持是我们更新的动力!
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)