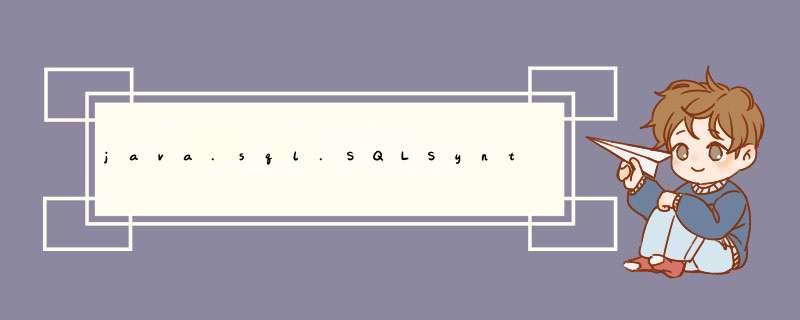
犯了低级错误,由于拼凑sql语句时对字符类型数据没有用引号引起来造成:java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column 'xxx' in 'where clause'
原始:
String sql = "select * from user where username= "+ name + " and password=" + pwd ;
当传入的name和pwd为int等整型则不会出任何错误,如果是字符或字符串则需要用引号引起来
就比如正常的不是传入参数:select * from user where name='11';就要用引号所以这里也必须拼接引号,将上面sql语句修改为:
String sql = "select * from user where username= '"+ name + "' and password= '" + pwd +"'";
问题解决!
2、SQL注入另外,这里还存在SQL注入的问题:
比如传入的name为sunny,pwd为1111’ or ‘1’=‘1
因为’1’='1’恒成立,所以相当于where后面的条件无效该sql语句可以查询出所有表中的数据,这种现象被称为SQL注入。
产生SQL注入的根本原因:
用户输入的信息中含有sql语句的关键字,并且这些关键字参与了sql语句的编译过程,导致sql语句的愿意被扭曲,进而形成了SQL注入。
方法1:只要用户提供的信息不参与SQL语句的编译过程,问题就解决了,要想如此则必须将数据库 *** 作对象Statement换成PreparedStatement(叫预编译的数据库 *** 作对象)。
PreparedStatemen的原理:预先对SQL语句的框架进行编译,然后再给SQL语句传“值”
举例:
package com.sunny;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 模拟用户登录
*/
public class JDBCTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> userInfo;
//进行初始化
userInfo = init();
String username = userInfo.get("用户名");
String pwd = userInfo.get("密码");
//登录验证
boolean result = login(username, pwd);
System.out.println(result ? "登录成功!" : "登录失败!");
}
/**
* 初始化
*
* @return Map返回用户输入的信息
*/
private static Map<String, String> init() {
Map<String, String> userInfo = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.nextLine();
userInfo.put("用户名", name);
userInfo.put("密码", pwd);
return userInfo;
}
/**
* 登录
* @param name 用户名
* @param pwd 密码
* @return 返回是否在数据库中找到匹配的记录
*/
private static boolean login(String name, String pwd) {
//进行数据库连接验证
//创建资源绑定器
//db.properties文件必须在src路径下
// ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db");//直接位于src目录下
ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com/sunny/db");//在src的子目录com/sunny下
String driver = resourceBundle.getString("driver");
String url = resourceBundle.getString("url");
String username = resourceBundle.getString("username");
String password = resourceBundle.getString("password");
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
boolean flag = false;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//获取数据库 *** 作对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//执行sql语句
String sql = "select * from user where username= '"+ name + "' and password= '" + pwd +"'";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//处理查询结果集
if (rs.next()) {
flag = true;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return flag;
}
}
db.properties:
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mytest?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username=root
password=123456
此时user表中数据为:
此时编写造成SQL注入的输入信息【name:sunny,pwd:1111’ or ‘1’=‘1’】,运行结果:
如上,是登录成功,说明产生了SQL注入。
改进:用PreparedStatement替代Statement,防止SQL注入
修改后代码:
package com.sunny;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 模拟用户登录(用PreparedStatement替代Statement,防止SQL注入)
*/
public class JDBCTest07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> userInfo;
//进行初始化
userInfo = init();
String username = userInfo.get("用户名");
String pwd = userInfo.get("密码");
//登录验证
boolean result = login(username, pwd);
System.out.println(result ? "登录成功!" : "登录失败!");
}
/**
* 初始化
*
* @return Map返回用户输入的信息
*/
private static Map<String, String> init() {
Map<String, String> userInfo = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.nextLine();
userInfo.put("用户名", name);
userInfo.put("密码", pwd);
return userInfo;
}
/**
* 登录
* @param name 用户名
* @param pwd 密码
* @return 返回是否在数据库中找到匹配的记录
*/
private static boolean login(String name, String pwd) {
//进行数据库连接验证
//创建资源绑定器
//db.properties文件必须在src路径下
// ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db");//直接位于src目录下
ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com/sunny/db");//在src的子目录com/sunny下
String driver = resourceBundle.getString("driver");
String url = resourceBundle.getString("url");
String username = resourceBundle.getString("username");
String password = resourceBundle.getString("password");
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
boolean flag = false;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//获取数据库 *** 作对象
//使用? 表示占位符,一个?接收一个值
String sql = "select * from user where username= ? and password= ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //使用prepareStatement要传入sql
//给占位符?传值(第一个问号的下标为1)
ps.setString(1,name);
ps.setString(2,pwd);
//执行sql语句
rs = ps.executeQuery();//不用再传入sql
//处理查询结果集
if (rs.next()) {
flag = true;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return flag;
}
}
运行结果:
成功防止SQL注入!
//如下,只能传入String类型的数据
ps.setString(1,name);
ps.setString(2,pwd);
综上所述,PreparedStatement使用较多,但是也有一些情况必须使用Statement
–>在有些业务中有要求必须支持SQL注入【需要拼接字符串】,则必须使用Statement。
这个内容见:演示业务中必须使用Statement完成字符串的拼接
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)