我们可以利用精灵的移动,然后在精灵的移动过程中,通过创建时间线程,逐步创建砖块精灵,这样就达到了用砖块画出图形的目的。该灵感来自于:http://www.jb51.cc/article/p-oyajubhs-vx.html
现在我们具体讲解下如何通过移动实现。首先,移动是一个动作,而一个LED数字,是会拐弯的,因此,这个需要连续N个动作的连接,这个我们可以用Sequence实现。如果是一笔就可以完成的动作,那么一个时间线程就足够了,但是,有些数字,是不能一笔画出的,比如数字3。那么这个时候,就需要再开一个线程了。为了避免节点间的相互独立,因此我们应该将精灵移动并创建砖块的过程封装在一个类中。
我们将精灵的移动,分为上下左右,然后在封装的类中存放每次移动的位置集合,方便我们任意修改移动精灵的起始坐标。
关键代码:
//drawnode.h
class DrawNumberAction : public Node{public: enum { tag_brick = 1,tag_move = 2,tag_move3 = 3,}; DrawNumberAction(std::vector<Vec2> & vct,bool first,float coeff,float pts,int tagval,Layer * pay) : m_pos(vct),isfirst(first),coefficIEnt(coeff),ts(pts),nodetag(tagval),player(pay) {} ~DrawNumberAction(); voID DrawActionMove(); voID DrawBrick(float dt); voID CreateBrick(const cocos2d::Vec2 & pos); voID CancelDraw(cocos2d::Object* pSender);private: std::vector<Vec2> & m_pos; bool isfirst; float coefficIEnt; float ts; int nodetag; Layer * player;}; //drawnode.cpp
voID DrawNumberAction::DrawActionMove(){ auto batchnode2 = SpriteBatchNode::create("gray_brick.png"); cocos2d::Vector<FiniteTimeAction*> vctmove; Sequence* seq = NulL; if (isfirst && m_pos.size() > 0) { CreateBrick(m_pos[0]); } for (int i = 0; i < m_pos.size() - 1; ++i) { auto actionMove = CCMoveto::create(ts * coefficIEnt,m_pos[i+1]); vctmove.pushBack(actionMove); if (i == 0) {//指定移动精灵的起始地址 batchnode2->setposition(m_pos[i]); //设置runaction batchnode2->setTag(nodetag); } } auto actionMoveDone = CallFuncN::create(CC_CALLBACK_1(DrawNumberAction::CancelDraw,this)); vctmove.pushBack(actionMoveDone); seq = Sequence::create(vctmove); batchnode2->runAction(seq); this->addChild(batchnode2); //设置schedule事件 this->schedule(schedule_selector(DrawNumberAction::DrawBrick),coefficIEnt);}voID DrawNumberAction::DrawBrick(float dt){ auto container = this->getChildByTag(nodetag); CreateBrick(container->getposition());}voID DrawNumberAction::CreateBrick(const cocos2d::Vec2 & pos){ //画出砖块 CCSprite* sprFlowerTmp = CCSprite::create("gray_brick.png"); sprFlowerTmp->setposition(pos); auto body = PhysicsBody::createBox(sprFlowerTmp->getContentSize()); body->setContactTestBitmask(0xFFFFFFFF); body->setGroup(-1); sprFlowerTmp->setPhysicsBody(body); sprFlowerTmp->setTag(tag_brick); player->addChild(sprFlowerTmp);}voID DrawNumberAction::CancelDraw(Object* pSender){ DrawBrick(1.0f); //取消画砖块的定时线程 this->unschedule(schedule_selector(DrawNumberAction::DrawBrick));} //helloworld.cpp
int HelloWorld::DrawNumeric(int num){ //假设个数字的大小 //底下必须留30个高度 auto visibleSize = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleSize(); auto origin = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleOrigin(); float xleft = visibleSize.wIDth/2 - 20; float yup = visibleSize.height - 20; Vec2 startpos(xleft,yup); DrawDecomposition3(num,startpos); return 0;}int HelloWorld::DrawDecomposition3(int num,cocos2d::Vec2 & startpos){ //如何画出数字3?数字3不能一笔搞定,因此,分两个线程去处理 vector<cocos2d::Vec2> result; result.push_back(startpos); if (0 == num) { //0就是一个大矩形 GetDestPos(draw_right,result[0],result); GetDestPos(draw_down,result[1],result[2],result); GetDestPos(draw_left,result[3],result); GetDestPos(draw_up,result[4],result[5],result); float ts = squaresize - 1; //画第一部分 DrawNumberAction * firstmove = new DrawNumberAction(result,true,coefficIEnt,ts,tag_move,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); } else if (1 == num) { GetDestPos(draw_down,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); } else if (2 == num) { //这是连串的一组 GetDestPos(draw_right,result); GetDestPos(draw_right,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); } else if(3 == num) { //这是连串的一组 GetDestPos(draw_right,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); //画第二部分 vector<cocos2d::Vec2> part2; part2.push_back(result[2]); GetDestPos(draw_left,part2[0],part2); DrawNumberAction * secmove = new DrawNumberAction(part2,false,tag_move3,this); secmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(secmove); } else if (4 == num) { //分两部分 //这是连串的一组 GetDestPos(draw_down,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); //画第二部分 vector<cocos2d::Vec2> part2; //第二部分的起始点有点特殊,需要额外计算 Vec2 start; start.x = result[2].x; start.y = result[0].y; part2.push_back(start); GetDestPos(draw_down,part2); GetDestPos(draw_down,part2[1],this); secmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(secmove); } else if (5 == num) { GetDestPos(draw_left,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); } else if (6 == num) { //是5的结尾后,再加一笔上 GetDestPos(draw_left,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); } else if (7 == num) { GetDestPos(draw_right,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); } else if (8 == num) { //画个矩形 GetDestPos(draw_right,this); firstmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(firstmove); //画第二部分 //以第二步的终点为起点 vector<cocos2d::Vec2> part2; part2.push_back(result[2]); GetDestPos(draw_down,part2); GetDestPos(draw_left,part2); GetDestPos(draw_up,part2[2],this); secmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(secmove); } else if (9 == num) { //8与9的区别,就在于没有最后向上的一笔 GetDestPos(draw_right,this); secmove->DrawActionMove(); this->addChild(secmove); } return 0;}int HelloWorld::GetDestPos(Direction dire,cocos2d::Vec2 & startpos,std::vector<cocos2d::Vec2> & vct){ Vec2 dest(startpos); switch (dire) { case draw_right: dest.x += (squaresize - 1)*bricksize.x; break; case draw_left: dest.x -= (squaresize - 1)*bricksize.x; break; case draw_down: dest.y -= (squaresize - 1)*bricksize.y; break; case draw_up: dest.y += (squaresize - 1)*bricksize.y; break; default: return 0; } vct.push_back(dest);} GetDestPos()函数的功能是根据方向,获取终点的位置坐标。代码大致就是这样。有点小问题的就是,当头和尾都已经存在时,再去画砖块时,会存在精灵重复覆盖。
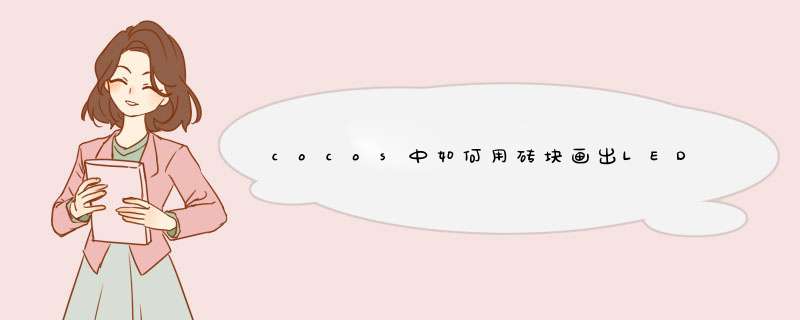
不知道怎么录制演示过程。只好放几张最终的效果图片了。
源码和资源文件路径可从下面路径下载:
http://git.oschina.net/codessheng/cocoslednumber
总结以上是内存溢出为你收集整理的cocos中如何用砖块画出LED数字全部内容,希望文章能够帮你解决cocos中如何用砖块画出LED数字所遇到的程序开发问题。
如果觉得内存溢出网站内容还不错,欢迎将内存溢出网站推荐给程序员好友。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)